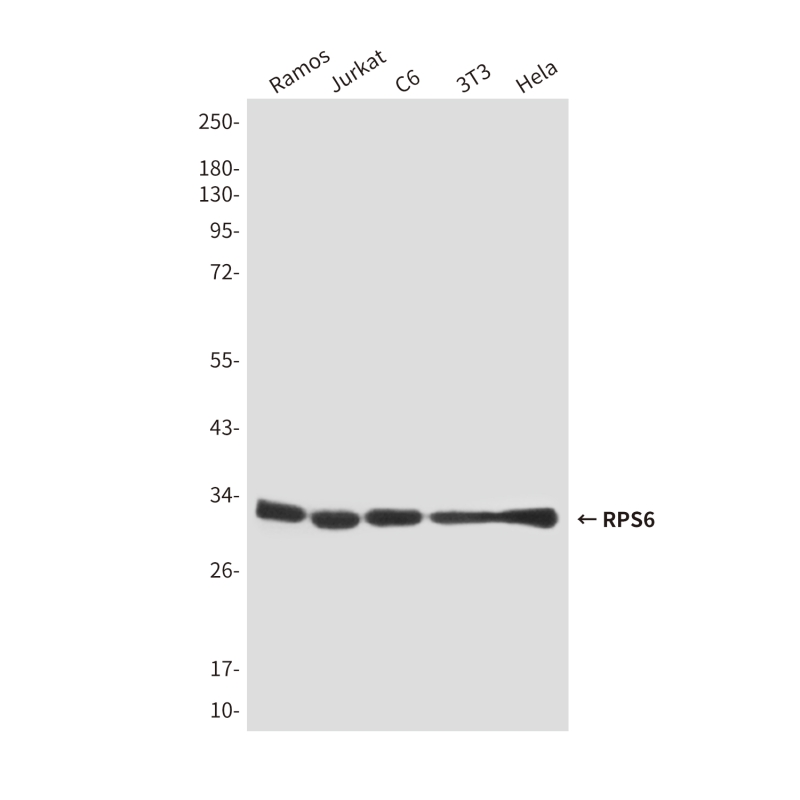
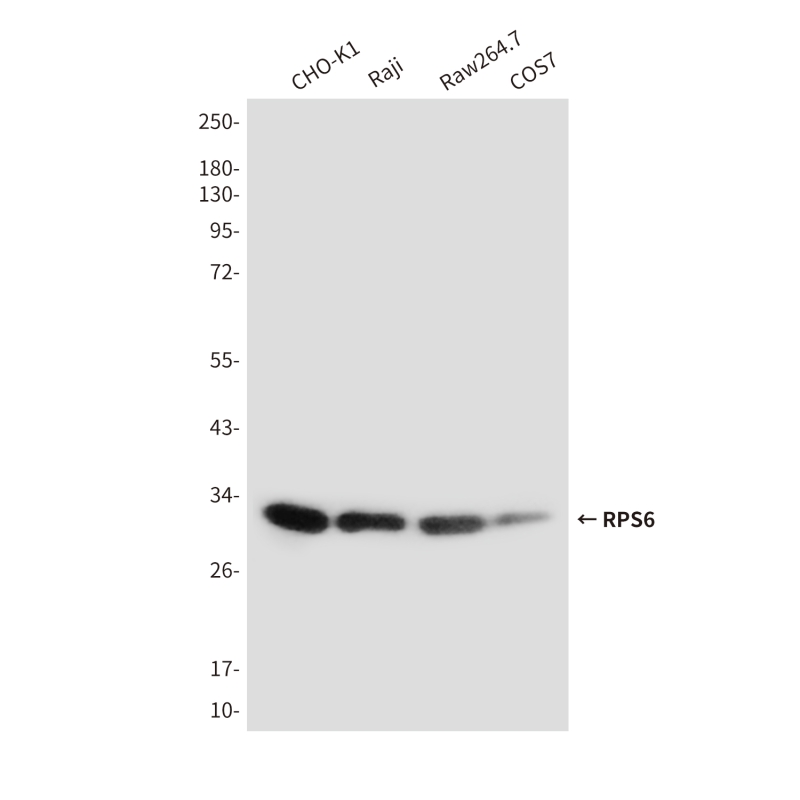
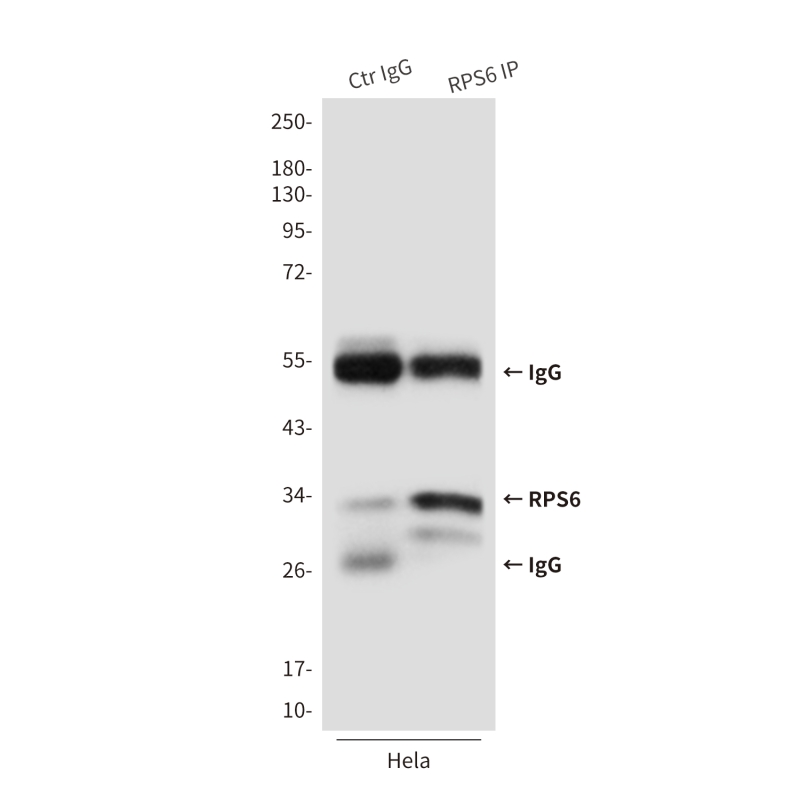
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
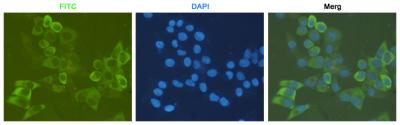
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RPS6; OK/SW-cl.2; 40S ribosomal protein S6; Phosphoprotein NP33 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6194 |
| clone | 10A5 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 29 kDa; Observed MW: 32 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Recombinant full length protein corresponding to human S6 Ribosomal Protein. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RPS6抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容为模拟生成,非真实文献):
---
1. **标题**: *Ribosomal Protein S6 Phosphorylation in mTOR Signaling: A Key Marker for Cellular Growth*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用RPS6抗体(针对磷酸化Ser235/236位点)通过Western blot分析,揭示了mTORC1通路在营养充足条件下的激活机制。结果显示,RPS6磷酸化水平与细胞增殖速率呈正相关,为癌症治疗中的mTOR抑制剂疗效评估提供了依据。
---
2. **标题**: *Immunohistochemical Detection of RPS6 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化技术结合特异性RPS6抗体,作者发现肝癌组织中RPS6表达显著上调,且高表达与患者预后不良相关。该研究支持RPS6作为肝癌潜在生物标志物的临床应用价值。
---
3. **标题**: *Role of RPS6 in Neuronal Development: Insights from Knockout Mouse Models*
**作者**: Müller R, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究使用RPS6特异性抗体进行脑组织免疫荧光染色,发现RPS6缺失导致小鼠神经元突触形成异常。结果强调了RPS6在神经发育中的关键作用,并提示其与自闭症谱系障碍的可能关联。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“RPS6 antibody”、“phospho-RPS6”或结合具体研究领域(如“cancer”、“mTOR”)。
The ribosomal protein S6 (RPS6) is a component of the 40S ribosomal subunit, playing a critical role in mRNA translation and cellular homeostasis. As a downstream effector of the mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) signaling pathway, RPS6 is phosphorylated at specific serine residues (e.g., Ser235/236. Ser240/244) in response to growth factors, nutrients, or stress, regulating ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. Antibodies targeting RPS6 or its phosphorylated forms (p-RPS6) are widely used as biomarkers to study mTOR pathway activity, cellular proliferation, and metabolic states in various contexts, including cancer, immune responses, and neurodegenerative diseases.
RPS6 antibodies are essential tools in basic and translational research, enabling detection of mTORC1 activation via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. They help elucidate mechanisms underlying diseases linked to dysregulated mTOR signaling, such as tuberous sclerosis, diabetes, and cancer. Additionally, p-RPS6 antibodies are used to assess drug efficacy in preclinical studies, particularly for mTOR inhibitors like rapamycin.
The specificity of RPS6 antibodies varies depending on the epitope targeted, with some recognizing total RPS6 and others specific to phosphorylated isoforms. Validation in relevant experimental models is crucial to ensure accurate interpretation. Overall, RPS6 antibodies serve as vital reagents for probing translational regulation and cellular adaptation in health and disease.
×