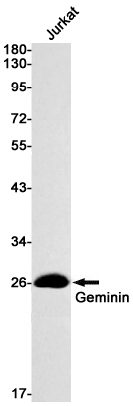
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Gem; Geminin; GMNN |
| Entrez GeneID | 51053 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 24 kDa; Observed MW: 24 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human Geminin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Geminin抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其应用及功能研究:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Geminin Prevents Rereplication during the Cell Cycle by Inhibiting Cdt1"*
**作者**:McGarry, T.J., Kirschner, M.W.
**摘要**:该研究首次揭示了Geminin通过抑制Cdt1蛋白来阻止DNA的重复复制,维持细胞周期正常进程。实验中利用Geminin抗体通过免疫沉淀技术验证了Geminin与Cdt1的相互作用,并证明其在S期至M期的周期性降解机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Geminin Promotes Neural Differentiation through Coordinated Regulation of Cell Cycle and Chromatin Structure"*
**作者**:Spike, B.T., et al.
**摘要**:文章探讨Geminin在神经干细胞分化中的作用,发现其通过调控细胞周期和染色质重塑促进分化。研究使用Geminin抗体进行免疫荧光染色,显示Geminin在未分化细胞中的核内定位及其在分化过程中的动态变化。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Regulation of Geminin Stability by APC/C and CDK1 in the Cell Cycle"*
**作者**:Tachibana, K.E., et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了Geminin的稳定性受APC/C复合体和CDK1激酶的调控。通过Western blot结合Geminin特异性抗体,作者证明Geminin在G1期的降解依赖于APC/C,而CDK1磷酸化可抑制其降解,确保DNA复制的精确性。
---
这些文献展示了Geminin抗体在解析蛋白功能、相互作用及细胞周期调控中的关键作用。
Geminin antibodies are essential tools for studying the role of Geminin, a critical regulatory protein involved in controlling DNA replication and cell cycle progression. Geminin functions as a key inhibitor of the DNA replication licensing factor Cdt1. ensuring that DNA is replicated only once per cell cycle by preventing re-loading of the mini-chromosome maintenance (MCM) complex during S phase and mitosis. Its expression peaks during the S and G2 phases and is degraded during mitosis via the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C). Dysregulation of Geminin has been linked to genomic instability, cancer, and developmental disorders, making it a focus of cell cycle and cancer biology research.
Antibodies targeting Geminin are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to analyze its expression, localization, and interactions in various cellular contexts. These antibodies are particularly valuable in studies exploring cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue development, as Geminin is also implicated in maintaining stem cell pluripotency and regulating neural differentiation. Commercial Geminin antibodies are typically developed against specific epitopes, often within its coiled-coil domain, and validated for species cross-reactivity (e.g., human, mouse, rat). Researchers must verify antibody specificity using knockout controls or siRNA-mediated depletion, as off-target binding can occur due to structural similarities with other proteins. Proper selection of Geminin antibodies depends on experimental needs, including detection of post-translational modifications or cell cycle stage-specific expression patterns.
×