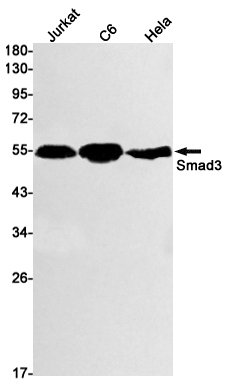
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
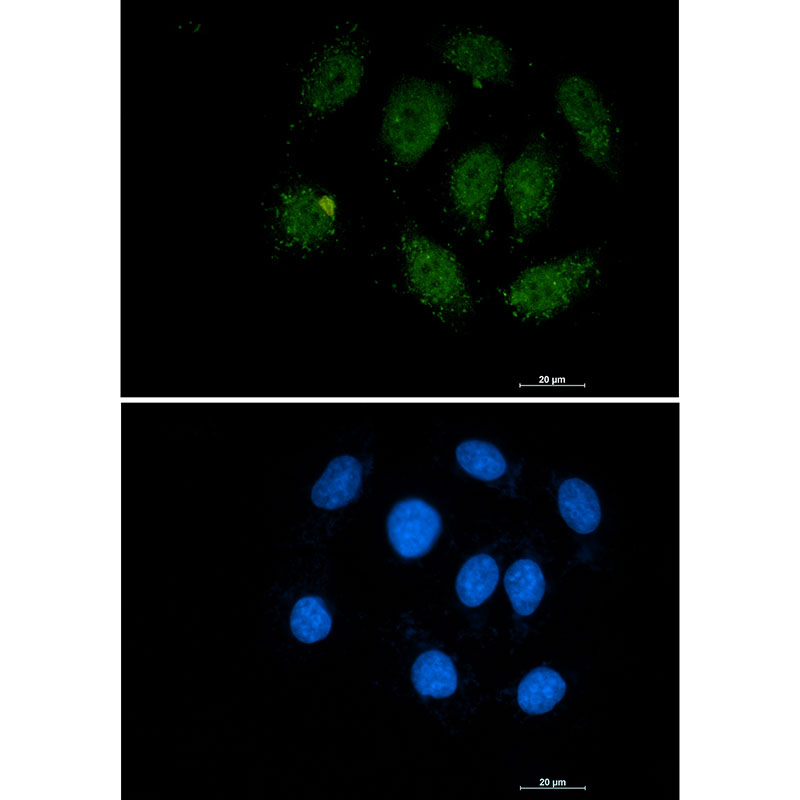
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
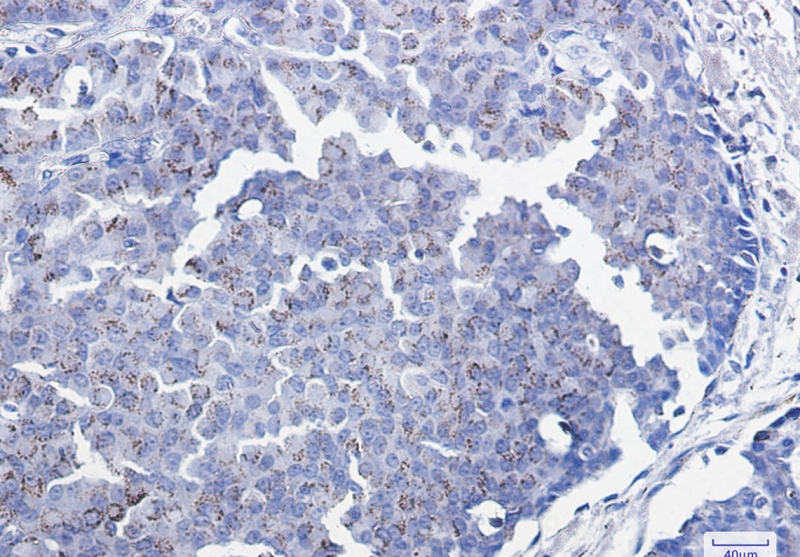
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SMAD3; MADH3; Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3; MAD homolog 3; Mad3; Mothers against DPP homolog 3; hMAD-3; JV15-2; SMAD family member 3; SMAD 3; Smad3; hSMAD3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4088 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 48 kDa; Observed MW: 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Smad3 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下为3-4篇关于Smad3抗体的参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"TGF-β/Smad3 signaling regulates renal fibrosis via angiotensin-converting enzyme 2"*
**作者**:Wysocki et al.
**摘要概括**:本研究利用Smad3特异性抗体(Western blot和免疫组化)探究TGF-β/Smad3信号在肾脏纤维化中的作用,发现Smad3的磷酸化水平与纤维化程度呈正相关,并揭示了ACE2对Smad3活性的调控机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Smad3 deficiency attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice"*
**作者**:Flanders et al.
**摘要概括**:通过Smad3基因敲除小鼠模型,结合Smad3抗体的免疫沉淀技术,证实Smad3在肺纤维化中的关键作用。研究发现Smad3缺失显著减少胶原沉积,提示其作为治疗纤维化靶点的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Phospho-Smad3-specific antibodies reveal distinct activation thresholds in TGF-β signaling"*
**作者**:Persson et al.
**摘要概括**:文章开发并验证了一种特异性识别磷酸化Smad3(p-Smad3)的抗体,证明其在流式细胞术和免疫荧光中的应用价值,揭示了TGF-β信号通路的激活阈值与细胞类型相关性。
---
4. **文献名称**:*"Smad3 promotes cancer progression by inhibiting E-cadherin expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma"*
**作者**:Ellenrieder et al.
**摘要概括**:通过Smad3抗体进行染色质免疫共沉淀(ChIP)分析,发现Smad3直接抑制胰腺癌中E-cadherin的表达,促进上皮-间质转化(EMT)和肿瘤转移,为Smad3在癌症中的促转移机制提供证据。
---
**备注**:以上文献均涉及Smad3抗体的具体应用(如Western blot、免疫组化、ChIP等),并关联疾病机制研究。建议通过PubMed或期刊官网输入标题或作者名获取全文。
**Background of Smad3 Antibody**
Smad3 is a critical intracellular mediator of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway, which regulates diverse cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix production. Upon TGF-β receptor activation, Smad3 is phosphorylated, forms complexes with Smad4. and translocates to the nucleus to modulate the transcription of target genes. Dysregulation of Smad3 is implicated in fibrosis, cancer, immune disorders, and cardiovascular diseases, highlighting its therapeutic and diagnostic relevance.
Smad3 antibodies are essential tools for studying TGF-β/Smad3 signaling dynamics. These antibodies are designed to detect specific epitopes of Smad3. often distinguishing between its inactive (non-phosphorylated) and activated (phosphorylated) forms. Commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry, Smad3 antibodies enable researchers to assess protein expression, localization, and post-translational modifications in various biological samples.
Commercial Smad3 antibodies are typically raised in hosts such as rabbits or mice, targeting regions like the N-terminal, C-terminal, or phosphorylated serine residues (e.g., p-Ser423/425). Specificity is validated using knockout controls or siRNA-mediated Smad3 depletion. However, variability in antibody performance across applications or species necessitates careful optimization. Recent advances in recombinant antibody technology have improved consistency, supporting high-throughput studies and translational research. As Smad3 remains a focal point in understanding disease mechanisms, its antibodies continue to be indispensable in both basic and clinical research.
×