| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
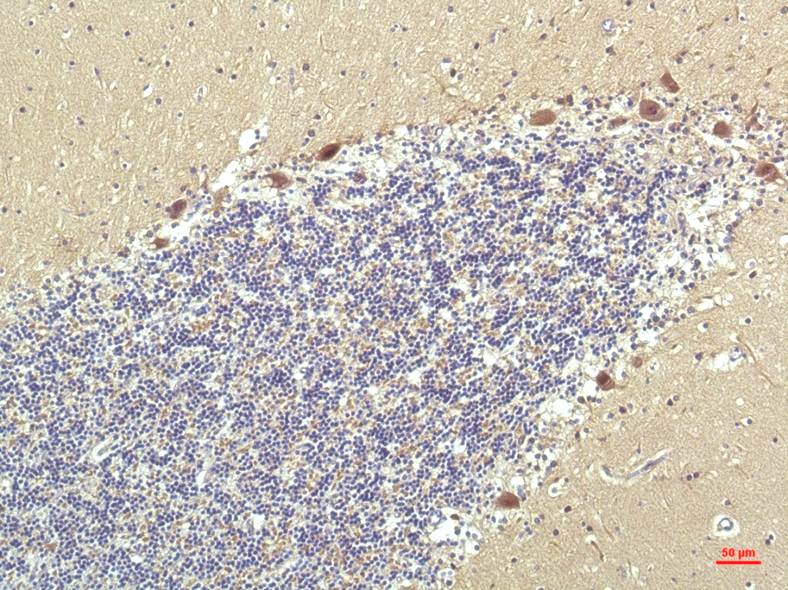
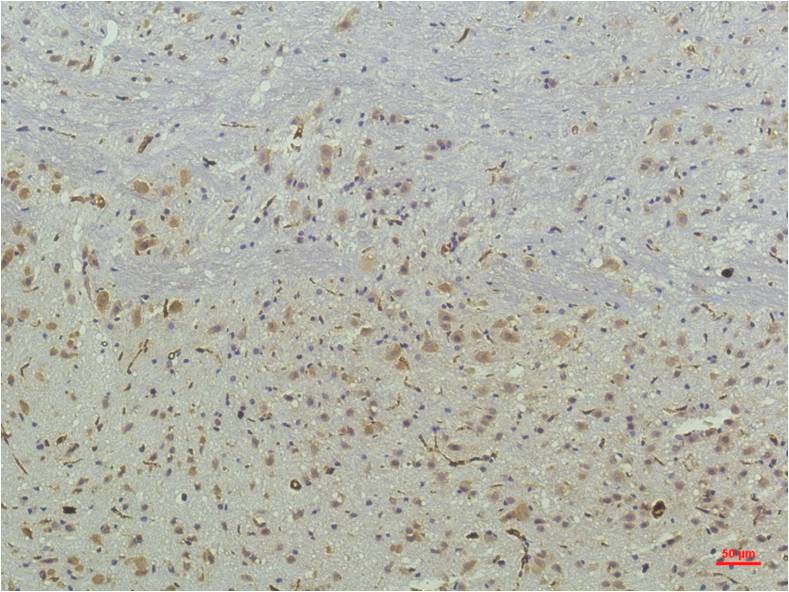
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FAAR; NR1C2; NUC1; Peroxisome proliferative activated receptor delta |
| Entrez GeneID | 5467 |
| clone | 7G5 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 50 kDa; Observed MW: 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant protein expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与PPARδ抗体应用相关的文献摘要概括:
---
1. **"PPARδ regulates glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity"**
*作者:Wang YX, et al.*
摘要:研究通过Western blot和免疫组化技术,利用PPARδ特异性抗体,揭示了该受体在调控小鼠肝脏葡萄糖代谢和胰岛素信号通路中的关键作用,为糖尿病治疗提供新靶点。
---
2. **"A role for PPARδ in macrophage lipid metabolism and inflammation"**
*作者:Lee CH, et al.*
摘要:通过流式细胞术和ChIP实验结合PPARδ抗体,证明PPARδ通过调节巨噬细胞中脂质代谢相关基因表达,影响动脉粥样硬化中的炎症反应。
---
3. **"PPARδ promotes running endurance by enhancing oxidative myofiber formation"**
*作者:Narkar VA, et al.*
摘要:使用PPARδ抗体进行免疫荧光染色,发现激活该受体可诱导小鼠骨骼肌纤维类型向氧化型转化,显著提高运动耐力,为代谢性疾病和肌肉退行性疾病研究提供依据。
---
4. **"Tissue-specific roles of PPARδ in lipid homeostasis"** (综述)
*作者:Schuler M, et al.*
摘要:总结PPARδ在脂肪组织、肝脏和肌肉中的功能差异,强调抗体技术在定位受体表达及评估组织特异性基因调控中的重要性,并讨论其作为代谢疾病治疗靶点的潜力。
---
以上文献均涉及PPARδ抗体的实验应用(如蛋白检测、组织定位),研究领域涵盖代谢、炎症及肌肉功能。
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPARδ), a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily, functions as a transcription factor regulating lipid metabolism, energy homeostasis, inflammation, and cell differentiation. It is ubiquitously expressed, with high levels in skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and the liver. PPARδ activates target genes by binding to peroxisome proliferator response elements (PPREs) upon heterodimerization with retinoid X receptor (RXR). Its role in metabolic diseases, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders has made it a key research focus.
PPARδ antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying PPARδ protein expression in research. They enable studies on its tissue-specific localization, post-translational modifications, and interactions with co-regulators. Commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), these antibodies aid in elucidating PPARδ's physiological and pathological mechanisms. For instance, they help investigate PPARδ's involvement in improving insulin sensitivity, promoting fatty acid oxidation, or driving tumor progression in certain cancers. Validation of antibody specificity is critical, as cross-reactivity with other PPAR isoforms (α/γ) may occur. Researchers often employ knockout controls or epitope mapping to confirm accuracy. Commercially available PPARδ antibodies are typically raised against conserved regions (e.g., N-terminal or ligand-binding domains) across species, facilitating cross-species studies in models of obesity, atherosclerosis, or Alzheimer’s disease.
×