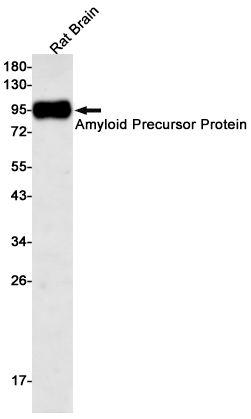
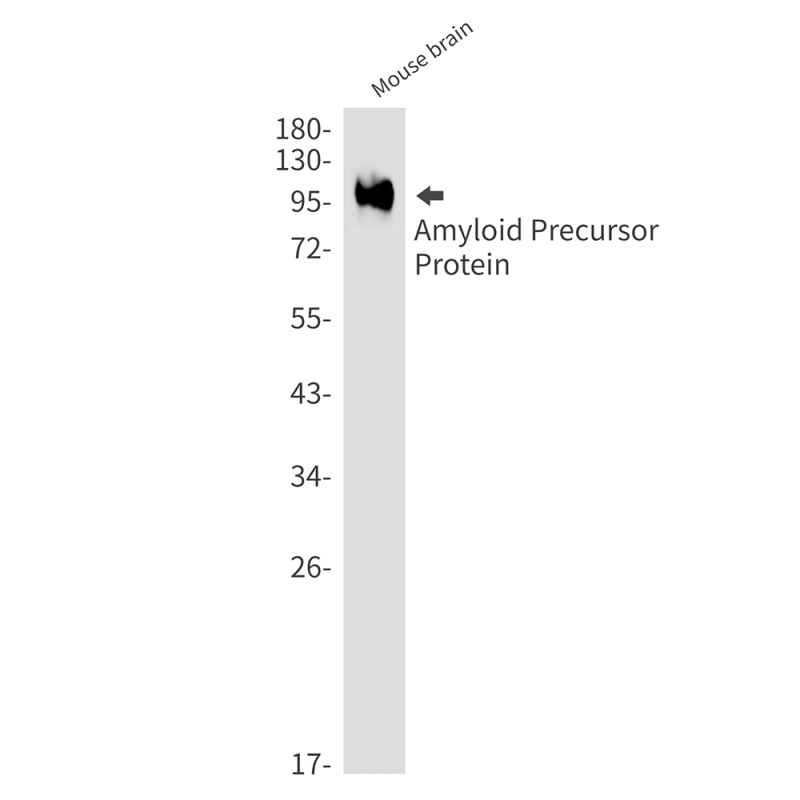

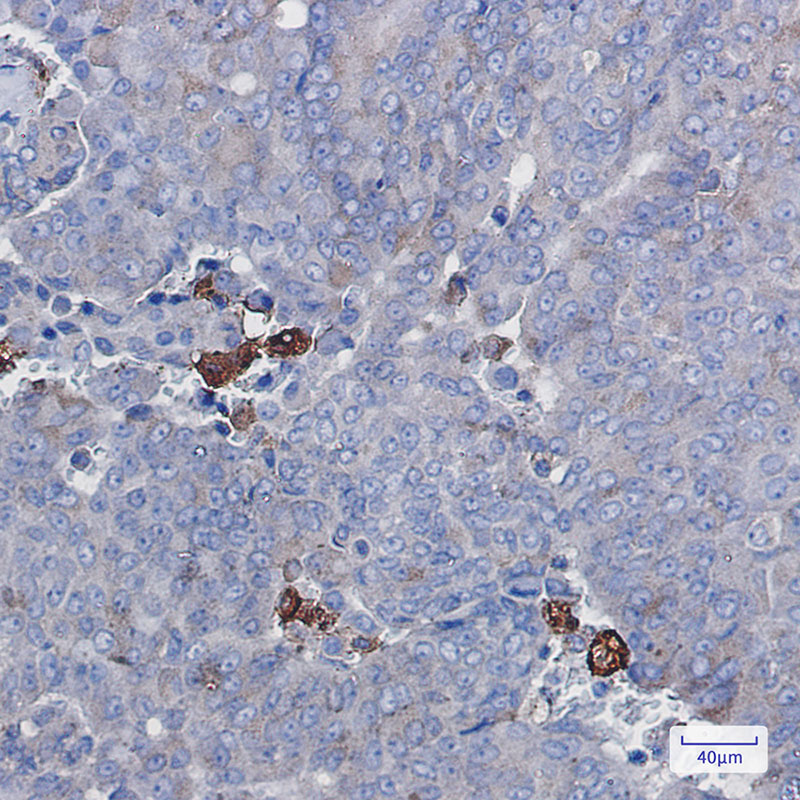
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | APP; A4; AD1; Amyloid beta A4 protein; ABPP; APPI; APP; Alzheimer disease amyloid protein; Cerebral vascular amyloid peptide; CVAP; PreA4; Protease nexin-II; PN-II |
| Entrez GeneID | 351 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 87 kDa; Observed MW: 100 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Amyloid Precursor Protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是与Amyloid Precursor Protein(APP)抗体相关的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
1. **文献名称**:*"The role of APP processing in Alzheimer’s disease"*
**作者**:Selkoe, D.J., Hardy, J.
**摘要**:该综述讨论了APP蛋白的代谢途径及其在阿尔茨海默病中的作用,重点分析了针对APP不同片段(如Aβ、sAPPα/β)的抗体在病理机制研究和治疗开发中的应用。
2. **文献名称**:*"Monoclonal antibodies against amyloid precursor protein for in vivo imaging of Alzheimer’s disease pathology"*
**作者**:Timmers, M., et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种靶向APP的特异性单克隆抗体,并验证其在活体小鼠模型中通过PET成像检测淀粉样斑块的能力,证明了抗体在阿尔茨海默病早期诊断中的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*"Antibody-mediated targeting of tau and APP in preclinical models of neurodegenerative disorders"*
**作者**:Jucker, M., Walker, L.C.
**摘要**:该文献比较了靶向APP和tau蛋白的抗体在神经退行性疾病动物模型中的效果,发现APP抗体可减少Aβ沉积并改善认知功能,提示其作为治疗策略的可能性。
如需更具体的研究方向或补充文献,可进一步说明。
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is a transmembrane glycoprotein widely expressed in various tissues, particularly in the brain. It plays roles in synaptic formation, neural plasticity, and intracellular signaling. APP is best known for its involvement in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), as its proteolytic processing by β- and γ-secretases generates amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides, which aggregate into toxic plaques, a hallmark of AD pathology. Antibodies targeting APP are critical tools for studying its physiological functions, proteolytic pathways, and disease-related alterations.
APP antibodies are designed to recognize specific epitopes within the protein, such as the N-terminal, C-terminal, or Aβ domain. These antibodies help distinguish between full-length APP and its cleavage products (e.g., soluble APPα/β, C-terminal fragments). Some antibodies specifically detect pathogenic Aβ isoforms (e.g., Aβ42. which is more aggregation-prone) or post-translationally modified APP variants (e.g., phosphorylated forms linked to neurodegeneration). They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA to investigate APP expression, localization, and processing in cellular and animal models, as well as human samples.
Research using APP antibodies has advanced understanding of Aβ generation and clearance mechanisms, aiding drug development for AD. However, challenges remain, including antibody cross-reactivity with APP homologs (APLP1/2) or nonspecific binding to protein fragments. Validation of specificity and standardization across experimental conditions are essential for reliable data interpretation.
×