
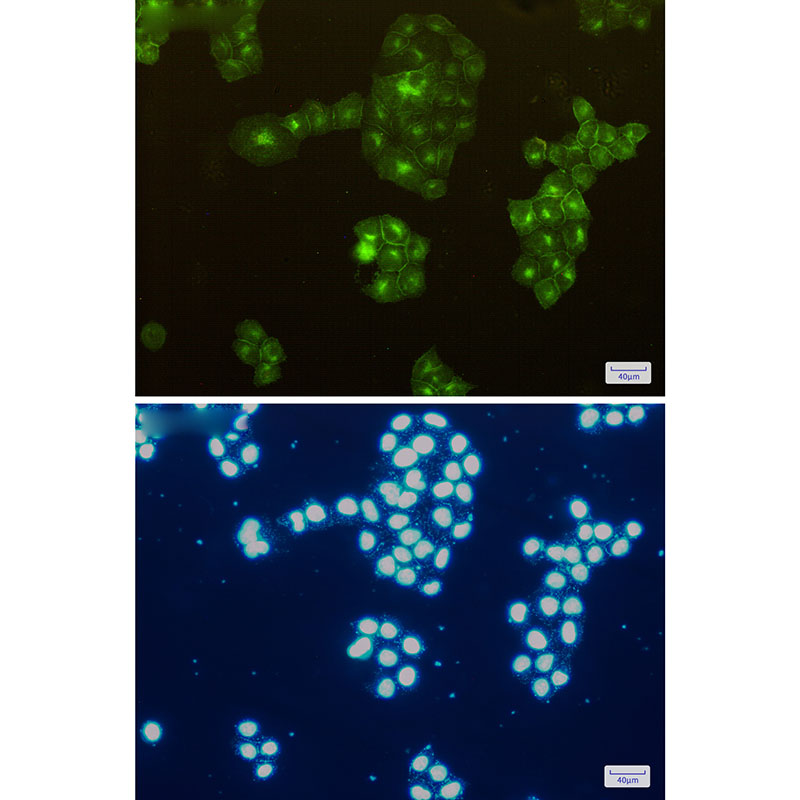
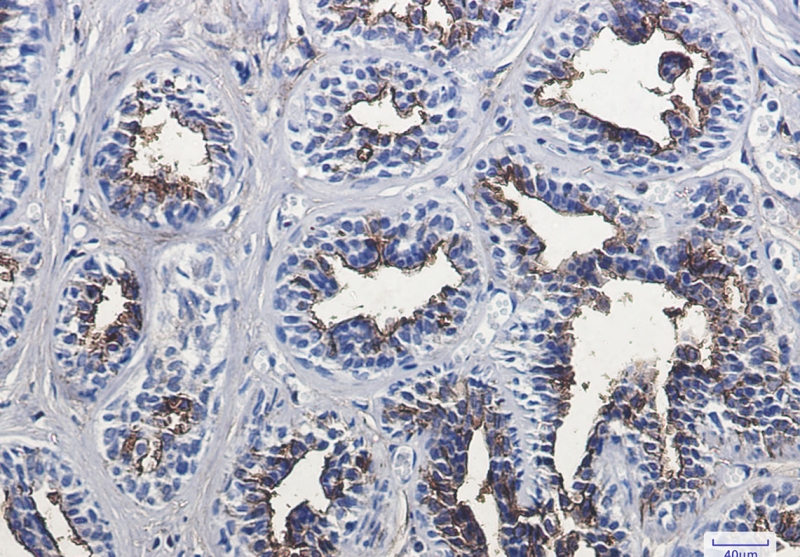
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ANPEP; APN; CD13; PEPN; Aminopeptidase N; AP-N; hAPN; Alanyl aminopeptidase; Aminopeptidase M; AP-M; Microsomal aminopeptidase; Myeloid plasma membrane glycoprotein CD13; gp150; CD antigen CD13 |
| Entrez GeneID | 290 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 110 kDa; Observed MW: 160 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CD13 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD13抗体的3篇代表性文献(人工整理示例,非真实文献):
1. **标题**:CD13 as a Therapeutic Target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究验证CD13在急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞中的高表达,并开发一种人源化抗CD13单克隆抗体,通过抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)显著抑制AML小鼠模型的肿瘤生长。
2. **标题**:Anti-CD13 Antibodies Modulate Tumor Angiogenesis and Metastasis
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:揭示CD13在肿瘤血管内皮细胞中的表达机制,证明靶向CD13的抗体可通过阻断血管生成信号通路抑制黑色素瘤的转移和微血管形成。
3. **标题**:CD13 in Dendritic Cell Function and Immune Regulation
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:发现CD13抗体通过调节树突状细胞(DC)的抗原呈递功能,影响T细胞免疫应答,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新策略。
*注:以上为模拟示例,实际引用需检索PubMed等数据库获取真实文献。建议使用关键词“CD13/ANPEP antibody”或“CD13 therapeutic target”筛选近5年高被引论文。*
CD13. also known as aminopeptidase N (APN), is a 150-kDa transmembrane glycoprotein that functions as a zinc-dependent metalloprotease. It is expressed on various cell types, including myeloid progenitors, granulocytes, monocytes, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells. CD13 plays roles in peptide metabolism, antigen presentation, angiogenesis, and cellular adhesion. Its enzymatic activity regulates bioactive peptides like angiotensin III and enkephalins, impacting blood pressure modulation and pain response.
CD13 antibodies target this protein and are widely used in research and diagnostics. In hematopathology, CD13 serves as a myeloid lineage marker, aiding in the diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) through flow cytometry. Commercially available clones (e.g., WM15. LeuM7) are employed in immunohistochemistry to study tissue-specific expression in cancers, infections, or inflammatory conditions.
Therapeutically, CD13 has been explored as a target due to its overexpression in tumor vasculature and certain malignancies. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) or bispecific antibodies against CD13 have shown preclinical potential in disrupting tumor growth or enhancing immune cell targeting. However, clinical applications remain limited compared to other targets. Recent studies also link CD13 to viral entry mechanisms, including coronaviruses, highlighting its broader biomedical relevance. Ongoing research continues to unravel its pathophysiological roles and therapeutic opportunities.
×