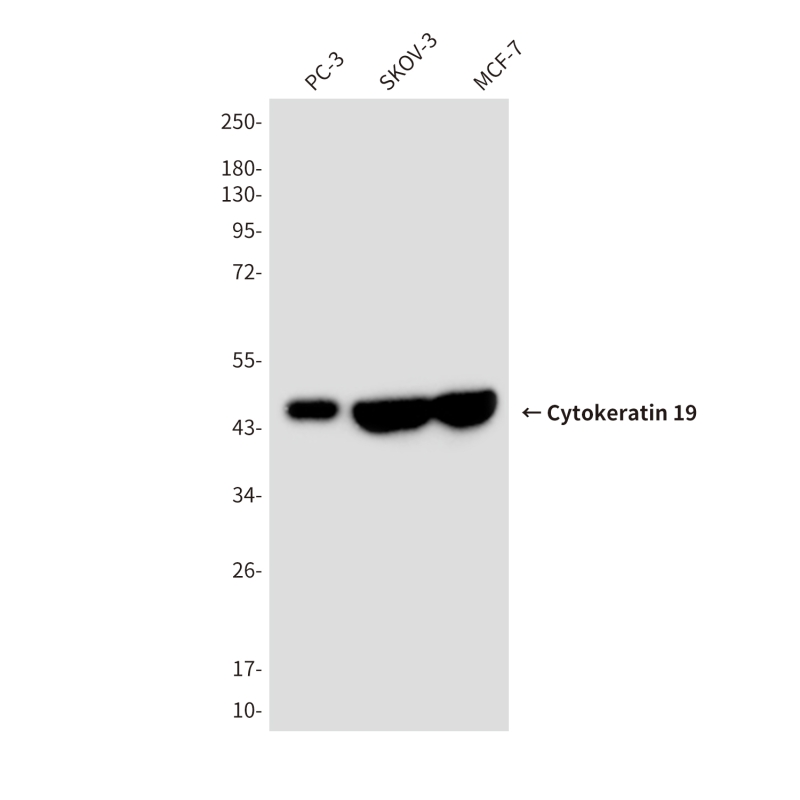
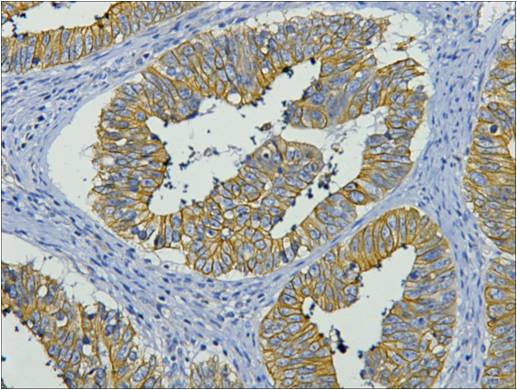
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KRT19; Keratin; type I cytoskeletal 19; Cytokeratin-19; CK-19; Keratin-19; K19 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3880 |
| clone | 5G10 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 44 kDa; Observed MW: 44 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of CK19 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于 **Cytokeratin 19(CK19)抗体** 的参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Cytokeratin 19 immunoreactivity in the diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma"*
**作者**: Sahoo S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫组化分析CK19在甲状腺病变中的表达,发现CK19在甲状腺乳头状癌(PTC)中显著高表达,而在良性甲状腺结节中表达较低,表明CK19抗体可作为鉴别PTC与良性病变的重要辅助标记物。
2. **文献名称**: *"Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood of patients with metastatic breast cancer using cytokeratin-19-specific antibodies"*
**作者**: Allard WJ, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用CK19抗体的特异性,开发了一种基于血液的循环肿瘤细胞(CTC)检测方法,证实CK19阳性CTC的存在与转移性乳腺癌患者的不良预后显著相关。
3. **文献名称**: *"Cytokeratin 19 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma versus cholangiocarcinoma: A comparative immunohistochemical study"*
**作者**: Fan Z, et al.
**摘要**: 研究比较CK19在肝细胞癌(HCC)和胆管癌(CCA)中的表达差异,发现CK19在大多数CCA病例中呈强阳性,而在HCC中罕见表达,提示CK19抗体可用于两者的病理鉴别诊断。
4. **文献名称**: *"Cytokeratin 19 as a biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma: Correlation with clinicopathological features"*
**作者**: Moll R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过分析CK19在肺癌亚型中的表达,研究发现CK19在肺腺癌中高度特异,其表达水平与肿瘤分化程度相关,支持CK19抗体在肺癌分型及预后评估中的应用价值。
---
以上研究均聚焦于CK19抗体在肿瘤诊断、分型及预后中的临床应用,涵盖甲状腺癌、乳腺癌、肝胆癌和肺癌等领域。
Cytokeratin 19 (CK19) is a member of the intermediate filament protein family, primarily expressed in epithelial cells, where it contributes to structural integrity and cellular mechanical stability. As a low molecular weight keratin, CK19 is predominantly found in simple and glandular epithelia, such as those in the liver, pancreas, and respiratory tract, as well as in basal layers of stratified epithelia. Its expression is tightly regulated during development and tissue differentiation, making it a valuable marker for identifying epithelial cell lineages.
Antibodies targeting CK19 are widely used in research and diagnostics to detect epithelial-derived cells, particularly in cancer pathology. For instance, CK19 immunohistochemistry helps distinguish carcinomas from non-epithelial tumors and is critical in identifying metastatic cells in lymph nodes or circulating tumor cells (CTCs). In clinical settings, CK19 antibodies aid in diagnosing malignancies like breast, lung, and colorectal cancers. Notably, CK19 is a key biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocarcinoma, where its overexpression correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis.
Additionally, CK19 antibodies are employed in studying epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cancer stem cells, as CK19 expression may reflect cellular plasticity. However, interpretation requires caution, as CK19 can be detected in benign conditions (e.g., reactive epithelial proliferations) and non-neoplastic cells. Techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, and immunofluorescence rely on CK19-specific antibodies, underscoring their versatility in both basic research and clinical applications. Overall, CK19 antibodies remain indispensable tools for exploring epithelial biology and improving cancer diagnostics.
×