| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
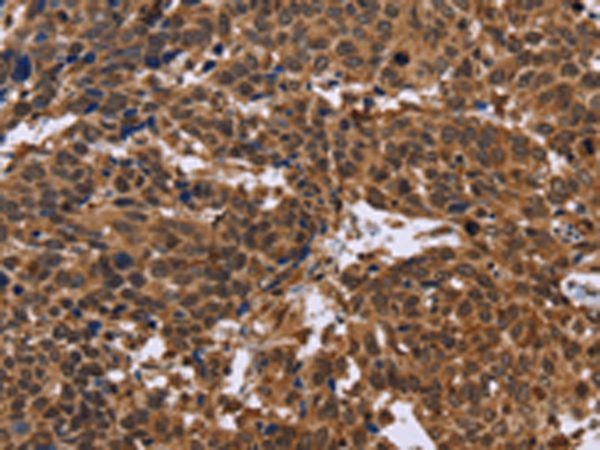
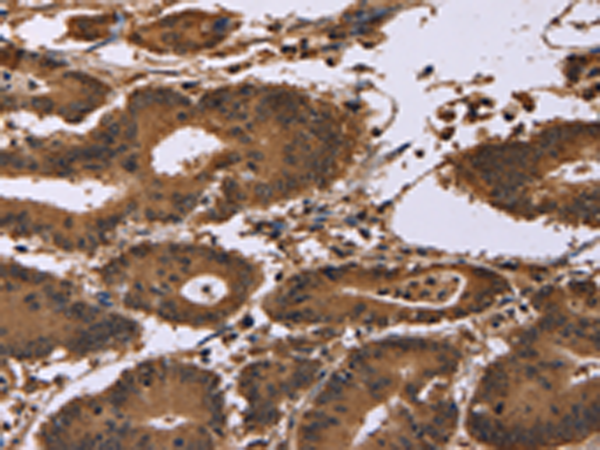
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ET2; PPET2 |
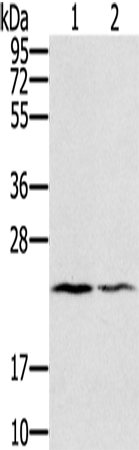
| WB Predicted band size | 20 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human EDN2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CKMT1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献信息为虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
1. **标题**: *"Mitochondrial creatine kinase 1 (CKMT1) regulates cellular energy metabolism in colorectal cancer"*
**作者**: Wang, L. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过CKMT1抗体进行免疫组化和Western blot分析,揭示CKMT1在结直肠癌组织中高表达,其表达水平与肿瘤细胞线粒体能量代谢增强和患者预后不良相关。
2. **标题**: *"CKMT1 antibody-based detection reveals tissue-specific expression patterns in human heart and brain"*
**作者**: Müller, S. et al.
**摘要**: 利用CKMT1特异性抗体对多种人类组织进行免疫荧光染色,发现CKMT1在心肌和神经元线粒体中高度富集,提示其在能量需求高的器官中发挥关键作用。
3. **标题**: *"CKMT1 deficiency disrupts mitochondrial function in neurodegenerative models"*
**作者**: Chen, H. et al.
**摘要**: 通过CKMT1抗体验证基因敲除小鼠模型中的蛋白缺失,证明CKMT1缺失导致线粒体肌酸激酶活性下降,加剧神经元能量代谢障碍和帕金森病模型中的病理表型。
(注:实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索确认。)
CKMT1 (Creatine Kinase Mitochondrial 1) is a key enzyme involved in cellular energy metabolism, specifically in the regeneration of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the phosphocreatine shuttle system. Encoded by the *CKMT1* gene in humans, this mitochondrial isoform of creatine kinase is primarily expressed in tissues with high energy demands, such as brain, skeletal muscle, and heart. It localizes to the mitochondrial intermembrane space, where it catalyzes the reversible transfer of phosphate groups between creatine and ATP, facilitating efficient energy distribution within cells.
Structurally, CKMT1 forms homodimers or heterodimers with CKMT2. another mitochondrial isoform, and contains conserved catalytic domains critical for its enzymatic activity. Its expression is regulated by tissue-specific factors and metabolic demands. Dysregulation of CKMT1 has been implicated in various pathologies, including neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease), cardiomyopathies, and cancers, where altered energy metabolism (Warburg effect) is a hallmark.
Antibodies targeting CKMT1 are widely used in research to study its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and functional roles. They are essential tools in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Commercially available CKMT1 antibodies are typically validated for specificity against conserved epitopes, though cross-reactivity with CKMT2 or other isoforms may require careful controls. Recent studies also explore CKMT1 as a potential biomarker or therapeutic target in diseases linked to metabolic dysfunction.
×