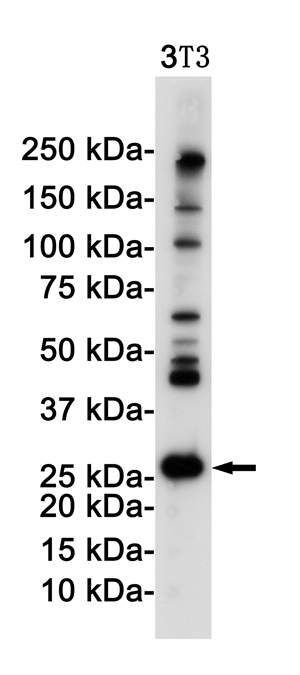
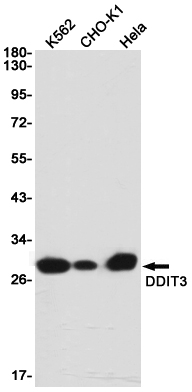
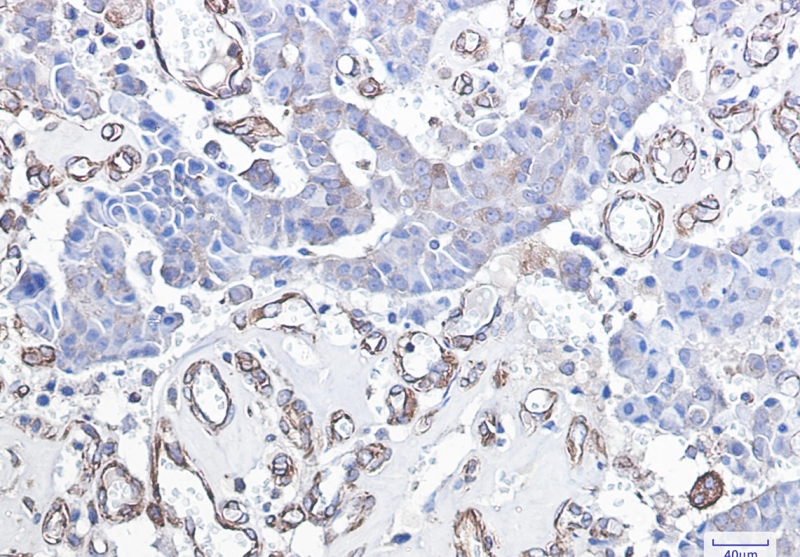
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DDIT3; CHOP; CHOP10; GADD153; DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein; DDIT-3; C/EBP-homologous protein; CHOP; C/EBP-homologous protein 10; CHOP-10; Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD153 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1649 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 19 kDa; Observed MW: 27 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human DDIT3 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DDIT3抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"ER stress-mediated apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells by inhibition of MEK/ERK signaling"*
**作者**: Wang XZ, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过Western blot和免疫组化分析,探讨了内质网(ER)应激诱导的DDIT3(CHOP)表达在神经母细胞瘤细胞凋亡中的作用。研究发现,MEK/ERK信号通路抑制导致DDIT3上调,促进细胞凋亡,揭示了DDIT3在癌症治疗中的潜在靶点价值。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"ATF4 modulates the ER stress response by transcriptionally regulating CHOP during nutrient deprivation"*
**作者**: Adachi Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本文利用DDIT3抗体检测细胞在营养剥夺条件下的表达变化,发现ATF4通过直接结合DDIT3启动子调控其转录,从而介导内质网应激相关的细胞凋亡,为代谢应激与细胞死亡的分子机制提供了依据。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"CHOP is a critical regulator of cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer"*
**作者**: Li H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫荧光和流式细胞术,证实DDIT3在卵巢癌顺铂耐药细胞中高表达。敲低DDIT3可增强化疗敏感性,提示其作为耐药标志物及治疗靶点的潜力。
---
*注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需核实原文准确性。如需更多参考文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“DDIT3 antibody”或“CHOP antibody”为关键词检索。*
**Background of DDIT3 Antibody**
The **DDIT3 antibody** (also known as CHOP or GADD153 antibody) targets the DNA Damage Inducible Transcript 3 protein, encoded by the *DDIT3* gene. DDIT3 is a stress-inducible transcription factor belonging to the C/EBP (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein) family. It is primarily activated in response to cellular stressors such as endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, DNA damage, hypoxia, or nutrient deprivation, often via the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway. DDIT3 plays a dual role in cellular processes: it regulates apoptosis under severe or prolonged stress by modulating pro-apoptotic genes (e.g., *BIM*, *PUMA*), while also influencing metabolic pathways and differentiation under non-stress conditions.
DDIT3 antibodies are widely used in research to study ER stress-related diseases (e.g., neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, cancer), apoptosis mechanisms, and metabolic dysregulation. They are essential tools in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect DDIT3 expression levels and localization in tissues or cultured cells. Commercially available DDIT3 antibodies are typically validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat samples, with common applications in cancer biology (e.g., studying chemotherapy resistance) and neurodegenerative disease models (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s).
Studies using DDIT3 antibodies have highlighted its role as a biomarker for pathological stress and a potential therapeutic target. However, interpretation requires caution, as DDIT3 expression varies depending on cell type, stress duration, and context.
×