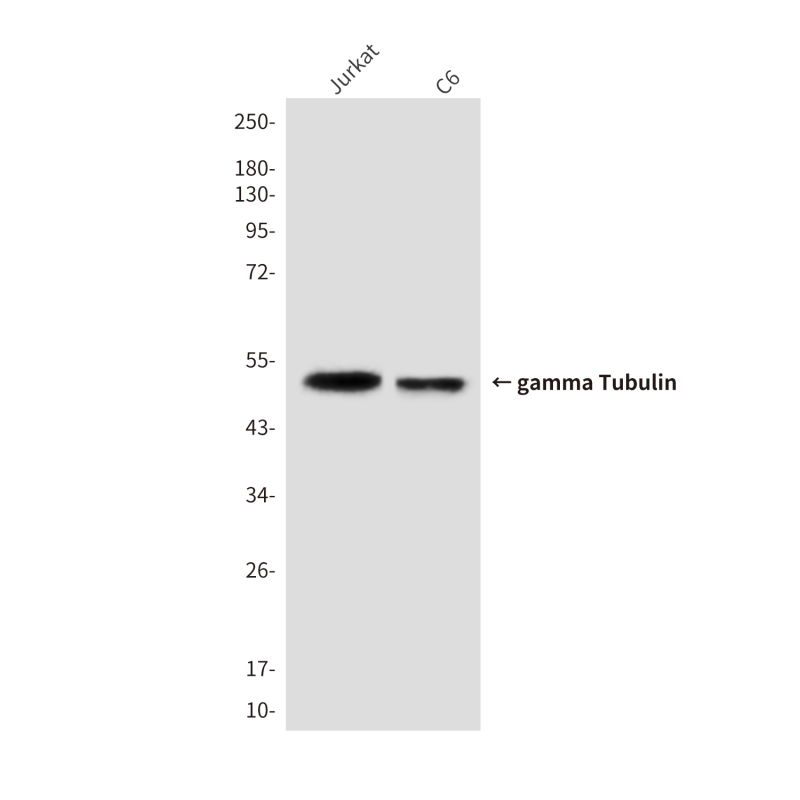
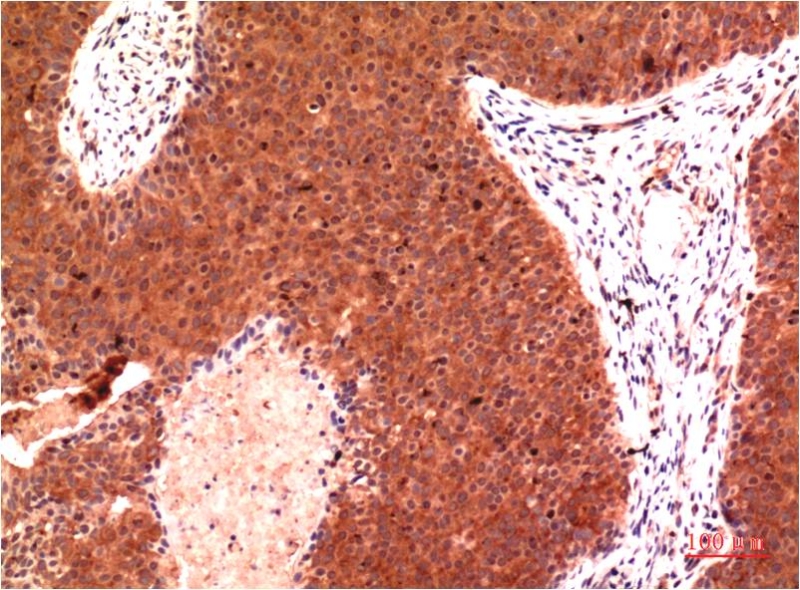
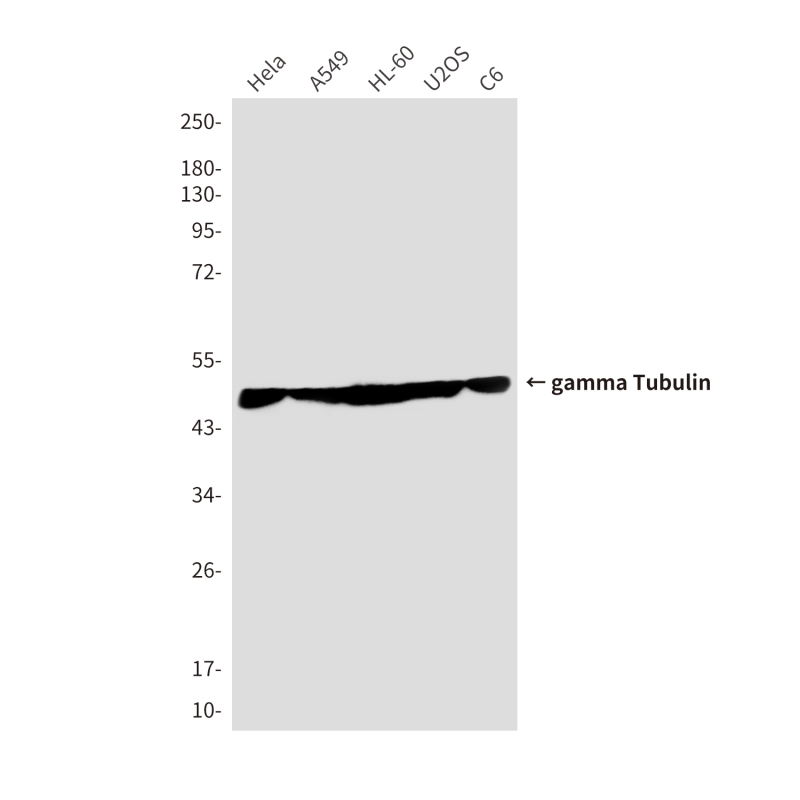
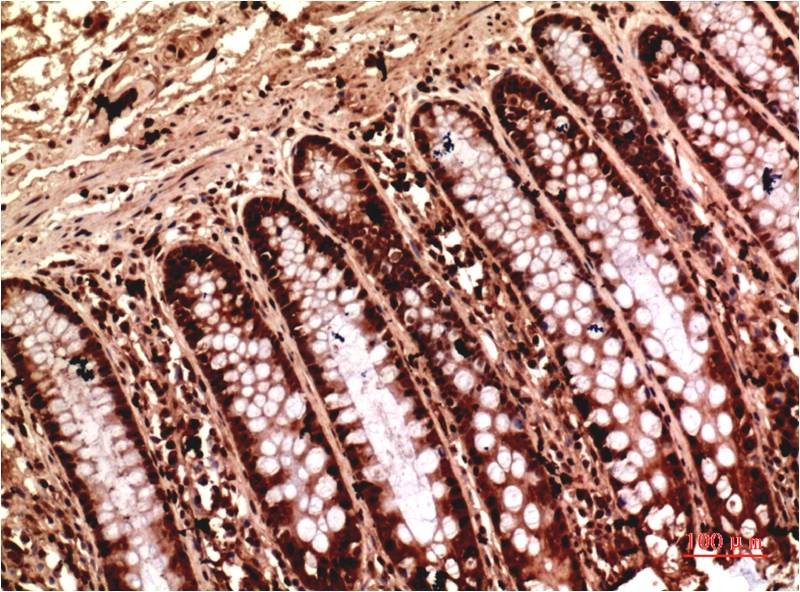
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TUBG1; TUBG; Tubulin gamma-1 chain; Gamma-1-tubulin; Gamma-tubulin complex component 1; GCP-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7283 |
| clone | 6C5 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 51 kDa; Observed MW: 51 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于γ-Tubulin抗体的经典文献概览,涵盖功能定位及结构研究:
---
1. **文献名称**: *γ-Tubulin is a centrosomal protein required for the assembly of microtubules*
**作者**: Oakley, B.R., Oakley, C.E. et al. (1990)
**摘要**: 首次在真菌中克隆γ-tubulin基因,通过抗体免疫定位证实其富集于中心体,并证明其缺失导致微管组装受阻,确立γ-tubulin作为微管成核核心分子。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Microtubule nucleation by γ-tubulin-containing complexes in mammalian cells*
**作者**: Joshi, H.C. et al. (1995)
**摘要**: 利用特异性抗体在哺乳动物细胞中证实γ-tubulin定位于中心体及胞质复合体(γ-TuRC),通过免疫沉淀揭示其与其他调控蛋白的相互作用,阐明其在微管成核中的分子机制。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Inhibition of γ-tubulin function disrupts mitotic spindle assembly*
**作者**: Shu, H.B., Joshi, H.C. et al. (1995)
**摘要**: 通过显微注射抗γ-tubulin抗体干扰其功能,发现纺锤体微管组装显著受损,导致细胞分裂停滞,证明γ-tubulin对有丝分裂进程的必要性。
---
**可选扩展文献**:
4. **文献名称**: *γ-Tubulin in microtubule nucleation and beyond*
**作者**: Moritz, M. & Agard, D.A. (2001)
**摘要**: 综述γ-tubulin复合体的冷冻电镜结构解析,讨论其在不同物种中的保守性及动态调控机制,并拓展其在非中心体微管组织中的作用。
---
如需具体期刊页码或DOI号,可提供论文关键词进一步检索!
