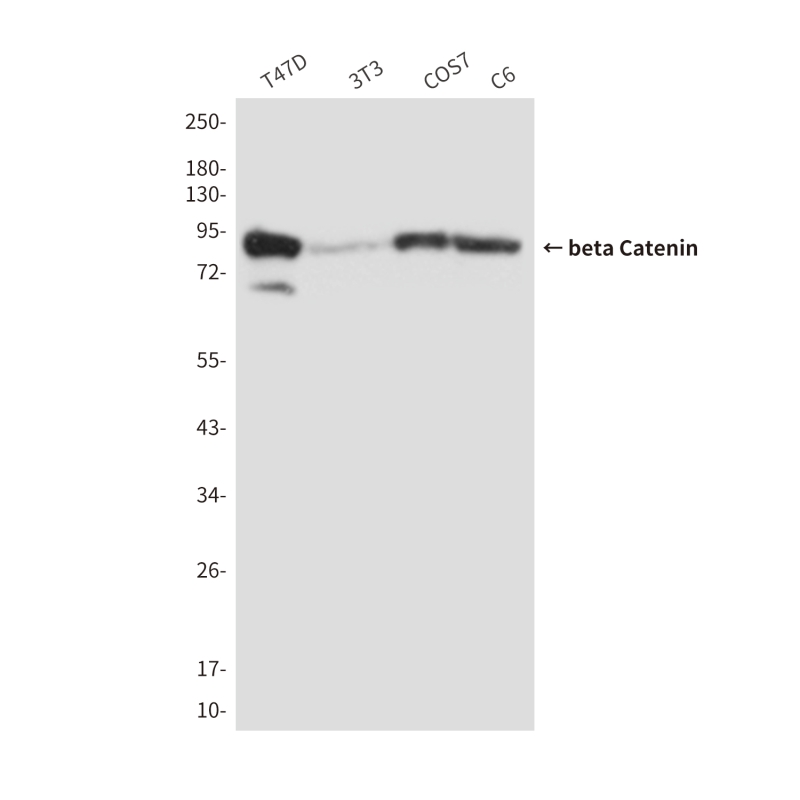
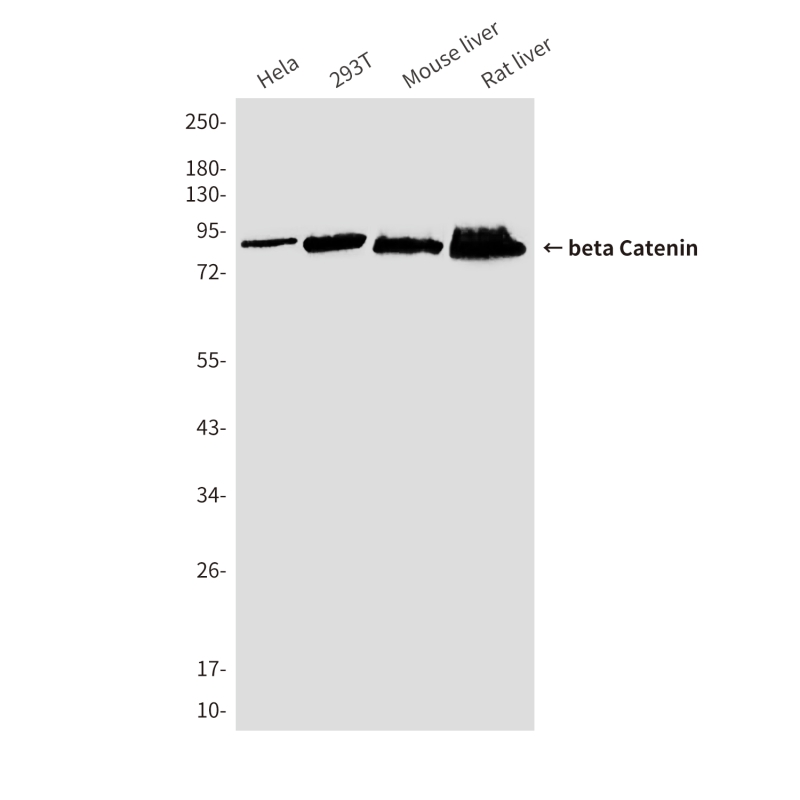

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CTNNB1; CTNNB; OK/SW-cl.35; Catenin beta-1; Beta-catenin |
| Entrez GeneID | 1499 |
| clone | 6F11 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 85 kDa; Observed MW: 92 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant Protein of Catenin-β |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于β-Catenin抗体的参考文献及简要摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: **"The β-Catenin/TCF Complex as a Novel Target of APC in Tumor Suppression"**
**作者**: Behrens, J. et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了APC蛋白通过调控β-Catenin稳定性抑制结直肠癌的机制,使用β-Catenin抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,证实APC直接结合并促进β-Catenin降解。
2. **文献名称**: **"β-Catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells"**
**作者**: Tetsu, O. & McCormick, F.
**摘要**: 通过β-Catenin抗体在免疫荧光和染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)中的实验,证明β-Catenin/TCF复合物直接激活细胞周期蛋白Cyclin D1的转录,促进结肠癌细胞增殖。
3. **文献名称**: **"Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Disease"**
**作者**: Clevers, H. & Nusse, R.
**摘要**: 综述总结了Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路的分子机制及其在癌症和发育中的作用,强调了β-Catenin抗体的应用(如免疫组化、Western blot)在检测其核定位及表达水平中的关键技术角色。
4. **文献名称**: **"Functional interaction of β-Catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1"**
**作者**: Huber, O. et al.
**摘要**: 利用β-Catenin抗体进行免疫沉淀和EMSA实验,揭示了β-Catenin与转录因子LEF-1的结合如何调控靶基因表达,并驱动上皮-间充质转化(EMT)。
---
以上文献均通过β-Catenin抗体在分子机制研究中发挥关键作用,涵盖癌症生物学、信号转导及基因调控等领域。
Beta-catenin is a multifunctional protein that plays a pivotal role in both cell-cell adhesion and Wnt signaling pathways. As a key component of the cadherin complex, it contributes to structural integrity at adherens junctions. In the canonical Wnt pathway, beta-catenin acts as a transcriptional co-activator: when Wnt signals are absent, it is phosphorylated and targeted for proteasomal degradation via the "destruction complex" (APC, Axin, GSK3β). Wnt activation stabilizes beta-catenin, allowing its nuclear translocation to regulate genes involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and embryonic development. Dysregulation of beta-catenin, often due to mutations in *CTNNB1* (its encoding gene) or upstream regulators (e.g., APC in colorectal cancer), is implicated in various cancers, fibrotic diseases, and developmental disorders.
Beta-catenin antibodies are essential tools for studying its localization, expression, and signaling activity. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to assess beta-catenin's cytoplasmic/nuclear accumulation—a hallmark of Wnt pathway activation. Specific antibodies target distinct epitopes (e.g., N-terminal phosphorylation sites, C-terminal transactivation domains) or post-translational modifications. Some antibodies differentiate between active (non-phosphorylated) and inactive forms. Validated antibodies are critical for diagnostic applications (e.g., identifying Wnt-driven tumors) and mechanistic research in cancer biology, stem cell regulation, and tissue homeostasis. Commercial antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with clones like E-5 and D10A8 being commonly referenced. Proper validation (knockout controls, functional assays) ensures specificity, as cross-reactivity with other catenins or proteins can yield misleading results.
×