| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
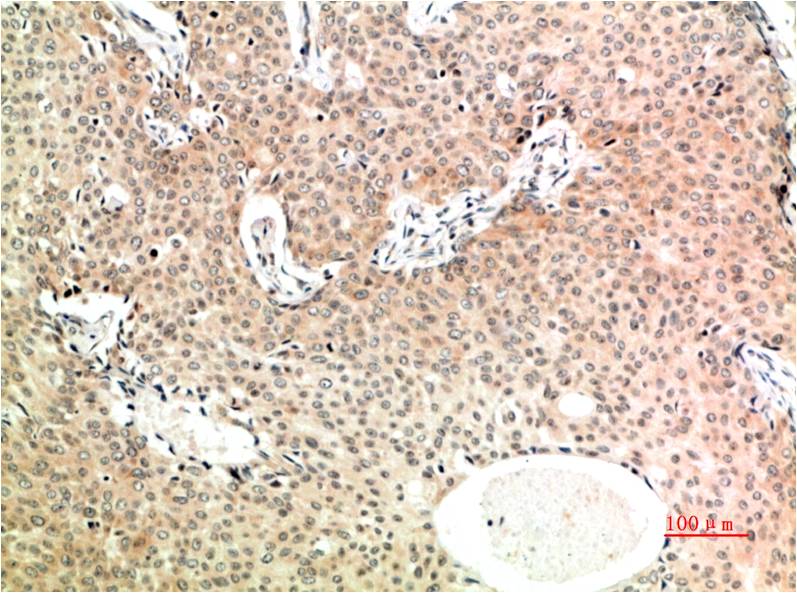
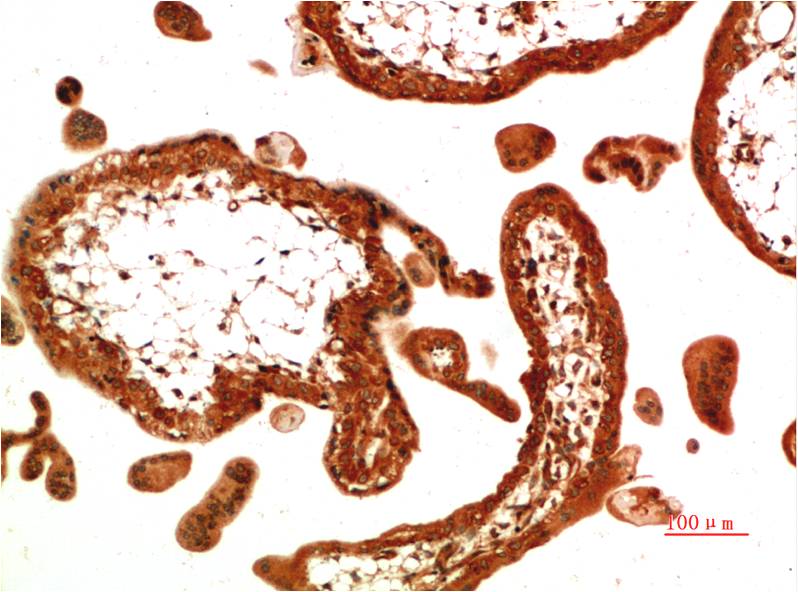
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TGF beta 1; TGFB; CED; LAP |
| Entrez GeneID | 7040 |
| clone | 9B7 |
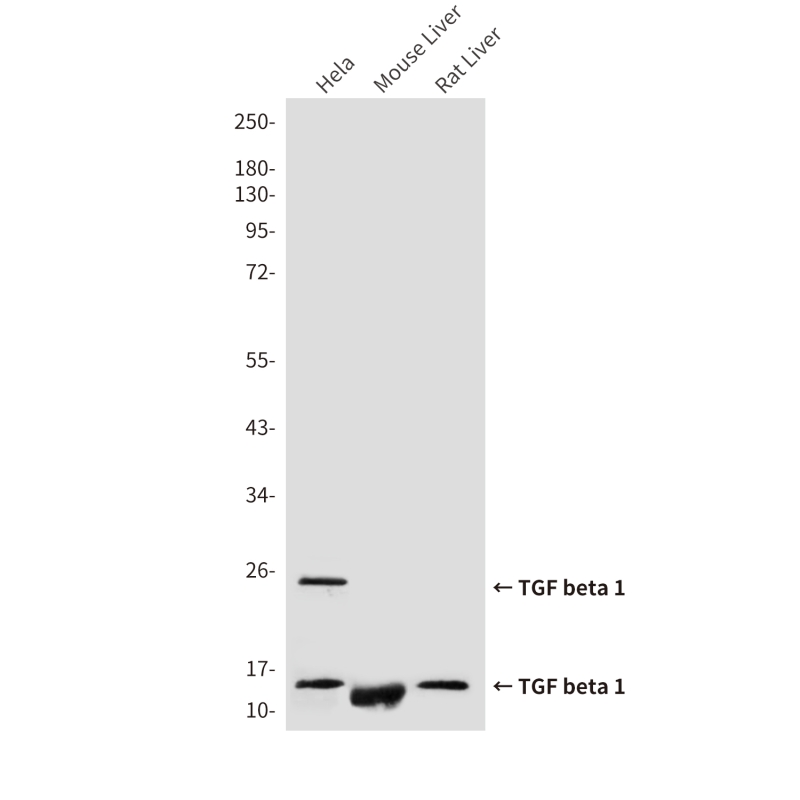
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 44 kDa; Observed MW: 12,25,45-65 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TGF-β1抗体的代表性文献摘要(示例为虚构内容,实际引用请通过学术数据库核实):
1. **文献名称**: "Targeting TGF-β1 with a neutralizing monoclonal antibody ameliorates renal fibrosis in mice"
**作者**: Li, J.Y., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过使用抗TGF-β1单克隆抗体(1D11)阻断小鼠模型中TGF-β1信号通路,显著减轻了肾纤维化程度,表明TGF-β1抗体在慢性肾病治疗中的潜在价值。
2. **文献名称**: "TGF-β1-neutralizing antibody suppresses tumor microenvironment immunosuppression and enhances chemotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer"
**作者**: Zhang, H., et al.
**摘要**: 实验证明,联合使用抗TGF-β1抗体与吉西他滨可降低胰腺癌小鼠的肿瘤相关成纤维细胞活性,并增强T细胞浸润,提示靶向TGF-β1可改善肿瘤免疫微环境。
3. **文献名称**: "A human anti-TGF-β1 antibody reduces fibrosis in bleomycin-induced lung injury models"
**作者**: Sato, M., et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了人源化抗TGF-β1抗体(GC1008),并在博来霉素诱导的肺纤维化模型中验证其有效性,显示其通过抑制胶原沉积和炎症反应缓解纤维化进程。
4. **文献名称**: "Dual role of TGF-β1 in cancer progression: Insights from antibody-mediated blockade experiments"
**作者**: Moses, H.L., et al.
**摘要**: 通过抗体阻断TGF-β1.揭示了其在早期抑制肿瘤发生和晚期促进转移的双重作用,为临床靶向治疗提供理论依据。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性质,具体文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索确认。)
