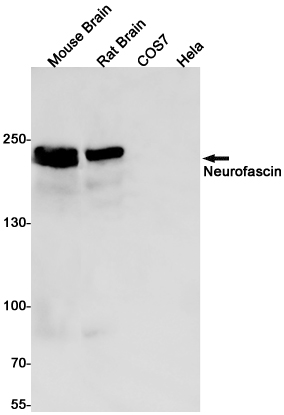
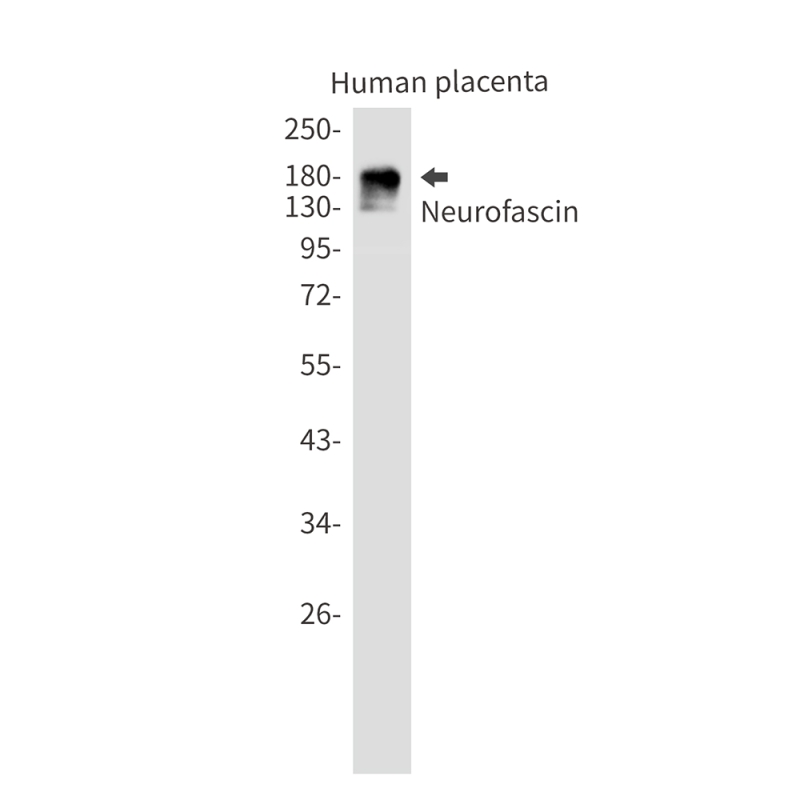
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Neurofascin |
| Entrez GeneID | 269116 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 138 kDa; Observed MW: 186,155,75 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse Neurofascin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Neurofascin抗体相关的研究文献概览:
1. **标题**:*Neurofascin antibodies in autoimmune neurological diseases*
**作者**:Querol L, Illa I
**摘要**:该研究综述了抗Neurofascin抗体(尤其是靶向NF155和NF186亚型)在慢性炎症性脱髓鞘性多发性神经病(CIDP)和多发性硬化症中的作用,强调其与临床表型(如严重运动障碍)的关联及对免疫治疗的响应差异。
2. **标题**:*Autoantibodies to nodal/paranodal proteins in neurological disorders*
**作者**:Dalakas MC
**摘要**:探讨了包括Neurofascin在内的节点/结旁蛋白抗体在格林-巴利综合征(GBS)和CIDP中的病理机制,指出抗NF155 IgG4抗体可能导致神经传导阻滞和难治性病程。
3. **标题**:*Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy with neurofascin IgG4 antibodies: a severe phenotype*
**作者**:Kadavath S, et al.
**摘要**:通过病例分析发现,携带抗NF155 IgG4抗体的CIDP患者常表现为对称性远端无力、震颤及对静脉免疫球蛋白(IVIg)治疗不敏感,提示此类抗体可能作为亚型分型的生物标志物。
如需具体文献来源或更新研究,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“Neurofascin antibody”及上述作者名获取全文。
Neurofascin antibodies are a group of autoantibodies targeting neurofascin, a cell adhesion molecule belonging to the L1CAM family. Neurofascins are critical for maintaining the structural integrity and function of the nervous system, particularly at the nodes of Ranvier and paranodal regions in myelinated axons. They interact with other proteins like contactin-1 and gliomedin to stabilize the axoglial junctions, ensuring efficient saltatory conduction of nerve impulses.
First identified in autoimmune neuropathies, these antibodies are predominantly IgG4 subclass and are associated with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP), especially in treatment-resistant or atypical cases. Anti-neurofascin antibodies disrupt paranodal architecture by interfering with neurofascin-contactin-1 complexes, leading to conduction block, severe motor deficits, and sensory abnormalities. Two major isoforms, neurofascin-155 (NF155) and neurofascin-186/NF166. are common targets. NF155. localized in paranodal glial membranes, is frequently linked to aggressive CIDP subtypes, while NF186/NF166 antibodies are less characterized but may influence nodal stability.
Clinically, their detection aids in diagnosing autoimmune neuropathies and guides immunotherapy (e.g., rituximab), as antibody-positive patients often respond poorly to standard IVIg therapy. Research continues to explore their pathogenic mechanisms, epitope specificity, and broader implications in CNS disorders like multiple sclerosis. Challenges remain in standardizing antibody assays and understanding long-term outcomes in seropositive cohorts.
×