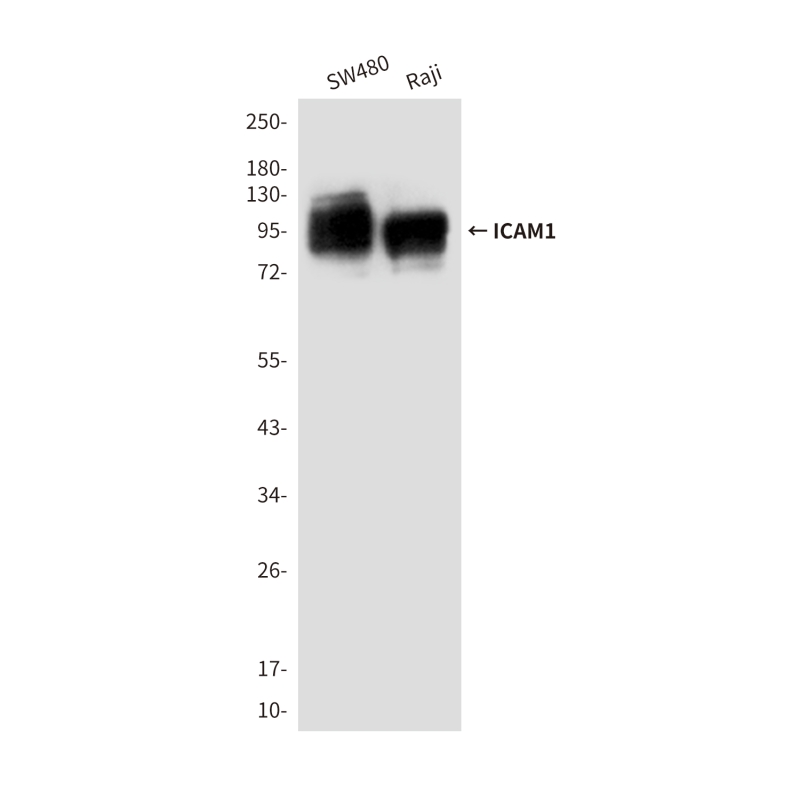
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ICAM1; Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; ICAM-1; Major group rhinovirus receptor; CD antigen CD54 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3383 |
| clone | 7H5 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 58 kDa; Observed MW: 96 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human CD54(ICAM-1) protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于ICAM1抗体的参考文献及简要摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Anti-ICAM-1 monoclonal antibody reduces inflammatory cell invasion in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis"*
**作者**: Rothlein, R. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过动物模型证明,抗ICAM1单克隆抗体能够抑制炎症细胞穿过血脑屏障的迁移,显著减轻实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(多发性硬化模型)的神经炎症损伤。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Targeted drug delivery via ICAM-1 antibody-conjugated nanoparticles in inflamed endothelial cells"*
**作者**: Muro, S. et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用抗ICAM1抗体修饰的纳米颗粒,实现在炎症内皮细胞中的靶向药物递送,证明其在动脉粥样硬化等疾病中提高局部药物浓度并减少全身毒性的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"ICAM-1 blockade inhibits tumor progression by impairing tumor-associated neutrophil recruitment"*
**作者**: Gho, Y.S. et al.
**摘要**: 文章发现抗ICAM1抗体可通过阻断肿瘤相关中性粒细胞(TANs)的募集,抑制肿瘤微环境中的促癌信号,从而减缓黑色素瘤和肺癌小鼠模型的肿瘤生长与转移。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"The role of ICAM-1 in endotoxin-induced lung injury: A study with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies"*
**作者**: Springer, T.A. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过中和性抗体阻断ICAM1.证实其在脓毒症相关急性肺损伤中的作用,结果显示抗体处理显著降低了肺组织中性粒细胞浸润和氧化应激损伤。
---
以上文献涵盖了ICAM1抗体在炎症、肿瘤、自身免疫病及靶向治疗中的应用机制。
ICAM-1 (Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1), also known as CD54. is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is constitutively expressed at low levels on endothelial cells, epithelial cells, and leukocytes, but its expression is significantly upregulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β) or oxidative stress. ICAM-1 mediates leukocyte adhesion and transmigration by binding to integrins LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18) and Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18), playing a pivotal role in inflammatory responses and immune surveillance.
ICAM-1 antibodies are valuable tools for studying inflammation-related diseases, including atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer. These antibodies, available as monoclonal or polyclonal forms, are widely used in techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and Western blot to detect ICAM-1 expression in tissues or cultured cells. In therapeutic contexts, anti-ICAM-1 antibodies have been explored to inhibit leukocyte infiltration in autoimmune disorders or to block tumor metastasis by targeting ICAM-1-mediated cell adhesion. However, clinical translation remains challenging due to off-target effects and variable efficacy.
Research also highlights ICAM-1's involvement in viral infections (e.g., rhinovirus, malaria), where it serves as a receptor for pathogen entry. Antibodies against ICAM-1 may thus offer strategies to interfere with microbial invasion. Overall, ICAM-1 antibodies continue to be essential for both mechanistic studies and therapeutic development in inflammation and immune dysregulation.
×