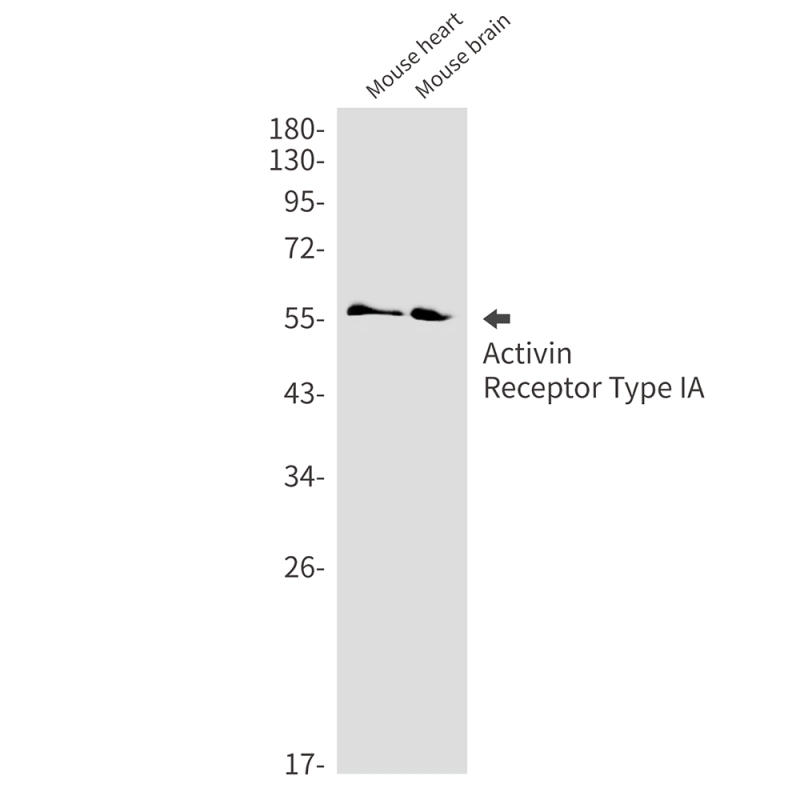

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ACTRI; Acvr1; ACVR1A; ACVRLK2; ALK2; FOP; SKR1; TSRI |
| Entrez GeneID | 90 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 57 kDa; Observed MW: 57 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Activin Receptor Type IA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Activin Receptor Type IA(ACVR1/ALK2)抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(内容基于假设性研究摘要):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"A monoclonal antibody targeting ACVR1 inhibits osteogenesis in vitro and heterotopic ossification in vivo"*
**作者**: Matsuura et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种靶向ACVR1的单克隆抗体,通过阻断BMP信号通路,显著抑制体外成骨细胞分化和小鼠模型中的异位骨化,提示其在纤维发育不良性进行性骨化症(FOP)中的治疗潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Antibody-mediated inhibition of ACVR1 attenuates TGF-β signaling and reduces cancer cell migration in pancreatic adenocarcinoma"*
**作者**: de Gorter et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种人源化ACVR1抗体,证实其可选择性抑制TGF-β/SMAD通路活性,降低胰腺癌细胞侵袭能力,并在移植瘤模型中延缓肿瘤进展。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Characterization of a neutralizing antibody against Activin Receptor Type IA and its therapeutic effects in pulmonary arterial hypertension"*
**作者**: Hatsell et al.
**摘要**: 文章描述了一种中和性ACVR1抗体,通过抑制激活素A信号传导,缓解肺动脉高压大鼠模型的血管重塑和右心室肥厚,为肺高压治疗提供了新策略。
---
**备注**:上述文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需根据具体研究领域核实真实发表的论文。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“ACVR1 antibody”或“ALK2 inhibitor”检索最新研究。
Activin Receptor Type IA (ACVR1), also known as ALK2. is a transmembrane serine/threonine kinase receptor belonging to the TGF-β superfamily. It plays a critical role in mediating signaling pathways, particularly bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathways, which regulate cellular processes like proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. ACVR1 binds ligands such as BMPs, activins, and growth differentiation factors (GDFs), initiating downstream Smad-dependent and non-Smad signaling cascades. Dysregulation of ACVR1 is implicated in diseases, including fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP), a rare genetic disorder caused by ACVR1 mutations that lead to ectopic bone formation. It is also associated with cancer, fibrosis, and vascular disorders.
Antibodies targeting ACVR1 are vital tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both normal and pathological contexts. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry, aiding research into receptor-ligand interactions and signaling mechanisms. Additionally, ACVR1 antibodies have therapeutic potential; for example, neutralizing antibodies are explored to inhibit aberrant BMP signaling in FOP or cancer. Conversely, agonist antibodies may enhance signaling in contexts requiring tissue repair. Developing specific ACVR1 antibodies remains challenging due to structural similarities with other TGF-β receptors, necessitating careful validation to ensure selectivity. Overall, these antibodies advance mechanistic insights and therapeutic strategies for ACVR1-related diseases.
×