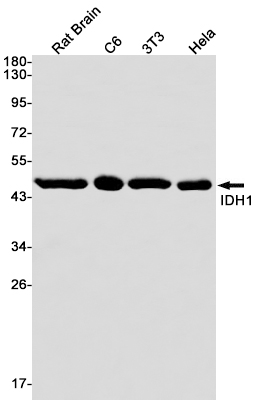
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
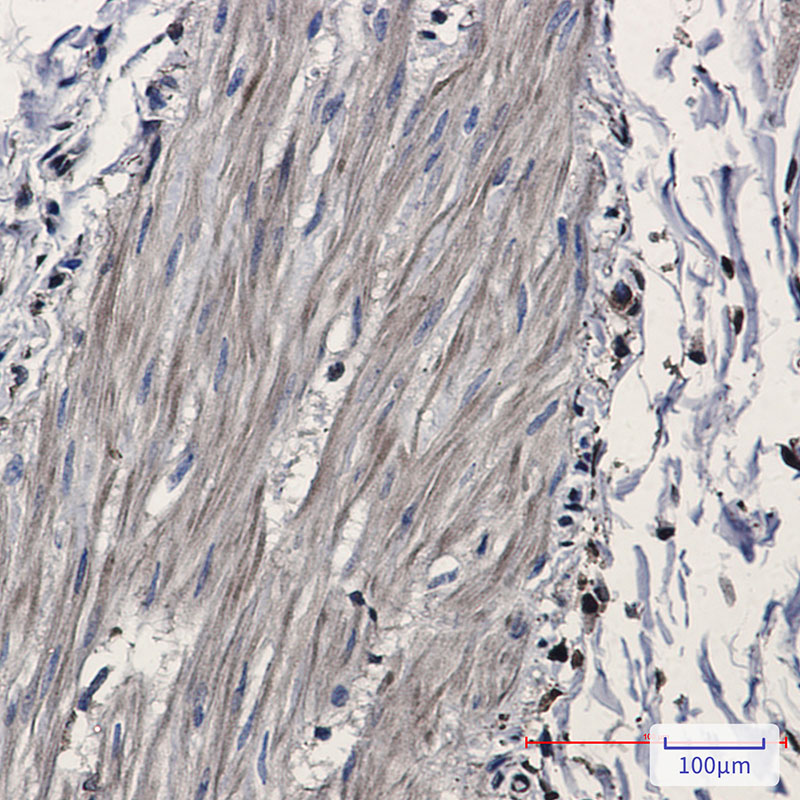
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IDH1; PICD; Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic; IDH; Cytosolic NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase; IDP; NADP(+)-specific ICDH; Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase |
| Entrez GeneID | 3417 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 47 kDa; Observed MW: 47 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IDH1抗体的3-4篇参考文献的简要概括:
1. **"IDH1 mutations are present in the majority of common adult gliomas but rare in primary glioblastomas"**
- **作者**: Yan H. et al. (2009)
- **摘要**: 该研究首次报道了IDH1基因突变在胶质瘤中的高频率(约70%),并开发了特异性抗体用于检测IDH1-R132突变蛋白。研究发现,突变型IDH1与患者较长生存期相关,为胶质瘤分子分型提供了重要依据。
2. **"Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate"**
- **作者**: Dang L. et al. (2009)
- **摘要**: 研究揭示了IDH1突变导致代谢产物2-羟基戊二酸(2-HG)的积累,提出其致癌机制。实验中利用IDH1抗体验证突变蛋白表达,并证明2-HG可能通过表观遗传调控促进肿瘤发生。
3. **"Type and frequency of IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in solid tumors"**
- **作者**: Hartmann C. et al. (2009)
- **摘要**: 通过免疫组化(使用IDH1-R132H特异性抗体)和测序,分析了多种实体瘤中IDH1/2突变的分布。结果显示,IDH1突变主要存在于胶质瘤和软骨肉瘤中,且抗体检测与基因测序结果高度一致。
4. **"A monoclonal antibody IMab-1 specifically recognizes IDH1-R132H, the most common glioma-derived mutation"**
- **作者**: Kato Y. et al. (2009)
- **摘要**: 研究团队开发了高特异性单克隆抗体IMab-1.可精准识别IDH1-R132H突变体。该抗体在胶质瘤病理诊断中表现出高灵敏度和特异性,为临床快速检测提供了可靠工具。
**备注**:以上文献均发表于2009年前后,为IDH1突变及抗体应用的奠基性研究,适用于肿瘤分子机制探索或诊断方法开发参考。
The IDH1 antibody is a crucial tool in cancer research and diagnostics, targeting isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1), a metabolic enzyme involved in cellular energy production and redox regulation. Normally, IDH1 catalyzes the conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) in the citric acid cycle. However, mutations in the IDH1 gene, particularly the R132H substitution, are frequently observed in gliomas, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and chondrosarcomas. These mutations confer neomorphic activity, enabling mutant IDH1 to produce the oncometabolite D-2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG), which disrupts cellular differentiation and promotes tumorigenesis via epigenetic dysregulation.
IDH1 antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) and molecular assays to detect mutant IDH1 protein in tumor samples. Their specificity for mutant IDH1 (e.g., R132H) aids in distinguishing tumor subtypes, guiding diagnosis, and predicting prognosis. For instance, IDH1-mutant gliomas are associated with better clinical outcomes compared to IDH-wildtype counterparts. Additionally, these antibodies support research into therapeutic strategies targeting mutant IDH1. such as small-molecule inhibitors (e.g., ivosidenib). By enabling precise identification of IDH1 mutations, these antibodies play a pivotal role in advancing personalized oncology and understanding metabolic reprogramming in cancer.
×