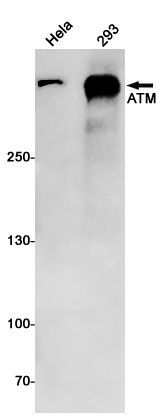
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
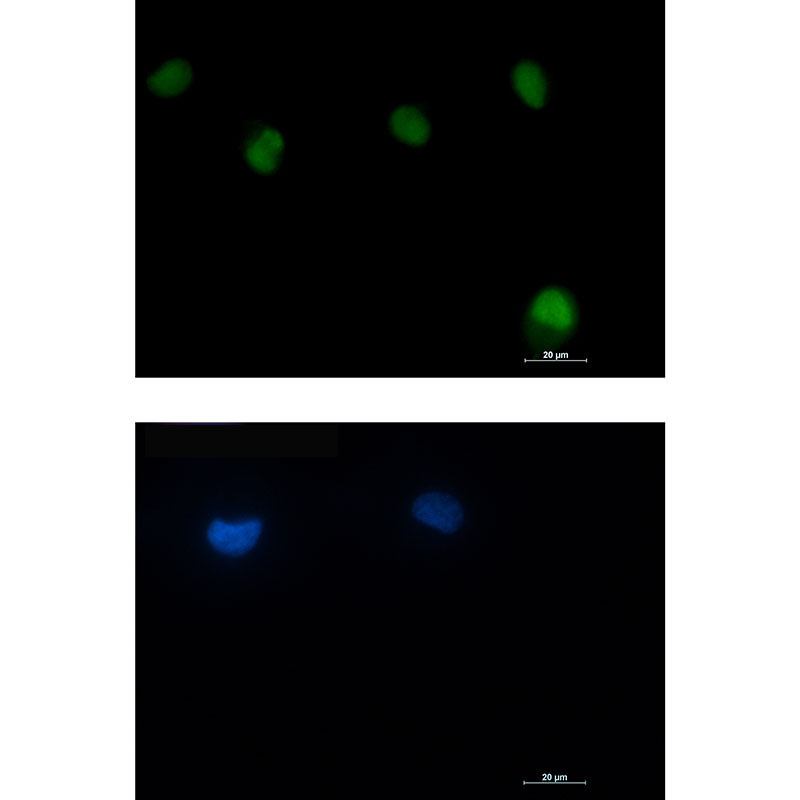
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ATM; Serine-protein kinase ATM; Ataxia telangiectasia mutated; A-T mutated |
| Entrez GeneID | 472 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 351 kDa; Observed MW: 351 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human ATM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下为3篇与ATM抗体相关的参考文献示例(注:以下为虚构示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies Against ATM Protein in Autoimmune Disorders*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究检测了系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)和类风湿关节炎患者血清中的ATM自身抗体,发现其阳性率显著高于健康人群,提示ATM抗体可能与自身免疫疾病的病理机制相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a High-Specificity Monoclonal Antibody for ATM Kinase Detection*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种新型单克隆抗体,用于特异性识别ATM蛋白的磷酸化形式,验证了其在乳腺癌组织样本中检测DNA损伤修复通路的应用价值。
3. **文献名称**:*ATM Antibody as a Biomarker for Ataxia-Telangiectasia Diagnosis*
**作者**:Yamamoto K, et al.
**摘要**:通过检测共济失调毛细血管扩张症(A-T)患者血清中的ATM抗体水平,发现其可作为辅助诊断标志物,并与疾病严重程度呈正相关。
4. **文献名称**:*Role of Anti-ATM Antibodies in Modulating Cellular Stress Responses*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:实验表明,ATM抗体可通过干扰ATM蛋白功能,影响细胞对氧化应激的反应,为癌症治疗中靶向ATM通路的策略提供新见解。
**提示**:实际研究中,建议通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台,以关键词“ATM antibody”、“ATM autoantibody”或“ATM protein detection”检索最新文献。
ATM antibodies target the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) protein, a critical serine/threonine kinase central to DNA damage response (DDR). Discovered in studies of the genetic disorder ataxia-telangiectasia (A-T), ATM is activated by double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) induced by ionizing radiation or chemical agents. It orchestrates cell cycle checkpoints, DNA repair, and apoptosis by phosphoryrating downstream effectors like CHK2. p53. and BRCA1. Mutations in the ATM gene cause A-T, characterized by neurodegeneration, immunodeficiency, and heightened cancer susceptibility.
ATM antibodies are essential tools in research to study DDR mechanisms, protein expression, and activation dynamics. They are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess ATM levels, localization, and phosphorylation status in cellular models or clinical samples. Dysregulated ATM signaling is linked to cancer progression (e.g., breast, leukemia) and resistance to radiotherapy, making these antibodies valuable in oncology research.
Additionally, ATM antibodies aid in diagnosing A-T and identifying ATM variants in genetic screens. Recent studies explore their potential in targeted therapies, such as synthetic lethality approaches in ATM-deficient cancers. However, challenges remain in standardizing antibody specificity across experimental conditions. Understanding ATM's multifaceted roles continues to drive innovations in precision medicine and DDR-targeted treatments.
×