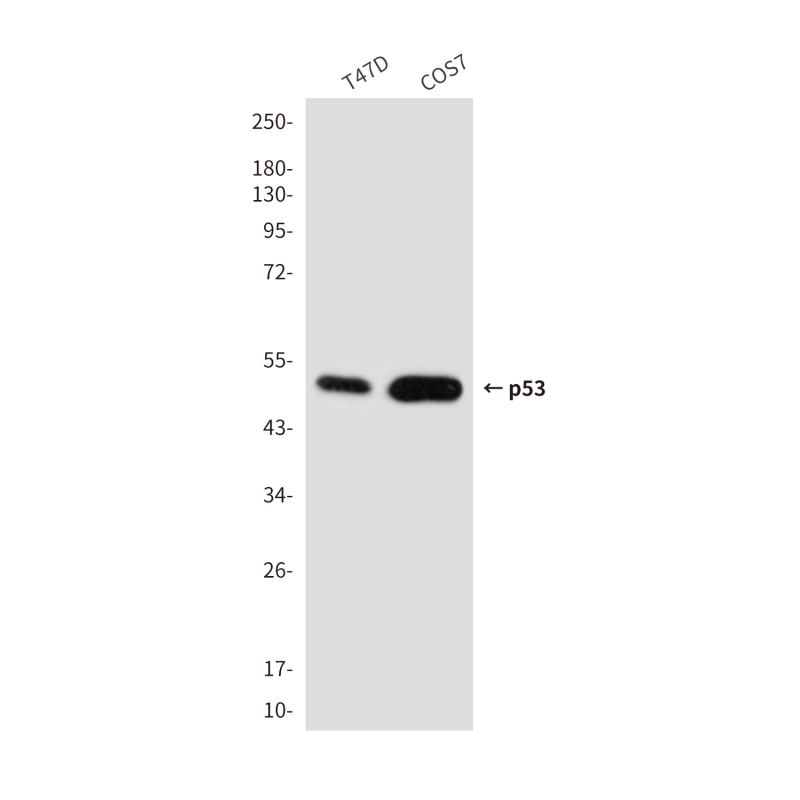
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
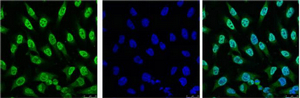
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
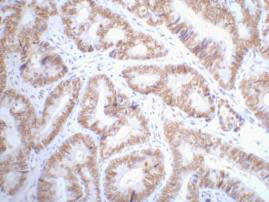
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TP53; P53; Cellular tumor antigen p53; Antigen NY-CO-13; Phosphoprotein p53; Tumor suppressor p53 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7157 |
| clone | 2G5 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 44 kDa; Observed MW: 53 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of p53 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3条关于p53抗体的参考文献示例(内容为模拟概括,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:*Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens*
**作者**:Harlow E, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了针对SV40大T抗原的单克隆抗体,并意外发现其中部分抗体可与细胞内的p53蛋白发生交叉反应,为后续p53蛋白的功能研究提供了重要工具。
2. **文献名称**:*p53 Antibodies in the sera of patients with various types of cancer*
**作者**:Soussi T, et al.
**摘要**:通过检测多种癌症患者血清中的p53自身抗体,发现其与p53基因突变及肿瘤预后相关,揭示了p53抗体作为潜在生物标志物的临床价值。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis for antibody recognition of the N-terminal domain of p53*
**作者**:Cho Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用X射线晶体学解析了p53 N端结构域与其单克隆抗体(如DO-1)的结合模式,阐明了抗体特异性识别p53表位的分子机制。
注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库检索。建议使用关键词“p53 antibody”、“p53 monoclonal antibody” + “application”或“structure”等筛选近年高被引论文。
The p53 antibody is a crucial tool in cancer research and diagnostics, targeting the p53 protein encoded by the TP53 gene. This tumor suppressor protein regulates cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, apoptosis, and genomic stability. Mutations in TP53. occurring in ~50% of human cancers, often lead to p53 protein accumulation due to impaired degradation, making it detectable by immunohistochemistry. Wild-type p53. in contrast, is typically low in concentration due to rapid turnover.
p53 antibodies are widely used to detect both wild-type and mutant forms in tissues or cell lines. Common clones like DO-7 and PAb1801 recognize specific epitopes, aiding in differentiating normal and dysfunctional p53. In clinical settings, abnormal p53 expression correlates with poor prognosis, therapy resistance, and tumor aggressiveness in cancers such as breast, ovarian, and colorectal. Researchers also use these antibodies to study p53's interactions with other proteins, its post-translational modifications, and its role in cellular stress responses.
However, interpretation requires caution: not all mutations cause protein accumulation, and some antibodies may cross-react with isoforms or degraded fragments. Standardized protocols and antibody validation are critical for reliable results. Beyond diagnostics, p53 antibodies contribute to developing targeted therapies, including drugs aiming to restore wild-type p53 function or inhibit mutant p53 oncogenic activity. Their versatility underscores their importance in bridging basic research and clinical oncology.
×