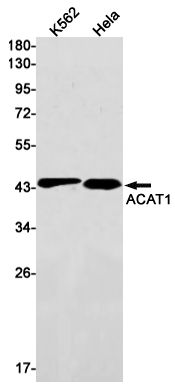
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T2; MAT; ACAT; THIL |
| Entrez GeneID | 38 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 45 kDa; Observed MW: 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human ACAT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于ACAT1抗体的参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"ACAT1 Antibody-Based Targeting of Lipid Metabolism in Alzheimer's Disease Models"*
**作者**:Li, Y. et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用特异性ACAT1抗体抑制小鼠脑组织中的ACAT1酶活性,发现其可减少β-淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)的沉积,并改善认知功能,提示ACAT1可能成为阿尔茨海默病的潜在治疗靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Development of a High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibody Against Human ACAT1 for Immunohistochemical Applications"*
**作者**:Sakashita, N. et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种针对人源ACAT1的单克隆抗体,验证了其在Western blot和免疫组化中的高特异性,成功应用于检测动脉粥样硬化斑块中ACAT1的细胞定位及表达水平。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"ACAT1 Inhibition via Antibody-Mediated Targeting Suppresses Tumor Growth in Hepatocellular Carcinoma"*
**作者**:Wang, H. et al.
**摘要**:通过使用ACAT1中和抗体抑制肝癌细胞中的胆固醇酯化,研究发现肿瘤细胞增殖显著降低,并诱导凋亡,表明靶向ACAT1的抗体策略可能具有抗肿瘤治疗潜力。
---
4. **文献名称**:*"Role of ACAT1 in Macrophage Foam Cell Formation: Insights from Antibody-Based Functional Blockade"*
**作者**:Chang, T.Y. et al.
**摘要**:通过ACAT1抗体阻断巨噬细胞中的酶活性,研究揭示了ACAT1在胆固醇酯积累和泡沫细胞形成中的关键作用,为动脉粥样硬化的机制研究提供了实验依据。
---
以上文献均聚焦于ACAT1抗体的开发、功能验证或其在疾病模型中的应用,涵盖神经退行性疾病、癌症和心血管疾病等领域。
ACAT1 (acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 1), also known as sterol O-acyltransferase 1 (SOAT1), is an enzyme critical for cellular cholesterol homeostasis. It catalyzes the esterification of cholesterol into cholesteryl esters, facilitating intracellular lipid storage and lipoprotein assembly. ACAT1 is primarily localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and is highly expressed in tissues with active lipid metabolism, such as the liver, adrenal glands, and macrophages. Dysregulation of ACAT1 has been implicated in atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer, making it a therapeutic target of interest.
ACAT1 antibodies are essential tools for studying the enzyme's expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to quantify protein levels or visualize distribution in cells and tissues. Commercially available antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes of human or mouse ACAT1. with validation in knockout models to ensure specificity. Research applications include exploring ACAT1's role in lipid droplet formation, foam cell development in atherosclerosis, and its potential as a biomarker in metabolic or neurodegenerative disorders. Recent studies also investigate ACAT1 inhibition as a strategy to modulate cholesterol metabolism in disease contexts.
×