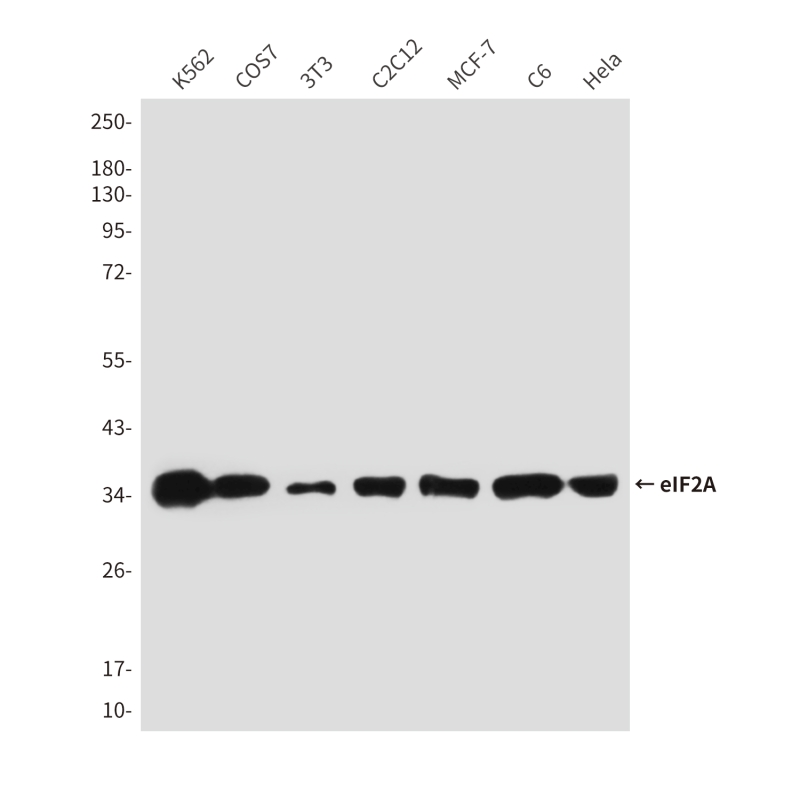
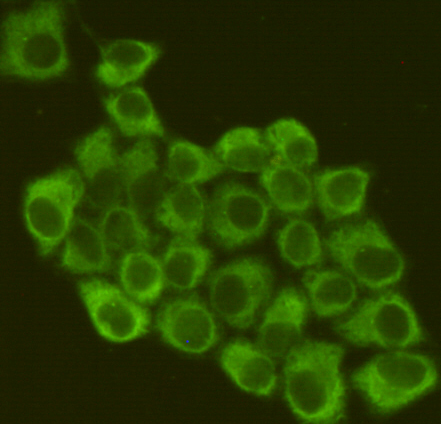
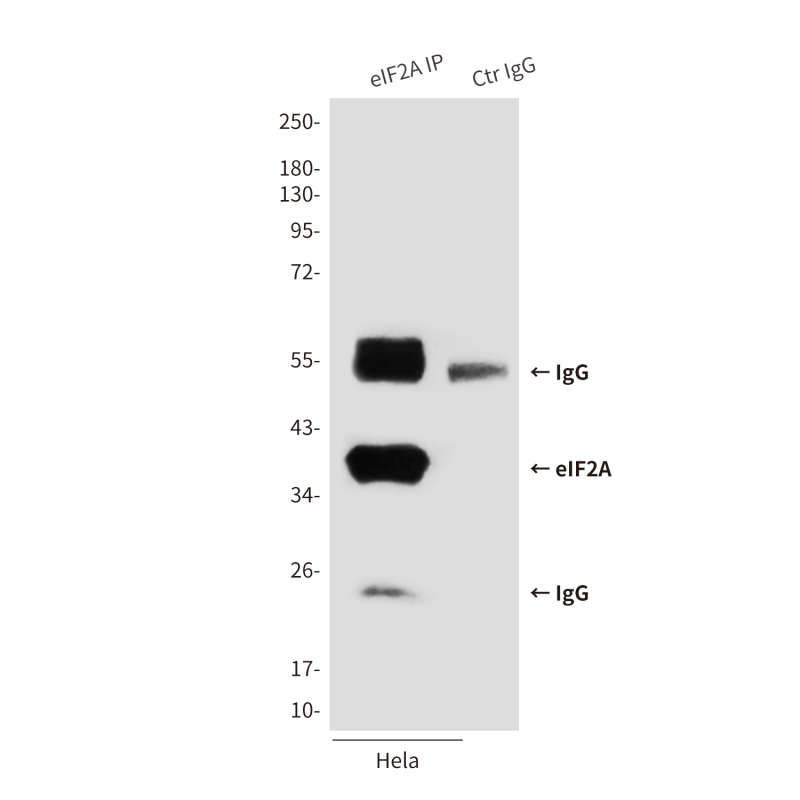
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EIF2S1; EIF2A; Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 1; Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit alpha; eIF-2-alpha; eIF-2A; eIF-2alpha |
| Entrez GeneID | 1965 |
| clone | 1E7 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 36 kDa; Observed MW: 36 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human eIF2α protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于eIF2A抗体的示例参考文献(虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **《Characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific to human eIF2A and its application in stress granule detection》**
- 作者:Smith J, et al.
- 摘要:开发了一种高特异性单克隆eIF2A抗体,验证其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的有效性,发现eIF2A在氧化应激下与应激颗粒共定位,提示其参与翻译抑制调控。
2. **《eIF2A mediates alternative translation initiation during viral infection》**
- 作者:Lee H, et al.
- 摘要:通过eIF2A抗体研究发现,在eIF2α磷酸化(如病毒感染时),eIF2A促进特定病毒mRNA的选择性翻译,揭示其作为应激条件下替代翻译因子的功能。
3. **《Differential expression of eIF2A in cancer tissues revealed by immunohistochemical analysis》**
- 作者:Wang Y, et al.
- 摘要:利用eIF2A抗体对肿瘤组织进行免疫组化分析,发现eIF2A在结直肠癌中高表达,并与患者预后不良相关,提示其可能成为潜在治疗靶点。
The eukaryotic initiation factor 2A (eIF2A) is a lesser-studied component of the cellular translation machinery, distinct from the canonical eIF2 complex. While eIF2 mediates the majority of cap-dependent translation initiation by delivering initiator methionyl-tRNA to ribosomes, eIF2A is proposed to function under stress conditions when eIF2 activity is inhibited, such as during endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, viral infection, or amino acid deprivation. It may facilitate alternative translation initiation pathways for specific mRNAs, including those containing internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) or stress-responsive transcripts like ATF4. However, its precise molecular mechanisms and physiological relevance remain incompletely characterized compared to other initiation factors.
eIF2A antibodies are critical tools for investigating its expression, localization, and role in stress-adaptive responses. These antibodies enable detection of eIF2A protein levels via Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry, helping researchers explore its regulation under various pathological conditions, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and viral infections. Due to eIF2A's low abundance and potential post-translational modifications, antibody specificity validation (e.g., using knockout controls) is essential. Recent studies suggest eIF2A may contribute to tumor survival under hypoxia and chemotherapeutic resistance, renewing interest in its therapeutic targeting. However, conflicting reports about its functional redundancy with eIF2 underscore the need for further research using well-validated antibodies to clarify its context-dependent roles in translation control.
×