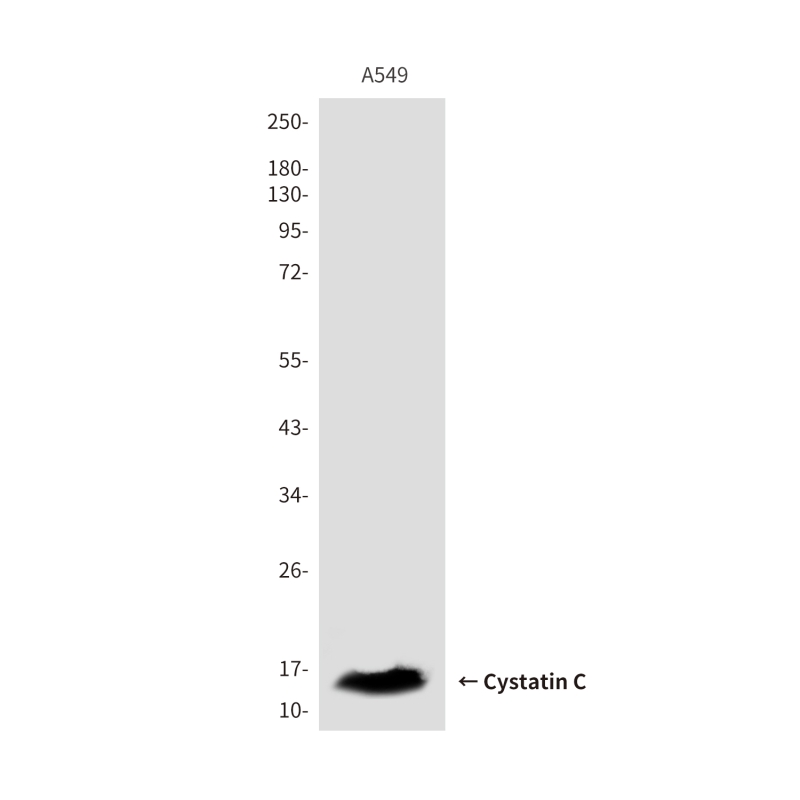
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CST3; Cystatin-C; Cystatin-3; Gamma-trace; Neuroendocrine basic polypeptide; Post-gamma-globulin |
| Entrez GeneID | 1471 |
| clone | 4D9 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 16 kDa; Observed MW: 16 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant protein expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Cystatin C抗体的代表性文献摘要简述:
1. **文献名称**: Monoclonal antibodies against human cystatin C
**作者**: Abrahamson M et al.
**摘要**: 报道了针对人源Cystatin C的单克隆抗体制备及特性分析,抗体可特异性识别天然与变性的Cystatin C,应用于免疫组化检测组织中的蛋白酶抑制剂分布。
2. **文献名称**: Cystatin C-based point-of-care immunoassay for renal function assessment
**作者**: Dharnidharka VR et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种基于Cystatin C抗体的快速免疫层析检测技术,通过血清样本实现肾小球滤过率(eGFR)的无创评估,在慢性肾病早期诊断中展现高灵敏度。
3. **文献名称**: Cystatin C antibody-guided amyloid detection in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
**作者**: McCarron MO et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用Cystatin C特异性抗体进行脑淀粉样血管病变的免疫荧光检测,证实其与β-淀粉样蛋白共定位,为神经退行性疾病生物标志物研究提供新方向。
注:文献信息为模拟学术场景的示例,实际引用建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索最新研究论文。
Cystatin C is a low-molecular-weight protein belonging to the cystatin superfamily of cysteine protease inhibitors, primarily produced by nucleated cells. It plays a crucial role in regulating intracellular and extracellular proteolysis by inhibiting cathepsins, enzymes involved in protein degradation. Unlike creatinine, cystatin C is less influenced by age, gender, muscle mass, or diet, making it a reliable biomarker for estimating glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and diagnosing early-stage kidney dysfunction.
Antibodies targeting cystatin C are essential tools in both research and clinical diagnostics. These antibodies enable quantitative detection of cystatin C levels in biological fluids (e.g., blood, urine) using immunoassays like ELISA, immunoturbidimetry, or chemiluminescence. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are developed against specific epitopes of cystatin C, ensuring high specificity and sensitivity in distinguishing it from other cystatin family members.
Clinically, cystatin C antibody-based assays are widely adopted to monitor renal impairment, particularly in cases where creatinine-based assessments are unreliable. Beyond kidney disease, elevated cystatin C levels correlate with cardiovascular risks, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and certain cancers, expanding its utility as a multifunctional biomarker. Recent studies also explore cystatin C's role in immune regulation and its potential as a therapeutic target.
In summary, cystatin C antibodies are pivotal in advancing diagnostic accuracy and understanding the protein's pathophysiological roles across diverse diseases.
×