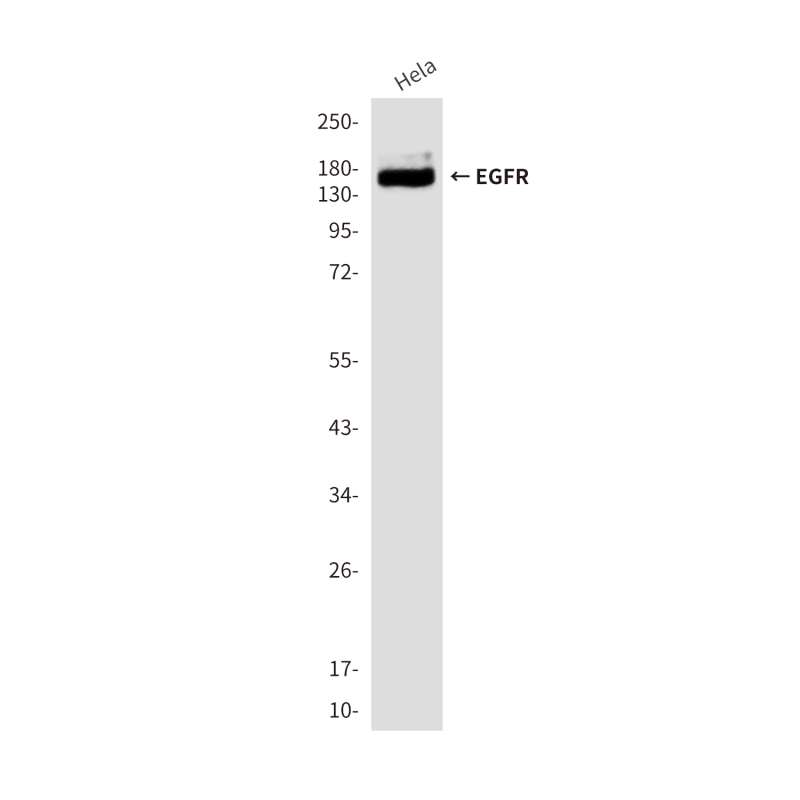
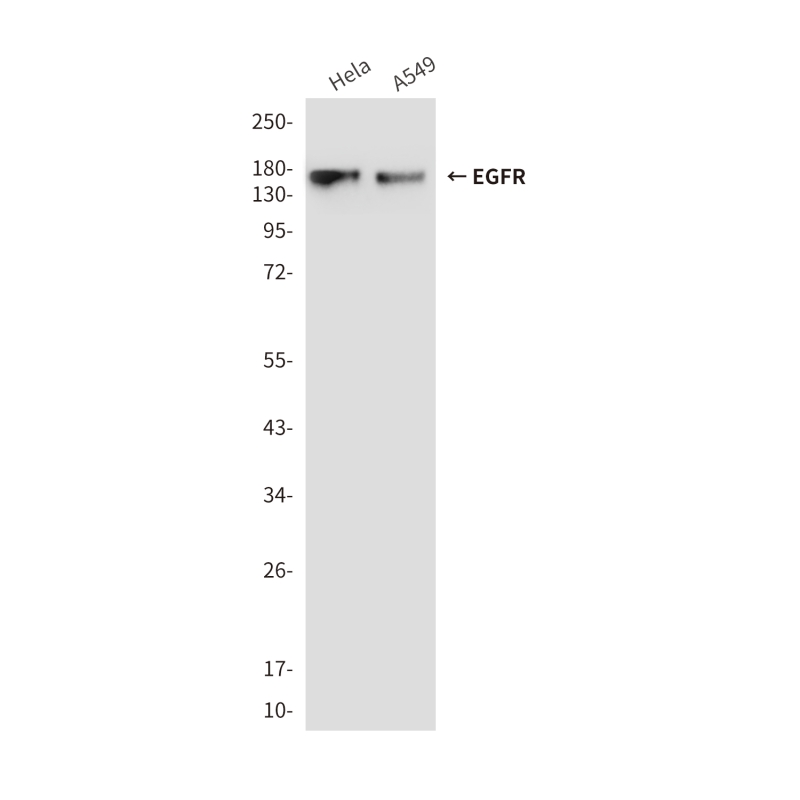
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
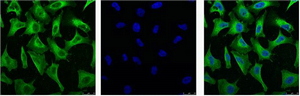
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
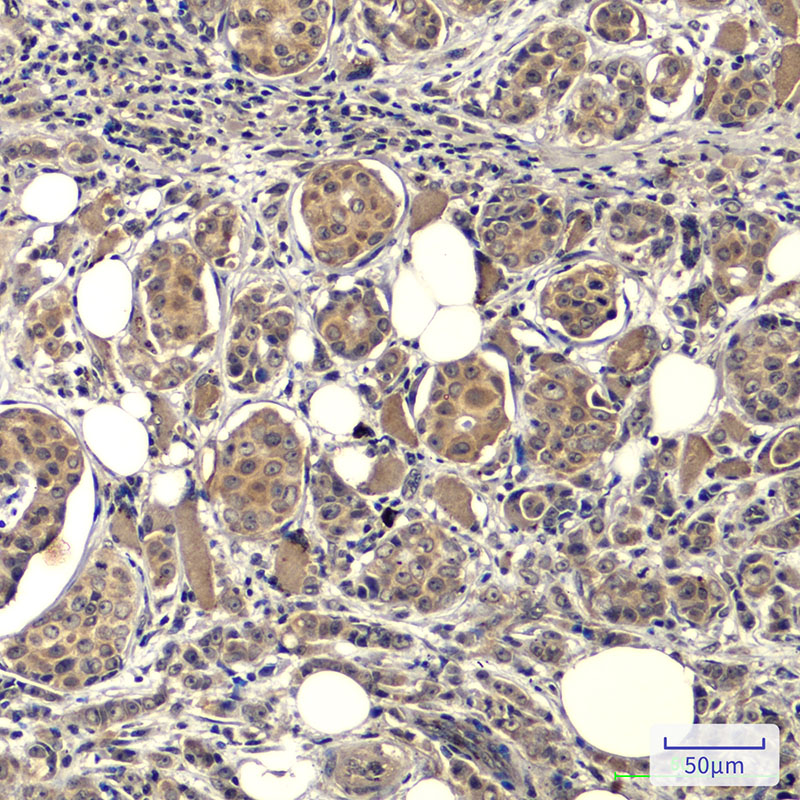
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EGFR; ERBB; ERBB1; HER1; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-1; Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1956 |
| clone | 6C9 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 134 kDa; Observed MW: 170 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of EGFR |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于EGFR抗体的参考文献,简要概括内容:
1. **"Cetuximab for the treatment of colorectal cancer"**
- **作者**: Jonker, D. J. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究(NEJM, 2007)报道了西妥昔单抗(Cetuximab)在转移性结直肠癌中的疗效,显示其联合化疗可显著延长KRAS野生型患者的生存期,验证了EGFR靶向治疗的临床价值。
2. **"Open-label phase III trial of panitumumab with chemotherapy in metastatic head and neck cancer"**
- **作者**: Vermorken, J. B. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究(NEJM, 2008)评估了帕尼单抗(Panitumumab)联合放化疗治疗头颈部鳞癌的效果,结果显示总生存期和无进展生存期显著改善,支持EGFR抗体在头颈癌中的联合应用。
3. **"EGFR targeting in drug-resistant cancer"**
- **作者**: Baselga, J. et al.
- **摘要**: 这篇综述(Nature Reviews Cancer, 2018)系统总结了EGFR抗体(如西妥昔单抗)的耐药机制,提出通过联合靶向下游信号通路(如MEK/ERK)克服耐药性的策略。
4. **"Activity of cetuximab in glioblastoma"**
- **作者**: Wheeler, S. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究(Clinical Cancer Research, 2010)探索了西妥昔单抗在EGFR扩增型胶质母细胞瘤中的效果,发现其可抑制肿瘤生长并增强放疗敏感性,但疗效受肿瘤异质性限制。
这些研究涵盖了EGFR抗体在实体瘤中的临床应用、耐药机制探索及不同癌种的扩展研究。
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor that regulates cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. Overexpression or mutation of EGFR is implicated in various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and head and neck cancers, driving uncontrolled cell growth and metastasis. EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), such as cetuximab and panitumumab, bind to the extracellular domain of EGFR, blocking ligand-induced activation and downstream signaling pathways like RAS/MAPK and PI3K/AKT. These antibodies also promote antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), enhancing immune-mediated tumor cell destruction.
Approved for cancers with wild-type RAS, EGFR antibodies improve survival in metastatic colorectal and squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. However, resistance often arises due to secondary mutations (e.g., EGFR T790M), alternative pathway activation, or tumor microenvironment adaptations. Current research focuses on combination therapies (e.g., with chemotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitors) and next-generation agents like bispecific antibodies or antibody-drug conjugates to overcome resistance. EGFR antibodies exemplify targeted therapy’s potential, though personalized approaches remain critical to optimize efficacy and manage side effects like skin toxicity. Ongoing studies explore predictive biomarkers and novel mechanisms to expand their clinical utility.
×