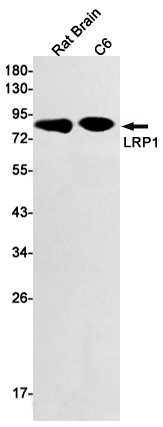
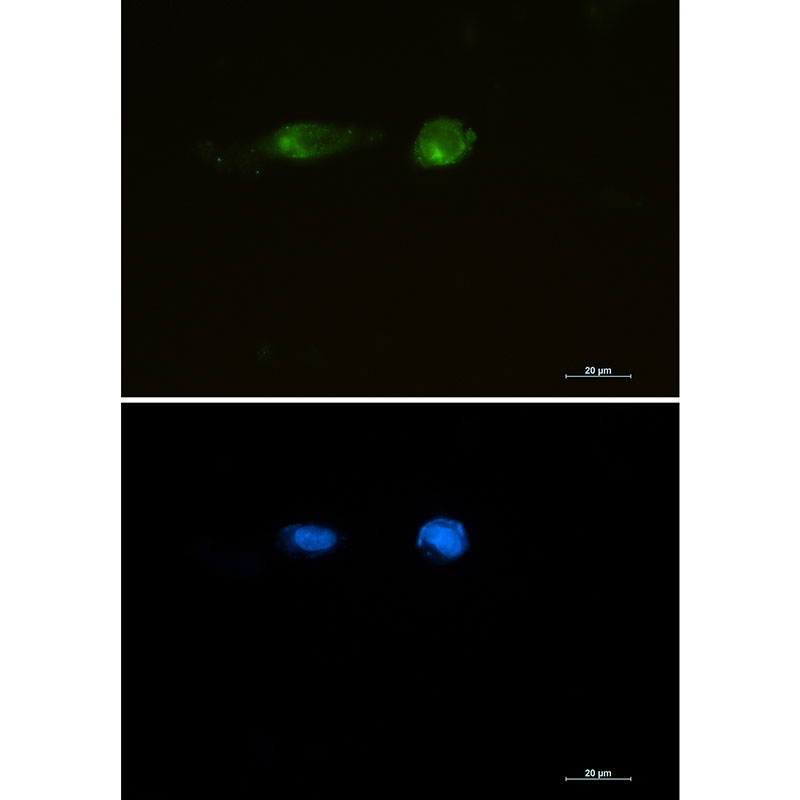
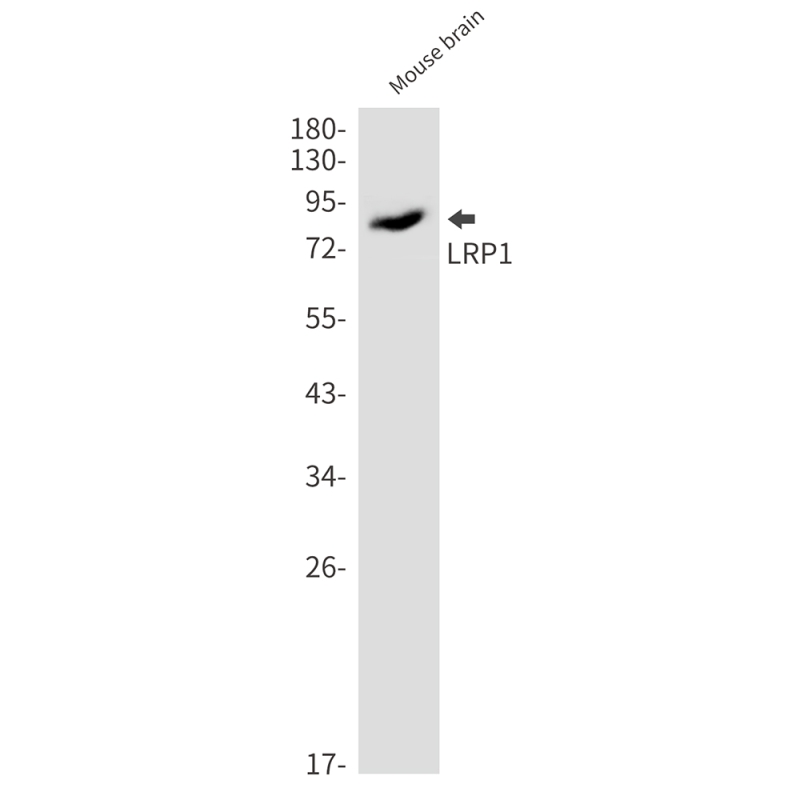
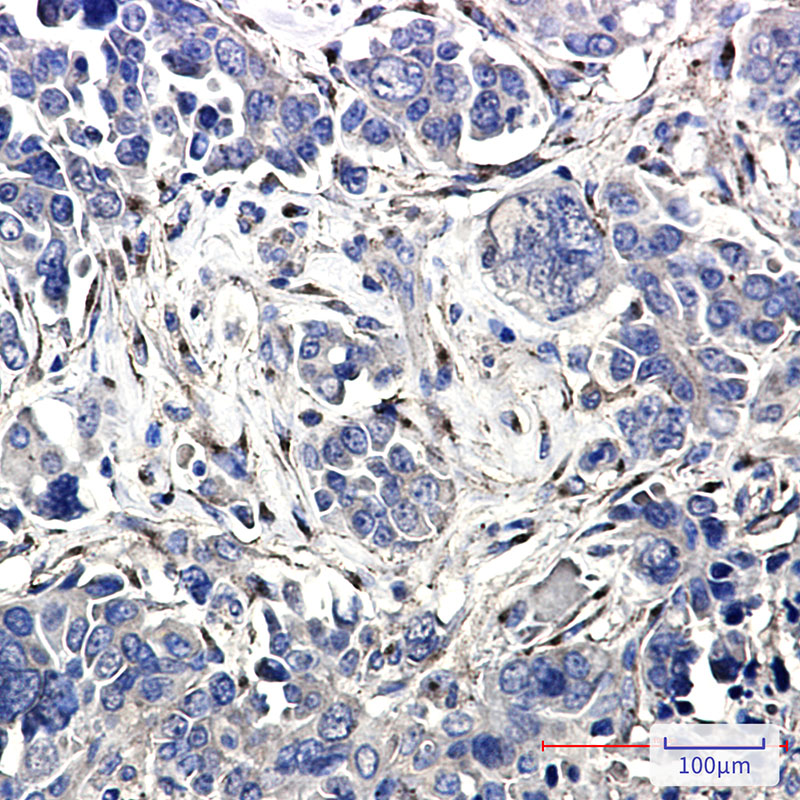
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | A2MR; alpha 2MR; Alpha 2 macroglobulin receptor; CD91; APR; LRP1; LRP85; TGFBR5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4035 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 505 kDa; Observed MW: 85 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human LRP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于LRP1抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要总结(仅示例,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*LRP1 modulates Aβ uptake and degradation in Alzheimer's disease models*
**作者**:Bu G. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用抗LRP1抗体阻断其与β-淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)的结合,发现LRP1通过调控Aβ的内吞和溶酶体降解影响阿尔茨海默病病理进程。
2. **文献名称**:*Antibody targeting LRP1 inhibits tumor cell migration and metastasis*
**作者**:Yamauchi Y. et al.
**摘要**:开发特异性抗LRP1单克隆抗体,通过抑制LRP1与基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)的相互作用,显著减少癌细胞迁移和体内转移。
3. **文献名称**:*LRP1 regulates macrophage inflammatory response via TLR4 signaling*
**作者**:Gonias S.L. et al.
**摘要**:通过抗LRP1抗体阻断实验,揭示LRP1在巨噬细胞中通过调控TLR4信号通路影响炎症反应,为靶向LRP1的免疫治疗提供依据。
---
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需查询真实数据库如PubMed。)