TGF-beta 1 (Transforming Growth Factor-beta 1) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the TGF-beta superfamily, playing pivotal roles in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, immune response, and tissue homeostasis. It is synthesized as a latent precursor that requires activation to bind to its receptors (TGFBR1/2), triggering downstream signaling pathways like SMAD-dependent and non-SMAD cascades. Dysregulation of TGF-beta 1 is implicated in fibrosis, cancer progression, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammation, making it a critical therapeutic and diagnostic target.
TGF-beta 1 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying this cytokine in research and clinical settings. These antibodies, available as monoclonal or polyclonal types, are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, ELISA, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and flow cytometry to assess TGF-beta 1 expression, localization, and activation in cells and tissues. Monoclonal antibodies offer high specificity for distinct epitopes, while polyclonal antibodies may detect multiple epitopes, enhancing sensitivity but requiring careful validation to avoid cross-reactivity.
In disease research, TGF-beta 1 antibodies help elucidate its dual role—acting as a tumor suppressor in early cancers but promoting metastasis in advanced stages. They also aid in studying fibrotic disorders (e.g., liver or lung fibrosis) and autoimmune conditions. Additionally, neutralizing TGF-beta 1 antibodies are explored therapeutically to inhibit its immunosuppressive or profibrotic effects, highlighting their translational potential in drug development and biomarker discovery.
×