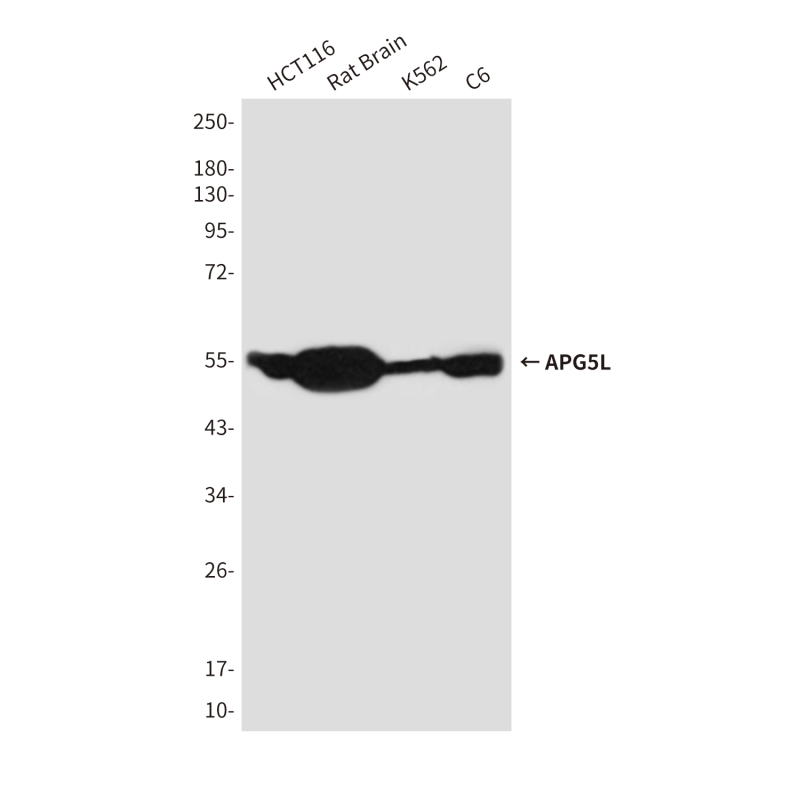
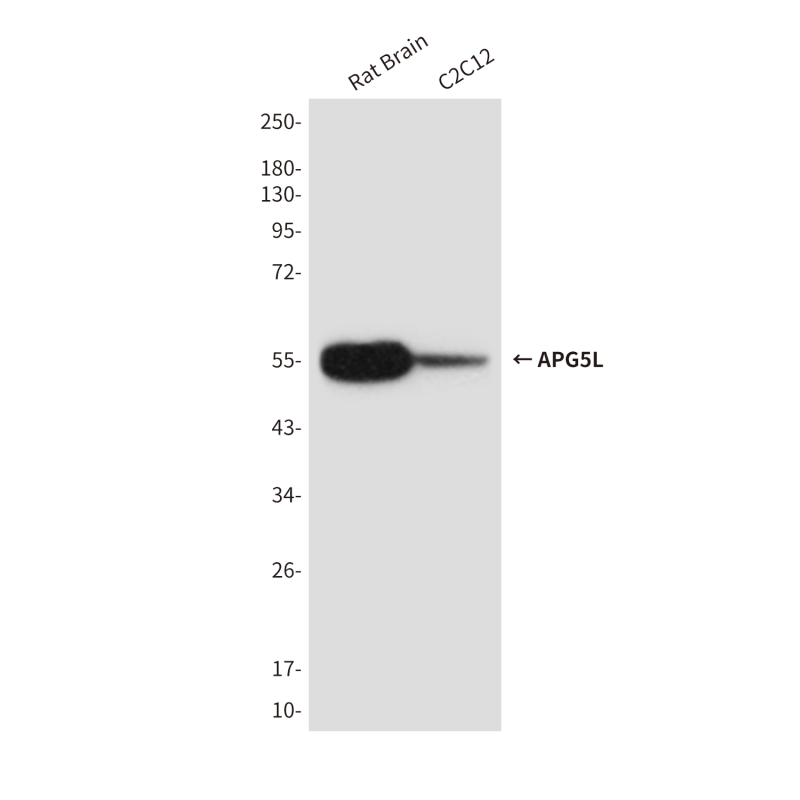
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | APG 5L; APG5; APG5 autophagy 5 like; APG5 like; APG5-like; Apoptosis specific protein; ASP; ATG 5; ATG5 autophagy related 5 homolog; Autophagy protein 5; hAPG5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9474 |
| clone | 10H1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 32 kDa; Observed MW: 55 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ATG5(APG5L)抗体的3篇代表性文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要简述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period*
**作者**:Mizushima, N., et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用ATG5抗体通过Western blot及免疫荧光技术,首次在小鼠模型中证实ATG5在自噬体形成中的关键作用。敲除ATG5导致自噬相关蛋白LC3-II积累受阻,揭示了自噬在新生儿营养缺乏期的存活机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis through elimination of p62*
**作者**:Komatsu, M., et al.
**摘要**:通过ATG5抗体进行组织特异性基因敲除实验,发现肝细胞中ATG5缺失导致p62蛋白聚集,引发氧化应激和肝癌发生。研究证明ATG5依赖的自噬通路具有抑癌作用,为癌症治疗提供新靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice*
**作者**:Hara, T., et al.
**摘要**:利用ATG5抗体检测神经元中自噬活性,发现条件性敲除ATG5的小鼠出现运动障碍及神经元内泛素化蛋白堆积,证实自噬在神经退行性疾病(如帕金森病)中的保护性机制。
---
**备注**:
- "APG5L"为ATG5的早期别名(Autophagy-related 5-like),现通用名称为ATG5.主要参与自噬体的生物合成。
- 上述文献均使用ATG5抗体进行蛋白表达验证或基因功能研究,适用于自噬机制、癌症及神经疾病等领域参考。
APG5L (Autophagy-related Protein 5-Like), also known as ATG5. is a critical protein involved in autophagy, a conserved cellular process responsible for degrading and recycling damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and pathogens. The APG5L gene encodes a 33-kDa protein that interacts with ATG12 to form a ubiquitin-like conjugation system essential for autophagosome formation. This complex facilitates the lipidation of microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3), a key step in autophagosome membrane expansion and cargo recruitment.
APG5L antibodies are widely used in research to detect and quantify ATG5 expression, monitor autophagy activity, and investigate its role in physiological and pathological contexts. Dysregulation of ATG5-mediated autophagy has been linked to cancers, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s), infectious diseases, and metabolic disorders. These antibodies are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study tissue-specific autophagy patterns or therapeutic responses.
As autophagy modulation emerges as a potential therapeutic strategy, APG5L antibodies also serve as tools for drug development, enabling researchers to assess the efficacy of autophagy-inducing or -inhibiting compounds. Their specificity and reliability make them indispensable for elucidating molecular mechanisms of autophagy-related pathways and validating biomarkers in disease models.
×