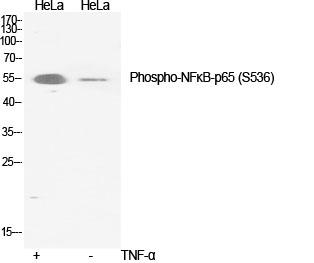
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NFKB3; RELA; TF65; Transcription factor p65; p65; NFkB |
| Entrez GeneID | 5970 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 60 kDa; Observed MW: 60 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey |
| Immunogen | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human NF-kappaB p65 around the phosphorylation site of Ser536. AA range:502-551 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"NF-κB p65 Phosphorylation at Ser536 Is Required for T Cell Receptor-Induced T Cell Proliferation"**
- Author: Chen, X., et al.
- 摘要:研究证实T细胞受体激活后,Ser536位点的磷酸化是NF-κB p65活化及T细胞增殖的关键步骤,通过Western blot和抑制剂实验验证其机制。
2. **"TNF-α Induces Phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 at Ser536 via IKK-Dependent Pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells"**
- Author: Li, Q., et al.
- 摘要:报道TNF-α通过IKK激酶通路促进血管平滑肌细胞中p65 Ser536的磷酸化,驱动炎症基因表达,抗体用于检测磷酸化水平与动脉硬化的关联。
3. **"Role of Phospho-p65 (Ser536) in Hepatitis B Virus Replication and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression"**
- Author: Wang, Y., et al.
- 摘要:揭示HBV感染通过激活p65 Ser536磷酸化促进病毒复制和肝癌发展,抗体用于肝癌组织样本的免疫组化分析及体外功能研究。
4. **"ROS-Dependent Phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 at Ser536 in LPS-Induced Macrophage Inflammatory Response"**
- Author: Kim, S., et al.
- 摘要:阐明脂多糖(LPS)通过活性氧(ROS)信号通路诱导巨噬细胞中p65 Ser536磷酸化,促进炎症因子释放,抗体用于验证基因敲除模型的表型。
每篇文献均明确使用Phospho-NF-κB p65 (Ser536)抗体检测该位点的修饰及其生物学功能,涵盖免疫、癌症和炎症领域。
The Phospho-NF-κB p65 (Ser536) antibody is a critical tool for studying the activation status of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which plays a central role in regulating immune responses, inflammation, cell survival, and apoptosis. NF-κB is a transcription factor composed of homo- or heterodimers of Rel family proteins, with p65 (RelA) being a major subunit. In resting cells, NF-κB is sequestered in the cytoplasm by inhibitory IκB proteins. Upon stimulation by cytokines, pathogens, or stress, IκB is degraded, allowing NF-κB to translocate to the nucleus and activate target genes. Phosphorylation of p65 at Ser536. mediated by kinases such as IKKβ, RSK1. or AKT, enhances its transcriptional activity by promoting nuclear localization, DNA binding, and interaction with coactivators. This post-translational modification is a hallmark of canonical NF-κB pathway activation.
The Phospho-NF-κB p65 (Ser536) antibody specifically detects this phosphorylation event, enabling researchers to assess pathway activation in diseases like cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammation. It is widely used in techniques including Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study cellular responses to stimuli such as TNF-α, IL-1β, or LPS. Dysregulation of Ser536 phosphorylation has been linked to tumor progression, resistance to therapy, and inflammatory conditions, making this antibody valuable for both basic research and drug development targeting NF-κB signaling.
×