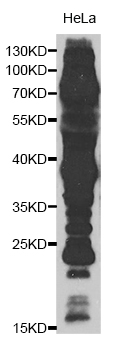
| WB | 咨询技术 | Transfected |
| IF | 1/20 | Transfected |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Transfected |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Transfected |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Transfected |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Transfected |
| WB Predicted band size | Refer to figures |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Transfected |
| Immunogen | Acetylated BSA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于Acetyl-Lysine抗体的参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究整理,建议通过数据库进一步验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Lysine Acetylation Targets Protein Complexes and Co-Regulates Major Cellular Functions*
**作者**: Choudhary, C., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用Acetyl-Lysine抗体结合质谱技术,系统分析了人类细胞中蛋白质的乙酰化修饰,揭示了超过2000个乙酰化位点,涉及代谢酶、核蛋白等多种非组蛋白,表明乙酰化在细胞功能调控中的广泛作用。
2. **文献名称**: *SIRT3 Regulates Breast Cancer Metastasis via Deacetylation of AKT1 and PDHA1*
**作者**: Kim, H.S., et al.
**摘要**: 通过Acetyl-Lysine抗体的Western blot和免疫沉淀技术,研究发现SIRT3通过去乙酰化AKT1和PDHA1抑制乳腺癌转移,揭示了乙酰化修饰在癌症代谢重编程中的关键机制。
3. **文献名称**: *Acetylation of p53 Augments Its Site-Specific DNA Binding In Vitro and In Vivo*
**作者**: Luo, J., et al.
**摘要**: 该文献利用Acetyl-Lysine特异性抗体证实p53蛋白的乙酰化修饰增强了其与DNA的结合能力,调控下游靶基因表达,阐明了乙酰化在肿瘤抑制中的直接功能。
4. **文献名称**: *Protocol for Protein Acetylation Analysis by Immunoprecipitation*
**作者**: Lin, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 方法学文章详细描述了使用Acetyl-Lysine抗体进行蛋白质乙酰化检测的标准化流程,包括免疫沉淀、Western blot及实验条件优化,为相关研究提供技术参考。
---
**建议**:通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索标题或作者,可获取全文及更准确的出版信息(如年份和期刊卷期)。
Acetyl-lysine antibodies are essential tools in studying protein acetylation, a key post-translational modification (PTM) involved in diverse cellular processes. Lysine acetylation, catalyzed by acetyltransferases (HATs) and reversed by deacetylases (HDACs), regulates protein function by neutralizing lysine's positive charge. This modification was first characterized in histones, where it modulates chromatin structure and gene expression by altering histone-DNA interactions. Beyond histones, acetylation impacts non-nuclear proteins, influencing metabolism, signal transduction, and protein stability.
The development of acetyl-lysine antibodies arose from the need to detect and map acetylation sites across proteomes. Early studies relied on radioactive labeling, but antibodies provided higher specificity and compatibility with routine techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. These antibodies recognize the acetylated ε-amino group of lysine, irrespective of protein context, enabling broad applications. However, target-specific acetyl-antibodies (e.g., anti-acetyl-H3K9) were later developed for precise localization.
Acetyl-lysine antibodies have advanced research in epigenetics, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. They help identify acetylation dynamics under physiological or pathological conditions, such as HDAC inhibitor effects or metabolic stress responses. Challenges remain in ensuring epitope specificity, as cross-reactivity with similar PTMs (e.g., crotonylation) can occur. Despite this, these antibodies remain indispensable for dissecting acetylation's regulatory roles in health and disease.
×