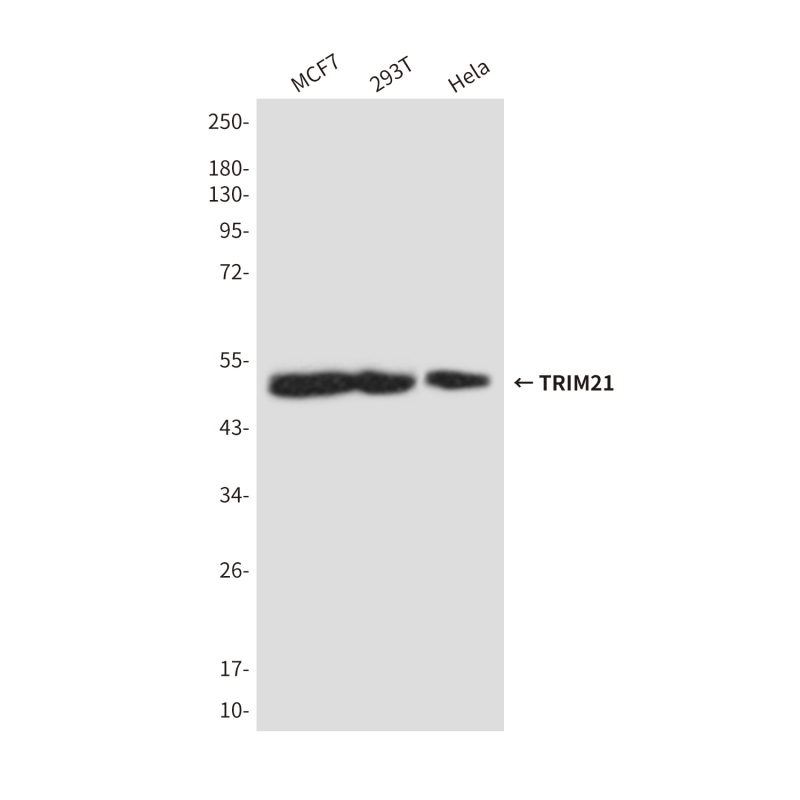
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SSA; RO52; SSA1; RNF81; Ro/SSA |
| Entrez GeneID | 6737 |
| clone | 5A9 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 54 kDa; Observed MW: 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human TRIM21 protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
TRIM21 (Tripartite motif-containing protein 21), also known as Ro52. is a member of the TRIM protein family characterized by its conserved N-terminal RING, B-box, and coiled-coil domains. It functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase due to its RING domain, enabling it to tag proteins with ubiquitin for proteasomal degradation. TRIM21 plays a critical role in innate immunity by recognizing antibody-coated viruses or intracellular pathogens. It binds to the Fc region of IgG antibodies attached to pathogens, triggering their ubiquitination and subsequent degradation via the proteasome. This process, termed "antibody-dependent intracellular neutralization," bridges adaptive and innate immune responses. Additionally, TRIM21 activates inflammatory signaling pathways, such as NF-κB and IRF pathways, amplifying antiviral responses.
Beyond immunity, TRIM21 is implicated in autoimmune diseases, particularly systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Sjögren's syndrome, where autoantibodies against TRIM21 are common. Its dysregulation may contribute to autoantigen presentation and immune hyperactivity. Research leverages TRIM21 antibodies to study viral pathogenesis, autoimmune mechanisms, and protein turnover. Recently, TRIM21 has been explored in biotechnological applications, such as targeted protein degradation (PROTACs), highlighting its dual role as a therapeutic target and tool in biomedical research.
×