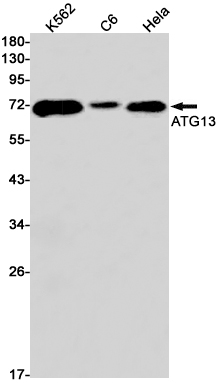
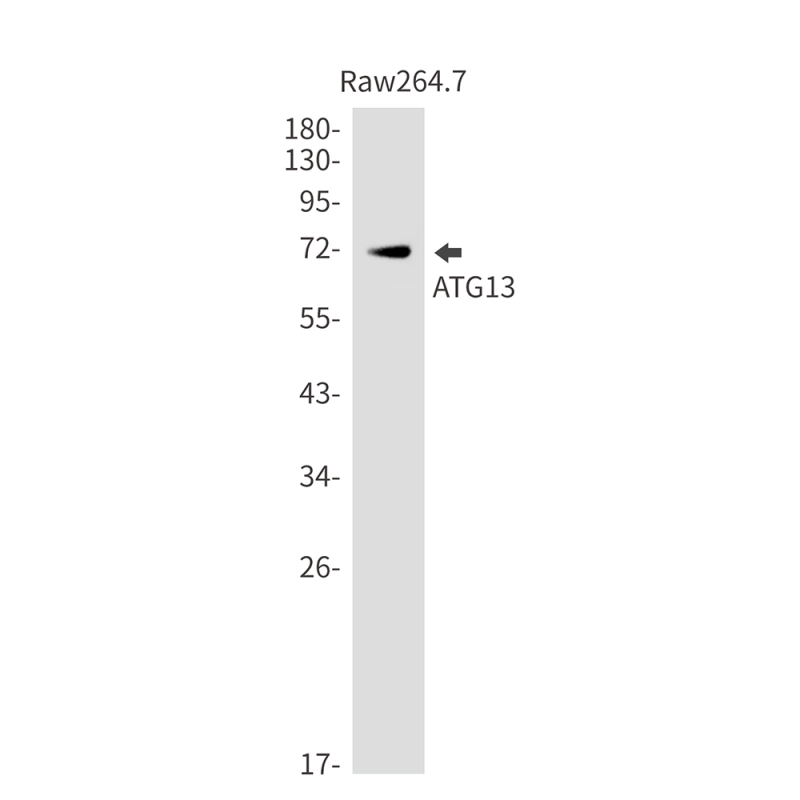
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Autophagy-related protein 13 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9776 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 57 kDa; Observed MW: 72 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human KIAA0652 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与ATG13抗体相关的参考文献及其摘要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**: *ULK-Atg13-FIP200 complexes mediate mTOR signaling to the autophagy machinery*
**作者**: Hosokawa, N. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究揭示了mTOR通过磷酸化ATG13调控自噬起始的机制。研究使用特异性ATG13抗体证实,在营养充足条件下,mTORC1磷酸化ATG13以抑制ULK1激酶活性;而在饥饿状态下,mTOR失活导致ATG13去磷酸化,进而激活ULK1复合体并启动自噬。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Regulation of Mammalian Autophagy in Physiology and Pathophysiology*
**作者**: Mizushima, N. & Levine, B.
**摘要**: 这篇综述系统总结了自噬调控的关键分子机制,包括ATG13在ULK1复合体中的核心作用。文中提及通过ATG13抗体的免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,验证了ATG13在不同生理条件下(如饥饿或雷帕霉素处理)的表达与定位变化。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: lessons from yeast*
**作者**: Nakatogawa, H. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过比较酵母和哺乳动物自噬机制,阐明了ATG13在自噬体形成中的进化保守性。利用ATG13抗体进行蛋白质相互作用分析(如Co-IP),揭示了ATG13与FIP200、ULK1的复合体组装过程及其对自噬通量的调控。
---
这些文献均涉及ATG13在自噬中的功能研究,并通过抗体实验(如Western blot、免疫沉淀等)验证其分子机制。如需具体实验细节,可进一步查阅原文方法部分。
ATG13 (Autophagy-related protein 13) is a critical component of the autophagy machinery, a conserved cellular process responsible for degrading and recycling damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and pathogens. It forms the ULK1/2 kinase complex with FIP200. ATG101. and ULK1/2. which acts as a central regulator of autophagosome initiation. ATG13 plays a scaffolding role in this complex, facilitating its activation under stress conditions such as nutrient deprivation. Phosphorylation of ATG13 by upstream kinases (e.g., mTOR, AMPK) modulates its interaction with ULK1/2. thereby regulating autophagic flux. Dysregulation of ATG13 function is linked to diseases like cancer, neurodegeneration, and metabolic disorders.
ATG13 antibodies are essential tools for studying autophagy mechanisms. They enable detection of ATG13 expression levels, post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation at specific serine residues), and subcellular localization using techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. These antibodies also help investigate interactions within the ULK complex and its dynamic assembly during autophagy induction. Commercially available ATG13 antibodies are often validated across species (human, mouse, rat) and tested for specificity using knockout controls. Researchers rely on these reagents to explore ATG13’s role in disease models, drug screening, and pathway validation, advancing therapeutic strategies targeting autophagy-related disorders.
×