
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
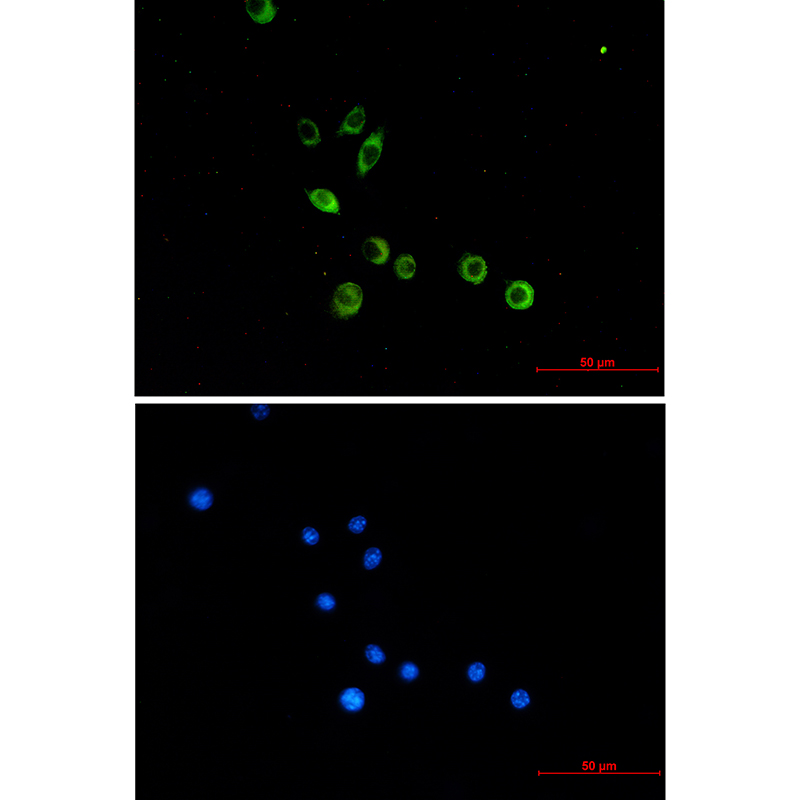
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
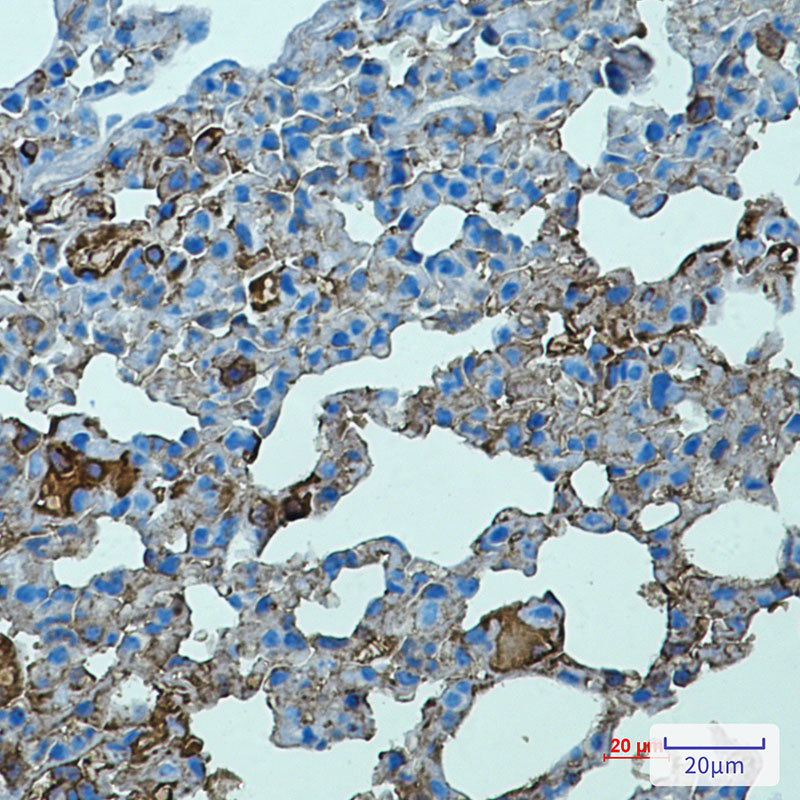
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Toll-Like Receptor 2; TLR2; CD282; TIL4; Toll-like receptor 2; Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-like protein 4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 24088 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 89 kDa; Observed MW: 89 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse TLR2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于Toll-Like Receptor 2(TLR2)抗体的关键文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components"*
**作者**:Takeuchi O. et al.
**摘要**:通过抗TLR2抗体阻断实验,证明TLR2特异性识别革兰氏阳性菌的肽聚糖(PGN),而TLR4主要响应革兰氏阴性菌的脂多糖(LPS),揭示了TLR2在细菌感染中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"Modulation of atherosclerosis in mice by Toll-like receptor 2"*
**作者**:Mullick A.E. et al.
**摘要**:利用抗TLR2抗体抑制TLR2活性,发现可减少动脉粥样硬化斑块中巨噬细胞浸润和促炎因子(如TNF-α、IL-6)表达,表明TLR2促进动脉粥样硬化的发展。
3. **文献名称**:*"TLR2 signaling in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis"*
**作者**:Tahara K. et al.
**摘要**:在多发性硬化症(EAE)小鼠模型中,抗TLR2抗体治疗显著减轻中枢神经系统炎症和脱髓鞘,提示TLR2参与神经炎症的病理过程。
4. **文献名称**:*"TLR2 and TLR1/6 heterodimerization regulates ligand-specific signaling"*
**作者**:Ozinsky A. et al.
**摘要**:通过抗体阻断和细胞转染实验,证明TLR2与TLR1或TLR6形成异源二聚体,分别识别细菌脂蛋白和酵母菌成分,揭示了TLR2依赖的配体特异性识别机制。
以上研究均通过抗TLR2抗体功能实验,阐明了TLR2在感染、自身免疫疾病及信号转导中的生物学意义。
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) is a key pattern recognition receptor in the innate immune system, responsible for detecting conserved microbial components such as lipoproteins, lipoteichoic acid, and peptidoglycans from bacteria, fungi, and viruses. TLR2 antibodies are essential tools for studying its role in immune responses, inflammation, and disease pathogenesis. These antibodies are widely used in research to block TLR2 signaling, detect its expression in tissues or cells via techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or Western blot, and investigate its interaction with ligands or downstream adaptor proteins.
TLR2 antibodies have revealed its involvement in conditions like sepsis, autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), and chronic inflammatory diseases. They also help explore TLR2's dual role in cancer—promoting tumor progression in some contexts while enhancing anti-tumor immunity in others. Monoclonal antibodies offer high specificity for functional studies, whereas polyclonal antibodies are often used for detection due to broader epitope recognition. Challenges include ensuring minimal cross-reactivity with other TLRs and validating functionality across experimental models.
Therapeutic TLR2-targeting antibodies are under investigation for modulating hyperactive immune responses, highlighting their translational potential in immunology and drug development.
×