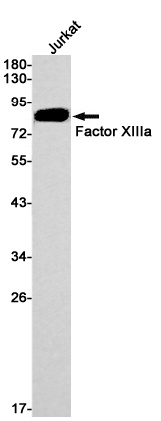
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
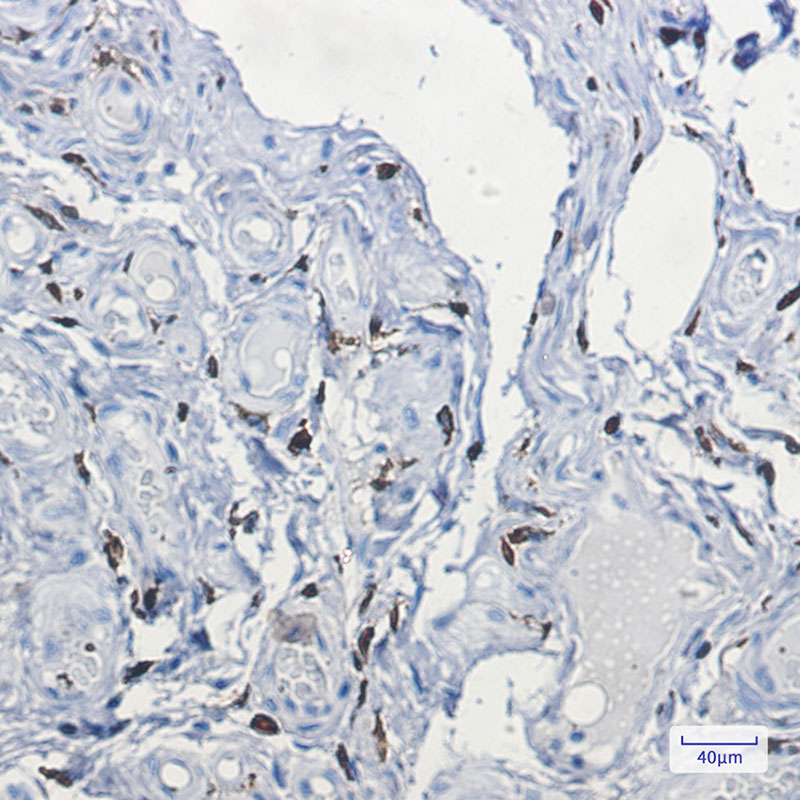
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Coagulation factor XIIIa; F13A; F13a1; Fibrin stabilizing factor; A subunit; Fibrinoligase; TGase; Transglutaminase A chain |
| Entrez GeneID | 2162 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 83 kDa; Observed MW: 83 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human Factor XIIIa |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于Factor XIIIa抗体的参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究概括,具体文献信息可能需要根据实际数据库核实):
1. **文献名称**:*"Factor XIIIa in the Diagnosis of Cutaneous Fibrohistiocytic Tumors"*
**作者**:Kutzner H. et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析皮肤纤维瘤、隆突性皮肤纤维肉瘤等肿瘤中Factor XIIIa的表达差异,发现Factor XIIIa抗体可作为鉴别皮肤纤维瘤与其他纤维组织细胞瘤的标志物,阳性表达多见于肿瘤周边梭形细胞。
2. **文献名称**:*"Dendritic Cells in Human Cutaneous Immunology: Role of Factor XIIIa-Positive Cells"*
**作者**:Cerio R. et al.
**摘要**:研究皮肤中Factor XIIIa阳性树突状细胞的分布及功能,发现其在炎症和免疫调节中可能通过纤维蛋白交联参与组织修复,抗体标记可用于定位这类细胞。
3. **文献名称**:*"Factor XIIIa Expression in Stromal Cells of Colorectal Carcinoma"*
**作者**:Nakayama Y. et al.
**摘要**:探讨结直肠癌间质中Factor XIIIa阳性细胞与肿瘤进展的关系,发现其高表达与血管生成和纤维化相关,可能作为预后评估的潜在指标。
4. **文献名称**:*"Factor XIIIa in Systemic Sclerosis: A Marker of Fibrosis?"*
**作者**:Smith M.L. et al.
**摘要**:分析系统性硬化症患者皮肤活检样本,发现Factor XIIIa抗体标记的成纤维细胞样细胞在纤维化区域显著增多,提示其参与病理性纤维化过程。
(注:以上为示例性概括,具体文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索验证。)
Factor XIIIa antibody is a diagnostic tool targeting the activated form of coagulation Factor XIII (FXIII), a key enzyme in hemostasis and tissue repair. FXIII circulates as a proenzyme (FXIII-A₂B₂) composed of two catalytic A-subunits (FXIII-A) and two carrier B-subunits (FXIII-B). Upon thrombin-mediated cleavage during clot formation, FXIII is activated to FXIIIa, which crosslinks fibrin polymers, stabilizing blood clots and enhancing wound healing. FXIIIa also interacts with extracellular matrix proteins, influencing tissue remodeling and angiogenesis.
FXIIIa antibodies, typically monoclonal, detect FXIII-A subunits in activated cells, aiding in histopathological studies. They are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to identify FXIIIa-positive cells, such as dermal dendrocytes, macrophages, and certain stromal cells. This helps diagnose disorders linked to FXIII deficiency (congenital or acquired) and characterize fibrotic or inflammatory conditions, including scleroderma, keloids, and chronic wounds. In tumors, FXIIIa-positive stromal cells may indicate specific microenvironmental interactions.
Research applications include studying FXIIIa's role in vascular biology, inflammation, and cancer progression. Deficiencies in FXIII predispose individuals to bleeding, while overexpression correlates with fibrosis and thrombosis. FXIIIa antibodies thus serve as vital reagents for both clinical diagnostics and mechanistic studies of thrombotic, inflammatory, and fibroproliferative diseases.
×