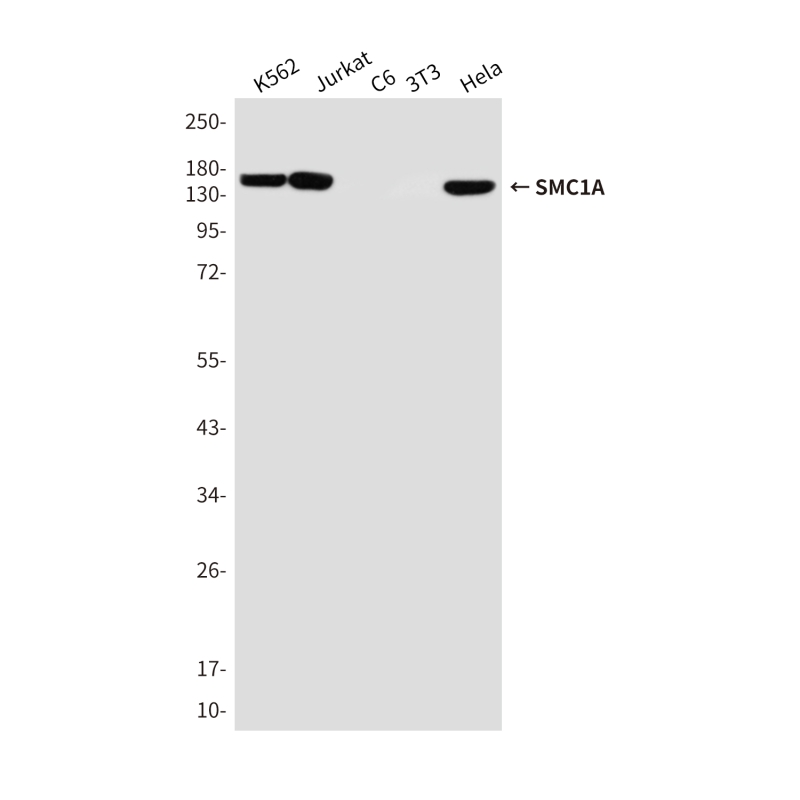
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Chromosome segregation protein SmcB; DXS423E; KIAA0178; MGC138332; Sb1.8; Segregation of mitotic chromosomes 1; SMC protein 1A; SMC-1-alpha; SMC-1A; SMC1 (structural maintenance of chromosomes 1 yeast) like 1; SMC1; SMC1 structural maintenance of chromosomes 1 like 1; SMC1A; SMC1A_HUMAN; SMC1alpha; SMC1L1; SMCB; Structural maintenance of chromosomes 1A; Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 1A. |
| Entrez GeneID | 8243 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 143 kDa; Observed MW: 143 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human SMC1A(C-term.) protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SMC1A抗体的3-4篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"SMC1A mutations promote tumorigenesis through mitotic checkpoint defects in human cancers"**
- **作者**: Musio, A., et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究探讨了SMC1A基因的体细胞突变在多种癌症(如结直肠癌和白血病)中的作用,发现突变导致有丝分裂检查点缺陷,从而驱动基因组不稳定性及肿瘤发生。研究通过抗体检测SMC1A蛋白表达异常与肿瘤进展的关联。
2. **"Mutations in cohesin complex members SMC3 and SMC1A cause Cornelia de Lange syndrome"**
- **作者**: Liu, J., & Krantz, I.D.
- **摘要**: 文章揭示了SMC1A基因突变与Cornelia de Lange综合征(CdLS)的遗传关联,利用抗体进行蛋白质功能分析,表明突变导致黏连蛋白复合体功能受损,引发发育异常和神经认知障碍。
3. **"Phosphorylation of SMC1A by ATM links cohesion to DNA damage response"**
- **作者**: Kitajima, T.S., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究发现ATM激酶在DNA损伤后磷酸化SMC1A,通过抗体特异性检测磷酸化位点,阐明这一修饰在协调姐妹染色单体黏连与DNA修复中的关键作用,维持基因组稳定性。
4. **"SMC1A overexpression as a prognostic marker in breast cancer"**
- **作者**: Bruening, E., et al.
- **摘要**: 该临床研究利用SMC1A抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现乳腺癌组织中SMC1A高表达与患者生存率降低显著相关,提示其作为预后生物标志物的潜在价值。
这些文献分别从癌症机制、遗传疾病、DNA修复响应及临床预后角度,展示了SMC1A抗体的应用及其功能研究的多样性。
The SMC1A antibody targets the Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes 1A (SMC1A) protein, a core component of the cohesin complex essential for chromosome organization, sister chromatid cohesion, and DNA repair. SMC1A, along with SMC3. RAD21. and STAG proteins, forms a ring-like structure that mediates chromatin loop formation and regulates gene expression. It plays critical roles in mitosis, meiosis, and transcriptional regulation.
Antibodies against SMC1A are widely used in research to study its expression, localization, and interactions in cellular processes. They are applied in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and immunohistochemistry to investigate cohesin dysfunction linked to developmental disorders (e.g., Cornelia de Lange syndrome) and cancers (e.g., acute myeloid leukemia).
SMC1A mutations are associated with chromosomal instability and neurodevelopmental abnormalities, making its detection vital for mechanistic studies. Commercial SMC1A antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or coiled-coil domains) and validated for reactivity in human, mouse, or rat samples. Proper validation (e.g., knockout controls) ensures specificity, as cross-reactivity with SMC1B (a meiosis-specific paralog) may occur. Research on SMC1A continues to clarify its roles in 3D genome organization and disease, driving demand for reliable antibodies.
×