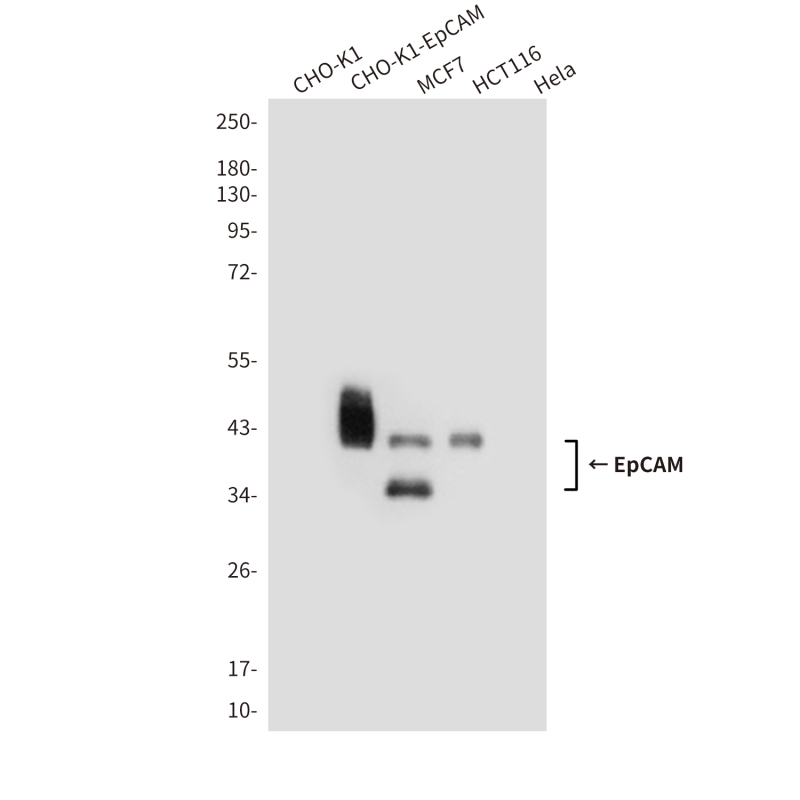
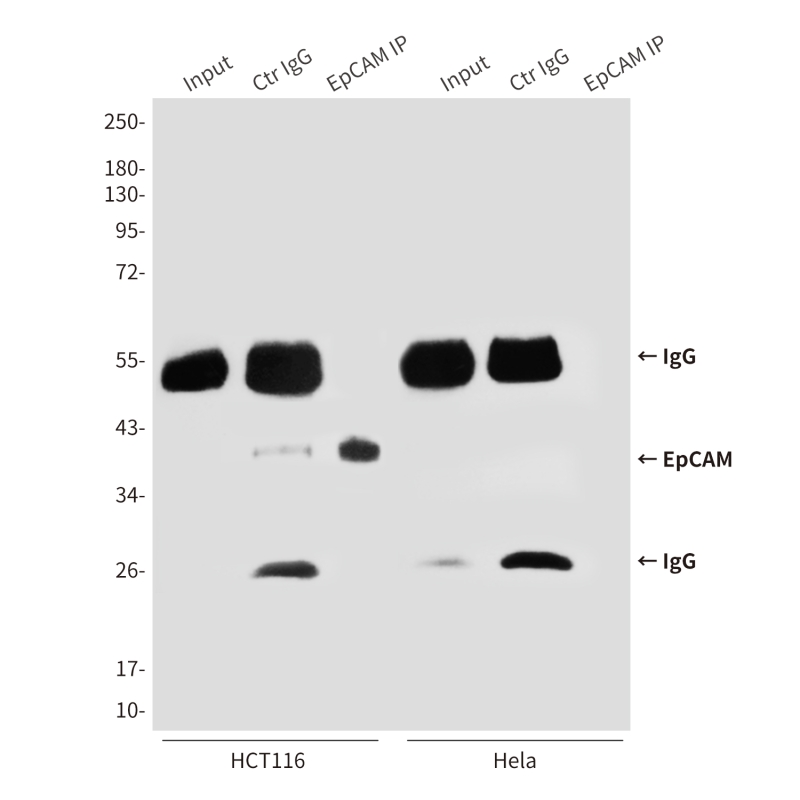
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EPCAM; GA733-2; M1S2; M4S1; MIC18; TACSTD1; TROP1; Epithelial cell adhesion molecule; Ep-CAM; Adenocarcinoma-associated antigen; Cell surface glycoprotein Trop-1; Epithelial cell surface antigen; Epithelial glycoprotein; EGP; Epithelial glycoprotein 314; EGP314; hEGP314; KS 1/4 antigen; KSA; Major gastrointestinal tumor-associated protein GA733-2; Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 1; CD326 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4072 |
| clone | 1G10 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 35 kDa; Observed MW: 39 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant EpCAM protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EpCAM抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*EpCAM: Structure and function in health and disease*
**作者**:Trzpis, M., et al.
**摘要**:综述EpCAM蛋白的分子结构、生理功能及其在癌症中的异常表达,重点讨论EpCAM抗体在肿瘤诊断、循环肿瘤细胞检测及靶向治疗中的应用潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Blood Using the CellSearch System*
**作者**:Riethdorf, S., et al.
**摘要**:描述基于EpCAM抗体的CellSearch技术用于富集和检测循环肿瘤细胞(CTC),验证其在转移性乳腺癌、结直肠癌等临床预后评估中的有效性。
3. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic bispecific antibodies against tumor-associated antigens*
**作者**:Munz, M., et al.
**摘要**:探讨双特异性抗体(如EpCAM×CD3抗体卡妥索单抗)通过同时靶向EpCAM和T细胞表面抗原激活免疫反应,在实体瘤治疗中的临床前及临床试验结果。
---
注:如需具体出版信息,可进一步提供DOI或PubMed ID。
EpCAM (Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule), also known as CD326. is a transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed on the basolateral surface of epithelial cells. It plays a key role in cell-cell adhesion, proliferation, and signaling. Structurally, it consists of an extracellular domain with two epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats, a single transmembrane domain, and a short intracellular tail. EpCAM is overexpressed in many epithelial-derived cancers, including breast, colorectal, lung, and pancreatic cancers, making it a valuable biomarker for tumor detection and targeted therapy.
EpCAM antibodies are immunoglobulins designed to specifically bind to the extracellular domain of EpCAM. They have become essential tools in cancer research and diagnostics. In diagnostics, these antibodies are used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) and flow cytometry to identify EpCAM-positive circulating tumor cells (CTCs) or tumor tissues. Therapeutically, EpCAM-targeting antibodies are employed in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), bispecific antibodies, and CAR-T cell therapies. For example, catumaxomab (anti-EpCAM × anti-CD3) was approved for malignant ascites treatment. However, challenges remain, such as heterogeneous EpCAM expression across tumors and potential off-target effects in normal tissues. Recent advances focus on improving antibody specificity and engineering novel formats (e.g., nanobodies) to enhance tumor penetration. Despite limitations, EpCAM antibodies continue to bridge translational research and clinical oncology.
×