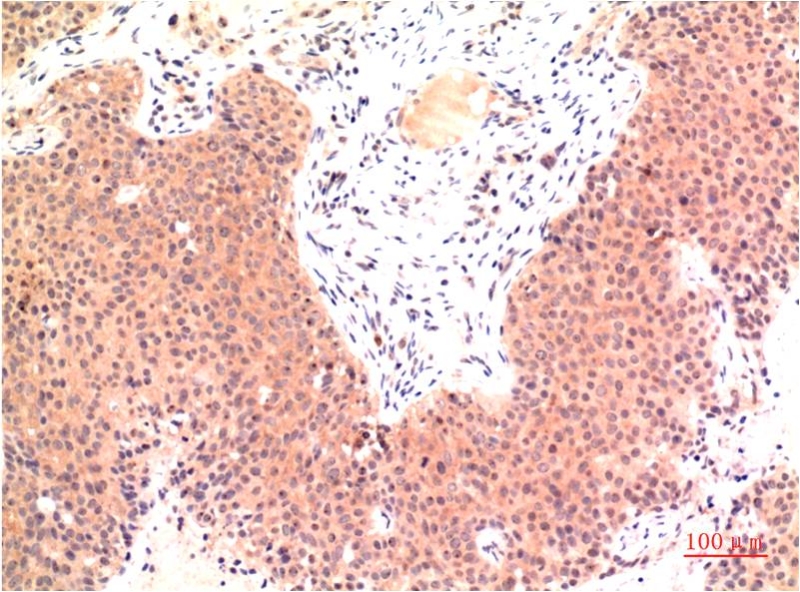
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
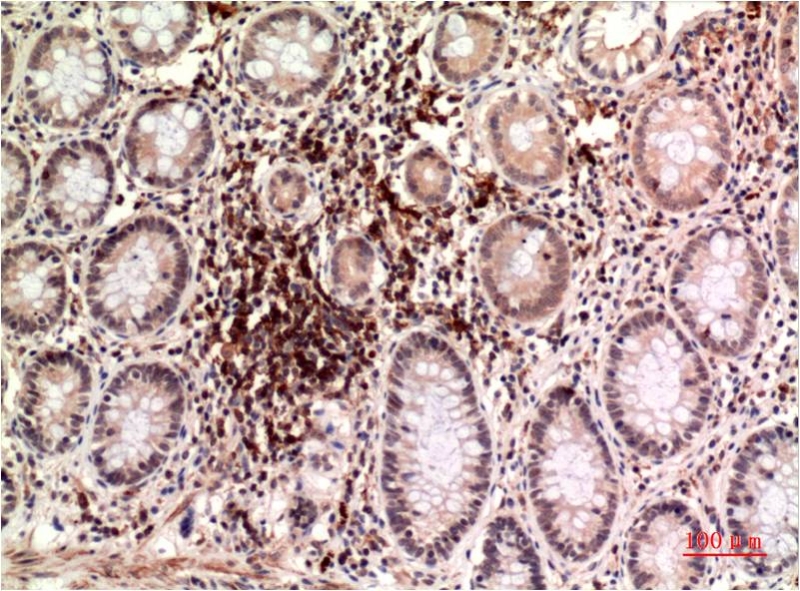
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FLJ22589; TUBE1; tubulin epsilon 1; ε tubulin |
| Entrez GeneID | 51175 |
| clone | 12C7 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ε-Tubulin抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:**"ε-Tubulin is an essential component of the centriole"**
**作者**:Chang, P., Giddings, T.H., Winey, M., Stearns, T.
**摘要**:该研究首次证实ε-Tubulin是中心体的关键组成成分,通过特异性抗体定位发现其参与中心体的组装与稳定性维持,并揭示其缺失会导致细胞分裂异常。
2. **文献名称**:**"Characterization of ε-tubulin antibodies and their use to study centrosome function"**
**作者**:Dutcher, S.K., Morrissette, N.S., Preble, A.M.
**摘要**:文章详细描述了ε-Tubulin多克隆抗体的制备与验证,并利用该抗体在纤毛虫和哺乳动物细胞中证明ε-Tubulin对中心体复制和微管组织的重要作用。
3. **文献名称**:**"Distinct roles of α-, β-, and γ-tubulin in the assembly and function of the centriole"**
**作者**:Hutchins, J.R.A., Toyoda, Y., Hegemann, B., et al.
**摘要**:通过结合ε-Tubulin抗体的免疫荧光技术,研究揭示了ε-Tubulin与其他Tubulin亚型(如γ-Tubulin)在中心体组装中的协同作用,并发现其缺失导致纺锤体极形成缺陷。
4. **文献名称**:**"ε-Tubulin regulates the localization and orientation of the third microtubule in the centrosome"**
**作者**:Wang, W., Moriwaki, Y., Uehara, R., et al.
**摘要**:利用ε-Tubulin特异性抗体进行功能研究,发现其在中心体微管定向排列中起关键作用,并阐明了其在维持细胞极性中的分子机制。
---
以上文献涵盖了ε-Tubulin抗体的开发、验证及其在中心体功能、微管动力学研究中的应用,可作为相关领域的重要参考。
Epsilon-tubulin (ε-tubulin) is a less-characterized member of the tubulin superfamily, which includes alpha (α), beta (β), gamma (γ), delta (δ), and epsilon (ε) isoforms. While α- and β-tubulins form microtubule polymers critical for cell structure and transport, ε-tubulin is primarily localized to centrioles and basal bodies, playing a role in centriole duplication, cilia formation, and mitotic spindle organization. It is evolutionarily conserved but exhibits functional divergence across species. For instance, in mammals, ε-tubulin interacts with other centriolar proteins like γ-tubulin and is essential for maintaining centrosome integrity. Its dysregulation has been linked to ciliopathies, microcephaly, and cancer.
Antibodies targeting ε-tubulin are vital tools for studying centriole biology and cell cycle dynamics. They enable visualization of centriolar structures via immunofluorescence, Western blotting, or immunoprecipitation, aiding research on centrosome amplification in tumors or ciliary defects. However, ε-tubulin antibodies require rigorous validation due to high sequence homology among tubulin isoforms. Specificity is often confirmed using knockout cell lines or siRNA knockdown. Commercial antibodies are typically raised against conserved C-terminal epitopes, with reactivity tested in human, mouse, or rat models. Recent studies also employ these antibodies to explore ε-tubulin's non-canonical roles, such as in DNA damage response or cellular senescence, highlighting its expanding significance in cell biology and disease mechanisms.
×