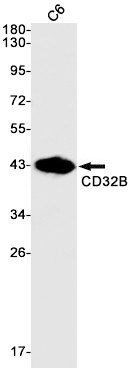
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
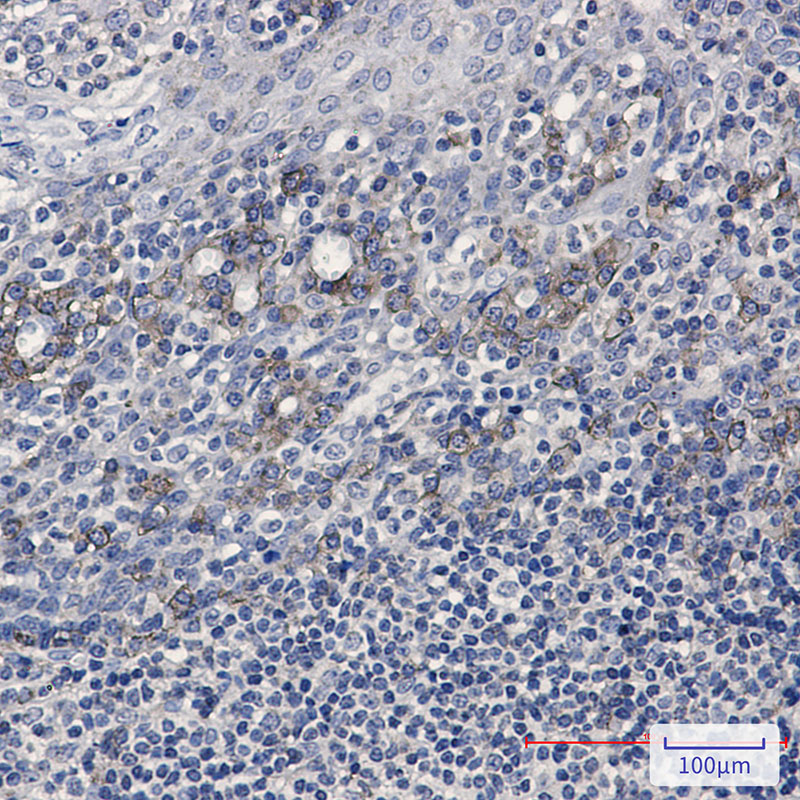
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Fc fragment of IgG; low affinity IIb; receptor (CD32); CD32; FCG2; CD32B; FCGR2; IGFR2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2213 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa; Observed MW: 44 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CD32B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD32B(FcγRIIB)抗体的代表性文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Targeting CD32B for immune checkpoint therapy in B-cell malignancies*
**作者**: Smith P, et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 研究证明CD32B抗体通过阻断FcγRIIB介导的抑制性信号,增强B细胞淋巴瘤模型中抗CD20抗体的ADCC效应,并逆转肿瘤微环境的免疫抑制,为B细胞恶性肿瘤的联合治疗提供新策略。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Structural basis of FcγRIIB recognition by a bispecific antibody for cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**: Li Y, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 通过解析CD32B与双特异性抗体(同时靶向CD32B和肿瘤抗原)的复合物晶体结构,揭示了抗体结合的关键表位,为设计优化靶向CD32B的免疫治疗药物提供结构生物学依据。
---
3. **文献名称**: *CD32B blockade enhances efficacy of CD47-targeted cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**: Ring NG, et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 研究发现阻断CD32B可协同增强抗CD47抗体的抗肿瘤效果,机制涉及抑制巨噬细胞对癌细胞的吞噬抑制作用,提出联合靶向CD32B和CD47的潜在疗法。
---
4. **文献名称**: *FcγRIIB regulates autoantibody responses by limiting marginal zone B cell activation*
**作者**: Nimmerjahn F, et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 在小鼠模型中证明,CD32B缺陷导致边缘区B细胞过度活化并产生自身抗体,提示CD32B抗体可能通过调节B细胞亚群功能干预自身免疫疾病。
---
以上文献涵盖CD32B抗体在肿瘤免疫、结构机制及自身免疫疾病中的研究,均为该领域的高影响力论文。
The CD32B antibody targets CD32B (FcγRIIB), a low-affinity inhibitory receptor for the Fc region of IgG antibodies. Expressed primarily on B cells, dendritic cells, and myeloid cells, CD32B plays a critical role in modulating immune responses by balancing activating signals from other Fc receptors (e.g., CD32A). It suppresses B cell receptor (BCR) signaling to prevent hyperactivation and maintains immune tolerance, making it a key checkpoint in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Research into CD32B antibodies has gained momentum due to their therapeutic potential. In cancer, blocking CD32B may enhance antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) by disinhibiting effector cells, improving the efficacy of monoclonal antibody therapies. Conversely, in autoimmune conditions, agonistic CD32B antibodies could dampen pathogenic B cell activity. Challenges include its structural similarity to activating Fc receptors, requiring high specificity to avoid off-target effects, and understanding context-dependent signaling. Recent studies also explore bispecific antibodies engaging CD32B to direct immune responses. Despite progress, its dual role in immune regulation—both suppressive and contextually pro-inflammatory—demands careful therapeutic design. Ongoing clinical trials aim to validate CD32B targeting strategies in oncology and autoimmunity, highlighting its versatility as a immunomodulatory tool.
×