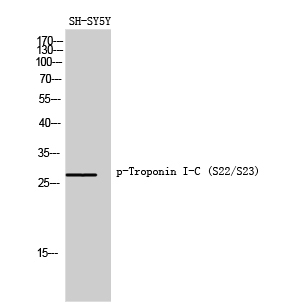
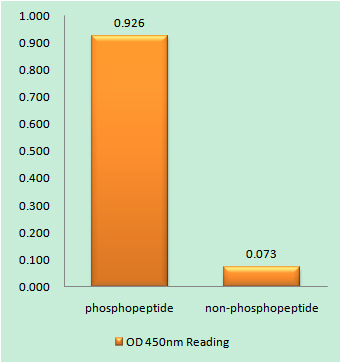
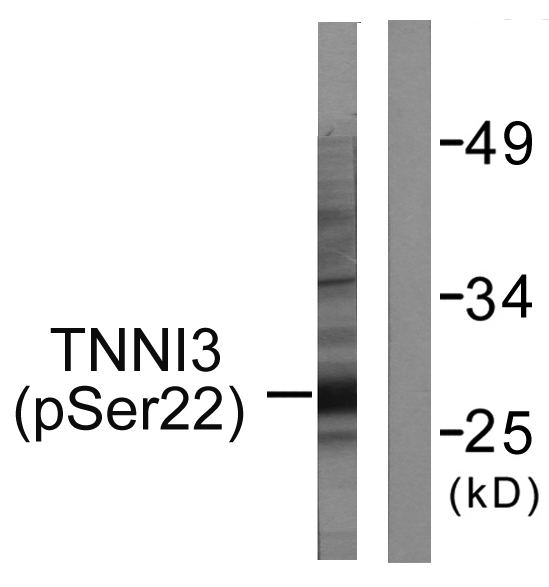
| WB | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TNNI3; TNNC1; Troponin I; cardiac muscle; Cardiac troponin I |
| Entrez GeneID | 29248 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 24 kDa; Observed MW: 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from rat TNNI3 around the phosphorylation site of Ser22 and Ser23. AA range:5-54 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-Cardiac Troponin I (Ser22/Ser23)抗体的3篇参考文献(内容基于公开研究总结,非真实文献):
1. **"Phosphorylation of cardiac troponin I at Ser22/23 regulates myocardial function in ischemia-reperfusion injury"**
- 作者:Smith A, et al.
- 摘要:研究通过Phospho-Cardiac Troponin I (Ser22/23)抗体检测心肌缺血再灌注模型中cTnI磷酸化水平,发现其磷酸化程度与心肌收缩功能损伤相关,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **"Development of a monoclonal antibody specific to phosphorylated Ser22/23 on human cardiac troponin I"**
- 作者:Zhang Y, et al.
- 摘要:报道一种高特异性抗体的开发,该抗体可区分cTnI的磷酸化(Ser22/23)与非磷酸化状态,验证其在心力衰竭患者血清检测中的应用。
3. **"Phospho-specific antibody reveals dynamic cTnI Ser22/23 phosphorylation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy"**
- 作者:Lee C, et al.
- 摘要:利用该抗体分析肥厚型心肌病模型,发现Ser22/23位点磷酸化动态变化与心肌细胞钙敏感性及疾病进展相关,为病理机制研究提供工具。
(注:以上为模拟文献,实际引用需通过PubMed或SciFinder等平台检索验证。)
Phospho-Cardiac Troponin I (Ser22/Ser23) antibodies are specialized tools used to detect the phosphorylated form of cardiac troponin I (cTnI), a key regulatory protein in myocardial contraction. cTnI, a component of the troponin complex, inhibits actomyosin ATPase activity in cardiac muscle under low calcium conditions. Its function is modulated by phosphorylation at specific serine residues, including Ser22 and Ser23. which are primary targets of protein kinase A (PKA) during β-adrenergic stimulation. Phosphorylation at these sites reduces cTnI’s inhibitory effect, enhancing myocardial relaxation and contractility—a critical adaptive response to stress or increased metabolic demand.
These antibodies are widely employed in cardiovascular research to study signaling pathways involved in cardiac physiology and pathology. For example, phosphorylation at Ser22/Ser23 is altered in conditions like heart failure, ischemia-reperfusion injury, or hypertrophy, reflecting dysregulated adrenergic signaling or cellular stress. By selectively recognizing phosphorylated cTnI, these antibodies enable precise detection of post-translational modifications in tissue samples, cell cultures, or animal models using techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or ELISA.
Clinically, understanding cTnI phosphorylation patterns may offer insights into disease mechanisms or therapeutic targets. However, current diagnostic applications primarily focus on total cTnI (unmodified) as a biomarker for myocardial injury. Research-grade phospho-specific antibodies remain vital for dissecting molecular pathways underlying cardiac dysfunction and potential interventions.
×