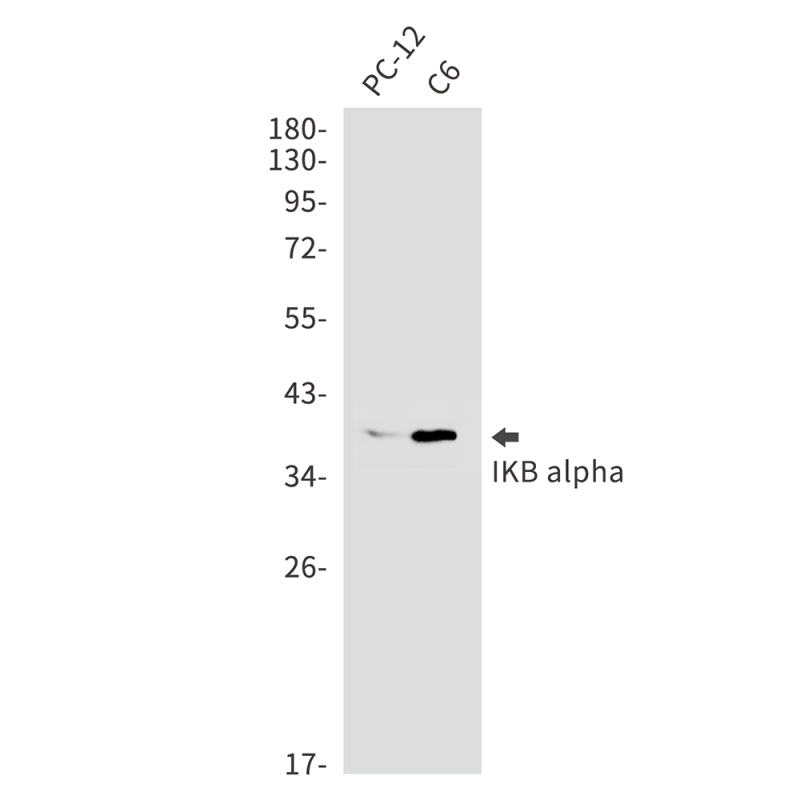
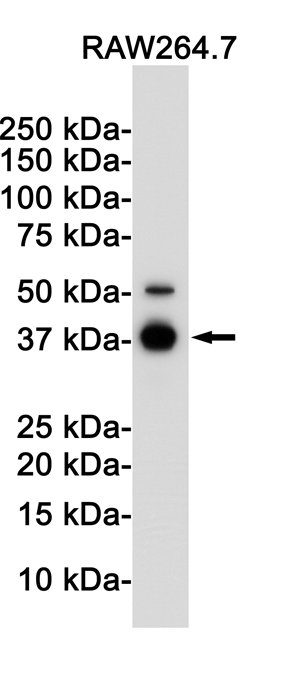

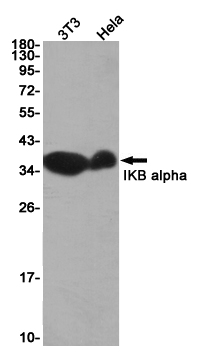
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NFKBIA; IKBA; MAD3; NFKBI; NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha; I-kappa-B-alpha; IkB-alpha; IkappaBalpha; Major histocompatibility complex enhancer-binding protein MAD3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4792 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 36 kDa; Observed MW: 39 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human IKB alpha |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及IκBα抗体的经典文献摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"Structure, Regulation and Function of NF-κB"*
**作者**:Ghosh, S., May, M.J., Kopp, E.B.
**摘要**:综述了NF-κB信号通路的关键调控机制,重点提到IκBα通过抑制NF-κB的核转位发挥作用,并强调使用IκBα抗体在Western blot等实验中检测其磷酸化及降解过程。
2. **文献名称**:*"Rapid proteolysis of IκB-α is necessary for activation of transcription factor NF-κB"*
**作者**:Chen, Z.J., Parent, L., Maniatis, T.
**摘要**:通过IκBα抗体验证,发现肿瘤坏死因子(TNF-α)刺激后IκBα被迅速磷酸化并降解,从而释放NF-κB进入细胞核激活靶基因转录。
3. **文献名称**:*"Signal-induced phosphorylation of IκBα by casein kinase II"*
**作者**:Barroga, C.F., et al.
**摘要**:利用特异性IκBα抗体证明,除经典IKK激酶外,酪蛋白激酶II(CK2)也能磷酸化IκBα,揭示其降解的多重调控机制。
4. **文献名称**:*"A cytokine-responsive IκB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-κB"*
**作者**:DiDonato, J.A., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫沉淀结合IκBα抗体,鉴定出IKK复合物(IKKα/β/γ)在炎症信号中直接磷酸化IκBα,导致其泛素化降解及NF-κB活化。
这些文献均通过IκBα抗体阐明了其在NF-κB信号通路中的核心调控作用,涵盖机制探索及实验方法学。
The IκB alpha (Inhibitor of κB alpha) antibody is a crucial tool for studying the NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) signaling pathway, which regulates immune responses, inflammation, and cell survival. IκB alpha, encoded by the NFKBIA gene, acts as a primary inhibitor of NF-κB by binding to its subunits (e.g., p65/p50) in the cytoplasm, preventing their nuclear translocation and DNA-binding activity. Upon stimulation by cytokines, pathogens, or stress signals, IκB alpha undergoes phosphorylation by the IKK (IκB kinase) complex, leading to its ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. This releases NF-κB, allowing it to activate target genes involved in immune and inflammatory processes.
Antibodies targeting IκB alpha are widely used to detect protein expression, phosphorylation status (e.g., at Ser32/36), and degradation dynamics via techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. These antibodies help researchers investigate dysregulated NF-κB signaling in diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammation. Commercial IκB alpha antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice using epitopes from the N-terminal (phosphorylation-sensitive) or C-terminal regions. Their specificity is validated using knockout controls or siRNA-based approaches.
By enabling precise tracking of IκB alpha’s regulatory role, these antibodies contribute to understanding cellular responses to therapeutic agents, pathogen interactions, and stress-induced signaling cascades.
×