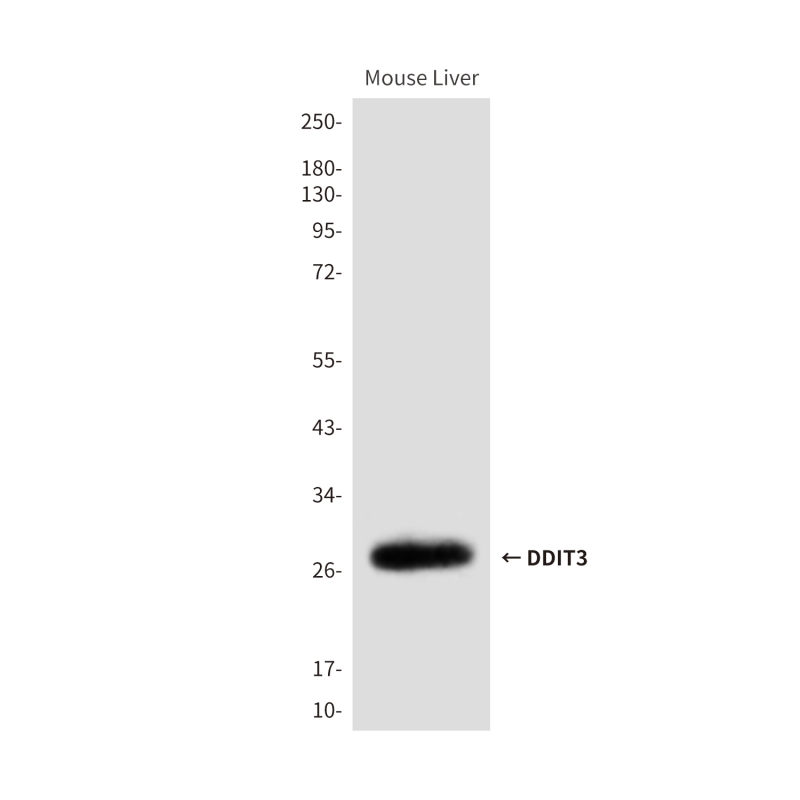

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
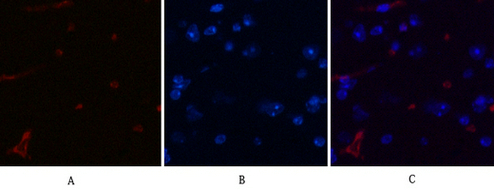
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
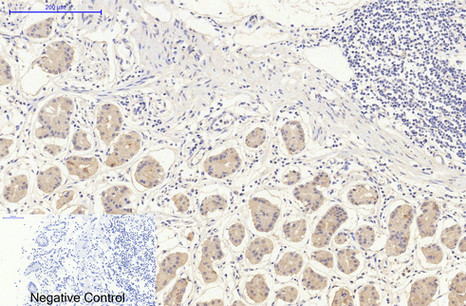
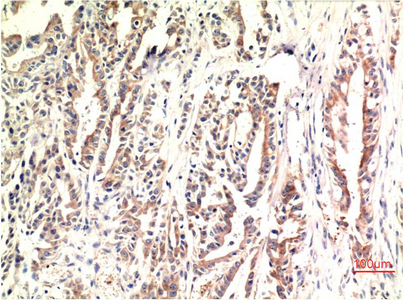
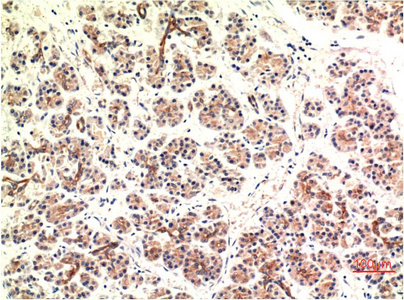
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DDIT3; CHOP; CHOP10; GADD153; DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein; DDIT-3; C/EBP-homologous protein; CHOP; C/EBP-homologous protein 10; CHOP-10; Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD153 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1649 |
| clone | 8D12 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 19 kDa; Observed MW: 27 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与DDIT3(CHOP)抗体相关的参考文献,按文献标题、作者及摘要概要整理:
1. **"CHOP is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by enhancing DR5 expression in human carcinoma cells"**
*作者:Yamaguchi H, Wang HG*
摘要:研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,利用DDIT3/CHOP抗体证明内质网应激通过上调DR5死亡受体增强肿瘤细胞凋亡,揭示了CHOP在调控癌细胞凋亡通路中的作用机制。
2. **"Endoplasmic reticulum stress activates cleavage of CREB3L3 to induce metabolic syndrome"**
*作者:Lee AH, Scapa EF, Cohen DE*
摘要:采用DDIT3抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现内质网应激通过CHOP信号通路促进CREB3L3蛋白切割,进而导致小鼠代谢综合征表型,证实CHOP在代谢疾病中的关键调控作用。
3. **"The unfolded protein response and chemical chaperones reduce protein accumulation in Parkinson’s disease patient-derived neurons"**
*作者:Chung CY, Khurana V, Yi S*
摘要:研究通过DDIT3抗体检测患者神经元中CHOP表达水平,证明化学伴侣药物可缓解帕金森病模型中的未折叠蛋白反应,降低内质网应激相关蛋白聚集,为神经退行性疾病提供治疗线索。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时请核对原文信息及发表年份)
**Background of DDIT3 Antibody**
The DDIT3 (DNA Damage Inducible Transcript 3) antibody is a crucial tool for studying the role of the DDIT3 protein, also known as CHOP (C/EBP Homologous Protein), in cellular stress responses. DDIT3. encoded by the *DDIT3* gene, is a member of the C/EBP (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein) family of transcription factors. It is primarily induced under endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, DNA damage, or nutrient deprivation, acting as a pro-apoptotic mediator in the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway. Structurally, DDIT3 contains a leucine zipper domain that facilitates dimerization with other C/EBP proteins, though these heterodimers often lack DNA-binding capacity, leading to transcriptional repression or activation of stress-related genes.
DDIT3 antibodies are widely used in research to detect DDIT3 expression and localization via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). These antibodies help elucidate DDIT3's involvement in pathologies such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s), diabetes, and ischemia-reperfusion injury, where ER stress and apoptosis are pivotal. Additionally, DDIT3 antibodies aid in studying crosstalk between stress pathways and therapeutic responses, including chemotherapy resistance.
Commercial DDIT3 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., human DDIT3 amino acids 50-150) and validated for specificity across species (human, mouse, rat). Their application continues to advance understanding of cellular stress mechanisms and biomarker discovery.
×