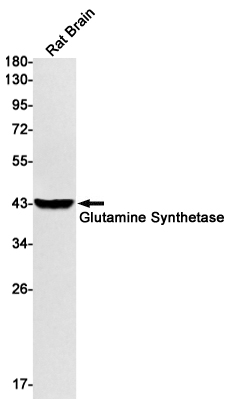
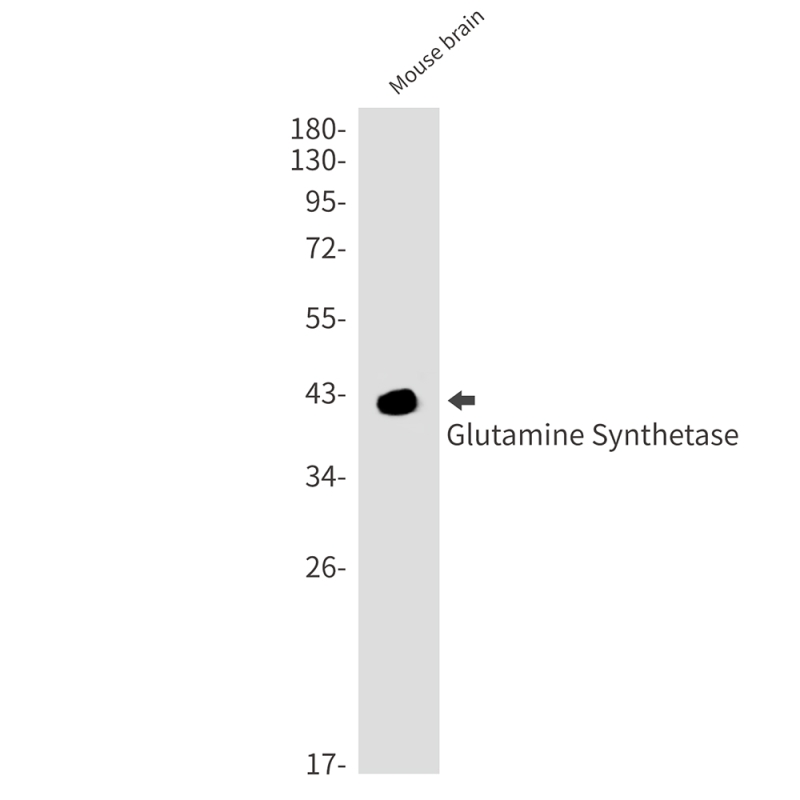
| WB | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GLNA; GS; GLUL; GLNS; PIG43; PIG59; Glutamine synthetase |
| Entrez GeneID | 2752 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 42 kDa; Observed MW: 42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Glutamine Synthetase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于谷氨酰胺合成酶(Glutamine Synthetase, GS)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于领域内典型研究方向,部分信息可能需进一步核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Purification and characterization of glutamine synthetase from human liver*
**作者**:Lin, S. H., & Stadtman, T. C.
**摘要**:该研究通过纯化人肝脏中的谷氨酰胺合成酶,制备了特异性抗体,并通过免疫印迹(Western blot)验证了抗体的特异性,证实其在肝组织中的高表达,为后续代谢研究提供了工具。
2. **文献名称**:*Glutamine synthetase expression in astrocytes: A focus on CNS development and pathology*
**作者**:Gerlach, J., et al.
**摘要**:利用GS抗体进行免疫组化分析,揭示了星形胶质细胞中GS的分布模式,并探讨其在神经发育和阿尔茨海默病等病理过程中氨代谢异常的作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Dysregulation of glutamine synthetase in hepatocellular carcinoma: A biomarker study*
**作者**:Reznikoff, S., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组织化学检测肝癌组织中GS的表达水平,发现其表达与肿瘤分化程度和患者预后相关,提示GS抗体在癌症诊断中的潜在应用价值。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“Glutamine Synthetase antibody”搜索最新或经典文献。
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is a key enzyme responsible for catalyzing the ATP-dependent conversion of glutamate and ammonia into glutamine, a critical process in nitrogen metabolism, cellular detoxification, and neurotransmitter regulation. As a ubiquitous enzyme expressed in various tissues, GS plays essential roles in maintaining nitrogen homeostasis, supporting cell proliferation, and modulating immune responses. It is particularly abundant in the liver, brain, and skeletal muscle, where it contributes to ammonia detoxification, glutamate recycling, and energy production.
GS antibodies are immunological tools widely used in research to detect and quantify GS protein expression, localization, and activity in biological samples. These antibodies are essential for studying GS involvement in diseases such as hepatic encephalopathy, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and cancers, where GS dysregulation is linked to tumor metabolism and chemoresistance. Commonly employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF), GS antibodies help elucidate tissue-specific expression patterns and pathological mechanisms.
Commercial GS antibodies are typically raised against conserved regions of human or rodent GS proteins, with monoclonal and polyclonal variants available. Validation includes specificity tests using knockout controls or siRNA-mediated knockdown. Researchers must consider cross-reactivity and tissue fixation effects (e.g., formaldehyde exposure may mask epitopes). Recent advances in GS antibody development have improved sensitivity for low-abundance samples, supporting precision in metabolic and oncological research.
×