| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SA; LBP; LRP; p40; 67LR; ICAS; lamR; 37LRP; LAMBR; LAMR1; LRP/LR; LBP/p40; NEM/1CHD4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3921 |
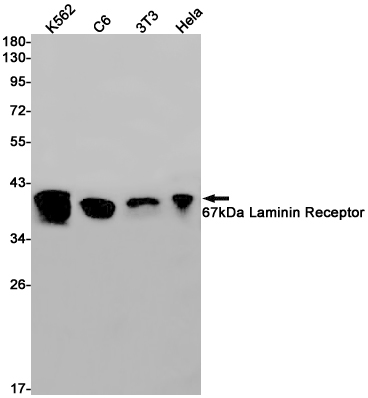
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 33 kDa; Observed MW: 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human 67kDa Laminin Receptor |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **《The 67 kDa laminin receptor: structure, function and role in disease》**
- 作者:Muramatsu T.
- 摘要:该综述总结了67kDa层粘连蛋白受体(67LR)的分子结构、生物学功能及其在癌症转移和感染性疾病中的作用,强调其作为潜在治疗靶点的价值。
2. **《A monoclonal antibody against the 67 kDa laminin receptor inhibits circulatory metastasis in nude mice》**
- 作者:Menard S. 等
- 摘要:研究开发了一种特异性抗67LR的单克隆抗体,通过动物实验证明其能显著抑制肿瘤细胞的血液循环转移,提示其在抗转移治疗中的应用潜力。
3. **《The 67 kDa laminin receptor as a prognostic biomarker in human colorectal cancer》**
- 作者:Vidalino L. 等
- 摘要:通过分析结直肠癌患者组织样本,发现67LR的高表达与肿瘤分期和不良预后显著相关,支持其作为临床预后标志物的可能性。
4. **《Interaction of the 67 kDa laminin receptor with prion protein promotes amyloid formation》**
- 作者:Hundt C. 等
- 摘要:研究发现67LR与朊蛋白相互作用,促进淀粉样纤维的形成,揭示了其在神经退行性疾病(如阿尔茨海默病)病理机制中的潜在作用。
The 67kDa laminin receptor (67LR) is a cell surface protein involved in mediating interactions between cells and the extracellular matrix, primarily through binding to laminin, a key component of the basement membrane. Initially identified as a non-integrin laminin-binding protein, 67LR is derived from a 37kDa precursor (37LRP) through post-translational modifications. It plays critical roles in cell adhesion, migration, and signaling, influencing processes like cancer metastasis, viral infection, and neuronal development.
Antibodies targeting 67LR are widely used in research to study its expression and function. Elevated 67LR levels are associated with tumor progression, as it enhances cancer cell invasion by facilitating interactions with laminin in the extracellular matrix. Additionally, 67LR serves as a receptor for pathogens, including prion proteins and certain viruses (e.g., dengue virus), making it relevant in infectious disease studies.
In neuroscience, 67LR contributes to neuronal differentiation and synaptic plasticity. Commercially available 67LR antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. However, challenges remain in distinguishing between the 37kDa precursor and mature 67kDa forms due to shared epitopes. Research continues to explore its therapeutic potential, particularly in targeting cancer metastasis and pathogen entry mechanisms.
×