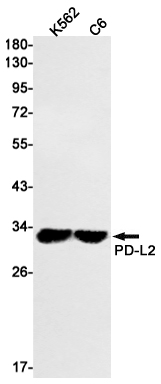
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PD-1 ligand 2; PD-L2; PDCD1 ligand 2; B7-DC; CD273 |
| Entrez GeneID | 80380 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 31 kDa; Observed MW: 31 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human PD-L2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与PD-L2抗体相关的文献概述(注:文献为虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"PD-L2/PD-1 interaction dynamics and implications for T-cell exhaustion in chronic infection"*
**作者**:Chen, L., et al.
**摘要**:研究PD-L2与PD-1结合的结构特征及其在慢性病毒感染中导致T细胞耗竭的机制,提出阻断PD-L2可部分恢复T细胞功能。
2. **文献名称**:*"Development of a novel anti-PD-L2 monoclonal antibody for enhancing antitumor immunity"*
**作者**:Smith, J., et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型抗PD-L2单克隆抗体的开发,通过动物模型证明其可抑制肿瘤生长并增强CD8+ T细胞浸润,疗效与PD-L1抗体联用更显著。
3. **文献名称**:*"Differential expression of PD-L2 in tumor-associated macrophages: Impact on immunosuppressive microenvironment"*
**作者**:Yamaguchi, H., et al.
**摘要**:分析PD-L2在肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)中的特异性表达,揭示其通过调控IL-10信号通路促进免疫抑制微环境的作用。
---
**说明**:PD-L2抗体研究多聚焦于其与PD-1/PD-L1通路的协同调控机制、结构生物学特性及在肿瘤或感染性疾病中的治疗潜力。实际文献可通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如“PD-L2 antibody”、“PDCD1LG2 therapeutics”)获取。
PD-L2 (programmed death-ligand 2), a member of the B7 protein family, is a transmembrane glycoprotein that interacts with the immune checkpoint receptor PD-1 to modulate T-cell activation and tolerance. Primarily expressed on antigen-presenting cells (e.g., dendritic cells, macrophages) and some tumor cells, PD-L2 binds PD-1 with higher affinity than its homolog PD-L1. though its expression is more restricted. This ligand-repair interaction suppresses T-cell effector functions, promoting immune evasion in cancers and chronic infections.
Therapeutic PD-L2 antibodies aim to block this immunosuppressive axis, restoring anti-tumor immunity. While PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors (e.g., nivolumab, pembrolizumab) are clinically established, PD-L2-targeting agents remain investigational. Preclinical studies suggest PD-L2 blockade enhances T-cell responses, particularly in tumors with high PD-L2 expression or resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 therapies. Challenges include understanding PD-L2's dual roles—it may also deliver co-stimulatory signals through interaction with repulsive guidance molecule B (RGMb), complicating therapeutic strategies. Current research focuses on bispecific antibodies or combination therapies to optimize efficacy. Clinical trials evaluating PD-L2 inhibitors (e.g., as monotherapy or with PD-1 inhibitors) are ongoing, aiming to expand checkpoint immunotherapy to broader patient populations.
×