**Background of Gamma-Tubulin Antibody**
Gamma-tubulin is a conserved member of the tubulin protein family, primarily localized to microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs), such as centrosomes in animal cells. Unlike alpha- and beta-tubulin, which form microtubule polymers, gamma-tubulin plays a critical role in nucleating and stabilizing microtubules. It acts as a structural template for microtubule assembly, ensuring proper spindle formation during mitosis and maintaining cell polarity, intracellular transport, and cytoskeletal organization.
Gamma-tubulin antibodies are essential tools for studying microtubule dynamics and cell cycle regulation. These antibodies specifically recognize gamma-tubulin epitopes, enabling researchers to visualize MTOCs via immunofluorescence microscopy or quantify protein expression using Western blotting. They are widely used to investigate centrosome abnormalities, mitotic defects, and diseases linked to microtubule dysfunction, such as cancer or neurodevelopmental disorders.
Most gamma-tubulin antibodies are raised against conserved regions of the protein, often derived from species like humans, mice, or yeast. Monoclonal antibodies offer high specificity, while polyclonal antibodies may detect broader epitopes. Validation includes confirming localization to centrosomes or spindle poles and verifying loss of signal in gamma-tubulin-depleted cells.
Applications extend to developmental biology, cancer research (e.g., studying centrosome amplification), and ciliopathy studies. Gamma-tubulin antibodies also aid in exploring fungal or plant cell biology, reflecting the protein’s evolutionary conservation. Their utility in both basic and clinical research underscores their importance in understanding cellular architecture and disease mechanisms.
×