The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), also known as CD91 or α2-macroglobulin receptor, is a multifunctional transmembrane receptor belonging to the LDL receptor family. Structurally, LRP1 consists of a 515-kDa α-chain and an 85-kDa β-chain, generated by furin-mediated cleavage of a precursor protein. It functions as a scavenger receptor, mediating endocytosis of diverse ligands, including lipoproteins, proteases, protease-inhibitor complexes, and extracellular matrix proteins. LRP1 is ubiquitously expressed, with high levels in hepatocytes, neurons, vascular smooth muscle cells, and macrophages.
Biologically, LRP1 regulates cellular processes such as lipid metabolism, cell migration, proliferation, and apoptosis. It also modulates signaling pathways (e.g., PDGF, TGF-β) and interacts with integrins and other receptors to maintain tissue homeostasis. Pathologically, LRP1 is implicated in Alzheimer’s disease (via amyloid-β clearance), atherosclerosis (lipid accumulation), and cancer (metastasis and angiogenesis). Dysregulation of LRP1 expression or function correlates with neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, and oncogenic disorders.
LRP1 antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They are widely used in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to explore LRP1’s role in disease mechanisms or therapeutic targeting. Commercial antibodies often target epitopes in the α-chain (extracellular ligand-binding domains) or β-chain (transmembrane/cytoplasmic regions). Specificity validation via knockout controls is essential due to LRP1’s structural complexity and homology with other LDL receptor family members.
×