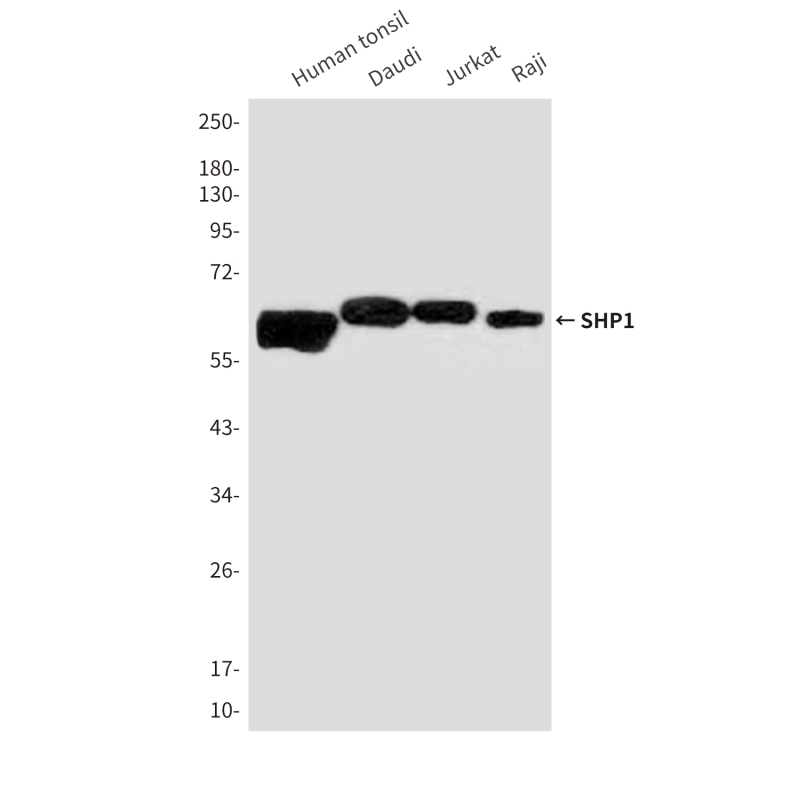
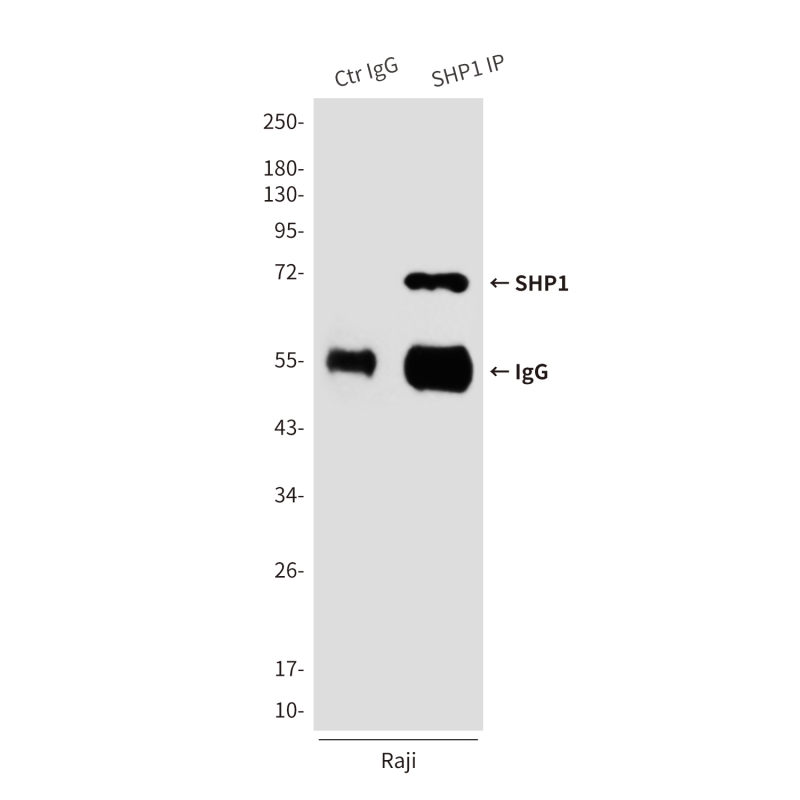
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PTPN6; HCP; PTP1C; Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 6; Hematopoietic cell protein-tyrosine phosphatase; Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1C; PTP-1C; Protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1; SH-PTP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5777 |
| clone | 2A7 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 68 kDa; Observed MW: 68 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human SHP-1 protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及SHP1抗体的代表性文献摘要,涵盖不同研究领域:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"SHP1 regulates TCR signaling in CD4+ T cells through interaction with Lck"*
**作者**: Lorenz, U. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用SHP1抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示SHP1磷酸酶通过结合Lck激酶负调控T细胞受体(TCR)信号通路,影响CD4+ T细胞活化和自身免疫疾病的发展。
2. **文献名称**: *"SHP1 deficiency in B cells promotes lupus-like autoimmunity"*
**作者**: Wu, J. et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和流式细胞术结合SHP1抗体,发现B细胞中SHP1表达缺失导致BCR信号过度激活,促进系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)样表型,为自身免疫治疗提供靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *"SHP1 inhibition enhances CAR-T cell efficacy by overcoming T cell exhaustion"*
**作者**: Tang, N. et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用SHP1抗体检测肿瘤微环境中T细胞SHP1的表达水平,发现抑制SHP1可逆转T细胞耗竭,提高CAR-T疗法对实体瘤的杀伤效果,为免疫治疗提供新策略。
---
以上文献展示了SHP1抗体在信号通路解析、疾病机制探索及治疗开发中的关键作用,实验方法涵盖免疫沉淀、Western blot和功能验证等。如需具体期刊或年份信息可进一步补充。
SHP1 (Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1), also known as PTPN6. is a protein tyrosine phosphatase predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cells. It plays a critical role in negatively regulating signaling pathways by dephosphorylating key tyrosine residues on target proteins. Structurally, SHP1 contains two N-terminal SH2 domains that mediate interactions with phosphorylated signaling molecules and a C-terminal catalytic domain responsible for its phosphatase activity. Its function is essential for modulating immune responses, cell differentiation, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of SHP1 has been implicated in autoimmune diseases, cancers (e.g., leukemia, lymphoma), and inflammatory disorders, where loss of function or reduced expression often correlates with hyperactive signaling in pathways like JAK/STAT, MAPK, or B-cell receptor signaling.
SHP1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and activity in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to detect SHP1 in research models or clinical samples. Specific clones or epitope-targeted antibodies are validated for applications, ensuring accurate quantification of SHP1 levels or phosphorylation states. Given its therapeutic potential as a drug target, SHP1 antibodies also aid in screening inhibitors or evaluating therapeutic efficacy in preclinical studies. Proper antibody validation remains crucial due to cross-reactivity risks with homologous phosphatases like SHP2 (PTPN11).
×