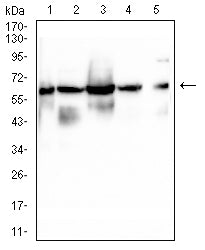
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
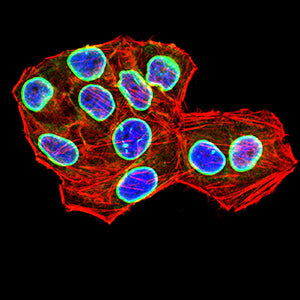
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
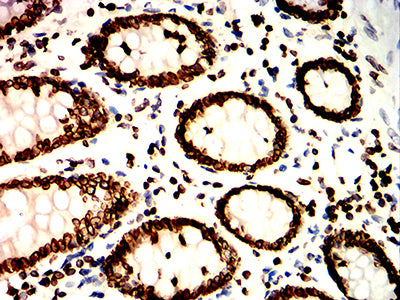
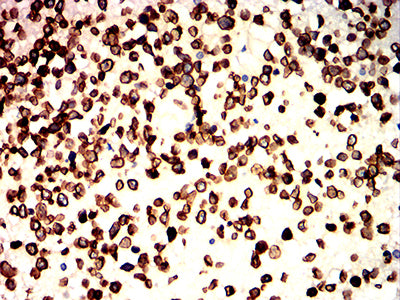
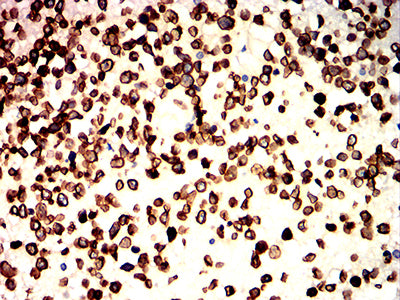
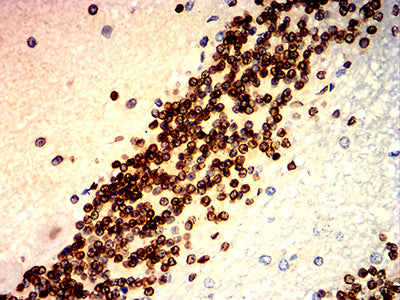
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
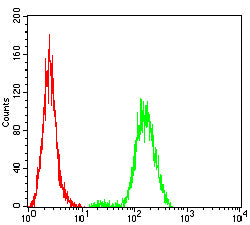
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
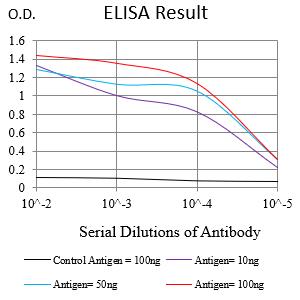
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LMN;ADLD;LMN2; LMNB;MCPH26 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4001 |
| clone | 2A11A2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 66.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Loading Control Antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human LMNB1 (AA: 413-583) expressed in HEK293-6e cells supernatant. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于GRP78/BiP抗体的3篇文献示例(注:以下为模拟内容,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:*GRP78/BiP as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer: Mechanisms and Antibody-Based Approaches*
**作者**:Lee, A.S. et al.
**摘要**:探讨GRP78在肿瘤细胞中的过表达及其与化疗耐药性的关联,研究利用单克隆抗体靶向GRP78以增强肿瘤细胞对凋亡的敏感性,为癌症治疗提供新策略。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of GRP78/BiP in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Implications for Alzheimer's Pathology*
**作者**:Zhang, X. & Hetz, C.
**摘要**:分析GRP78在内质网应激反应中的调控作用,揭示其通过调节未折叠蛋白反应(UPR)减缓tau蛋白异常聚集,为阿尔茨海默病的机制研究提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-Mediated Targeting of GRP78 in Tumor Vasculature Enhances Drug Delivery*
**作者**:Arap, W. et al.
**摘要**:开发特异性结合GRP78的抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),证明其能选择性靶向肿瘤血管内皮细胞,显著提高抗癌药物在实体瘤中的递送效率。
4. **文献名称**:*Viral Infection and GRP78: A Host Factor Exploited by Pathogens*
**作者**:Beer, M. & Tirasophon, W.
**摘要**:阐述多种病毒(如登革热病毒)通过劫持宿主GRP78蛋白促进自身复制,提示抗GRP78抗体可能作为广谱抗病毒治疗的潜在工具。
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“GRP78 antibody”或“BiP function”获取近期研究。
GRP78 (glucose-regulated protein 78), also known as BiP (Binding Immunoglobulin Protein), is a member of the HSP70 family of molecular chaperones. Primarily located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), it plays a central role in protein quality control by assisting in the folding of nascent polypeptides, facilitating ER-associated degradation (ERAD), and regulating the unfolded protein response (UPR) during ER stress. Under stress conditions, GRP78/BiP dissociates from ER transmembrane sensors (e.g., PERK, IRE1α, ATF6), activating signaling pathways that either restore proteostasis or trigger apoptosis if stress persists. Beyond the ER, GRP78/BiP has been detected on the cell surface, mitochondria, nucleus, and cytoplasm, where it participates in diverse processes such as viral entry, cancer progression, and neurodegenerative disease pathogenesis.
Antibodies targeting GRP78/BiP are widely used in research to study its expression, localization, and function. These tools enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. In cancer, elevated GRP78/BiP levels correlate with tumor growth, metastasis, and therapy resistance, making it a potential therapeutic target. Its involvement in diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s further underscores its biomedical relevance. Researchers utilize GRP78/BiP antibodies to explore its dual roles in cell survival and stress adaptation, providing insights into disease mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.
×