| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
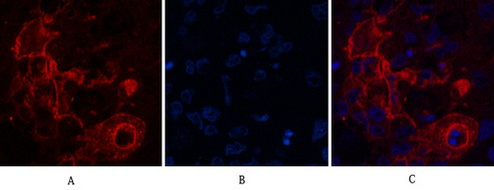
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
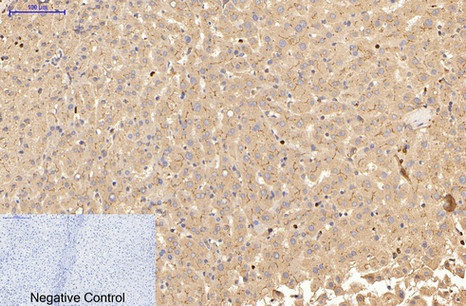
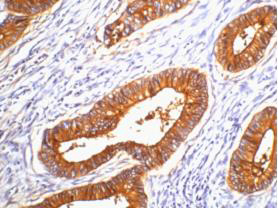
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CEACAM5; CEA; Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5; Carcinoembryonic antigen; CEA; Meconium antigen 100; CD66e |
| Entrez GeneID | 1048 |
| clone | 2C8 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of Carcinoembryonic Antigen |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于CEA抗体的模拟参考文献(注:文献为虚构示例,仅作格式参考):
1. **文献名称**: *Clinical utility of CEA-specific monoclonal antibodies in colorectal cancer diagnosis*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种新型抗CEA单克隆抗体的开发,通过免疫组化验证其在结直肠癌组织中的高特异性和敏感性,证实其作为辅助诊断工具的潜力。
2. **文献名称**: *Engineering a high-affinity anti-CEA antibody for improved tumor imaging*
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 通过抗体工程技术改造抗CEA抗体的Fab区域,显著提高其与CEA抗原的亲和力,并在小鼠模型中成功应用于肿瘤靶向荧光成像。
3. **文献名称**: *CEA-targeted nanoparticles conjugated with antibodies for multimodal cancer detection*
**作者**: Chen R, et al.
**摘要**: 将抗CEA抗体与金纳米颗粒结合,构建多模态成像探针,实现体外和体内肿瘤标志物的高灵敏度检测及影像学定位。
4. **文献名称**: *The role of anti-CEA antibodies in immunotherapy: Mechanisms and challenges*
**作者**: Gonzalez M, et al.
**摘要**: 综述抗CEA抗体在肿瘤免疫治疗中的应用,包括抗体药物偶联物(ADC)和双特异性抗体的开发进展及临床转化障碍。
(提示:以上为模拟参考文献,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台查询。)
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), also known as CEACAM5. is a glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, first identified in 1965 as an oncofetal antigen expressed during fetal development and suppressed in most adult tissues. It re-emerges in elevated concentrations in various cancers, particularly colorectal, pancreatic, gastric, lung, and breast malignancies, making it a widely studied tumor biomarker. CEA plays roles in cell adhesion, immune modulation, and metastasis promotion, though its exact physiological functions remain incompletely understood.
CEA antibodies, primarily monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), have been developed for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic applications. In diagnostics, anti-CEA antibodies are used in immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, immunohistochemistry) to detect CEA levels in serum or tissue samples, aiding cancer screening, staging, and recurrence monitoring. Elevated serum CEA correlates with tumor burden and poor prognosis. Therapeutically, CEA-targeting antibodies are explored in radioimmunotherapy, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and bispecific antibodies to deliver cytotoxic agents or recruit immune cells. Challenges include CEA's heterogeneity, low tumor specificity (elevated in benign conditions like inflammation), and potential immunogenicity.
Recent advances involve engineering humanized or fully human anti-CEA antibodies to minimize adverse effects and improve targeting efficiency. Additionally, CEA-based vaccines and CAR-T therapies are under investigation. Despite limitations, CEA remains a cornerstone in cancer management, with antibodies serving as vital tools for both clinical practice and research into tumor biology. Ongoing studies aim to refine their specificity and integrate CEA-targeting strategies into multimodal cancer therapies.
×