| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TP53; P53; Cellular tumor antigen p53; Antigen NY-CO-13; Phosphoprotein p53; Tumor suppressor p53 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7157 |
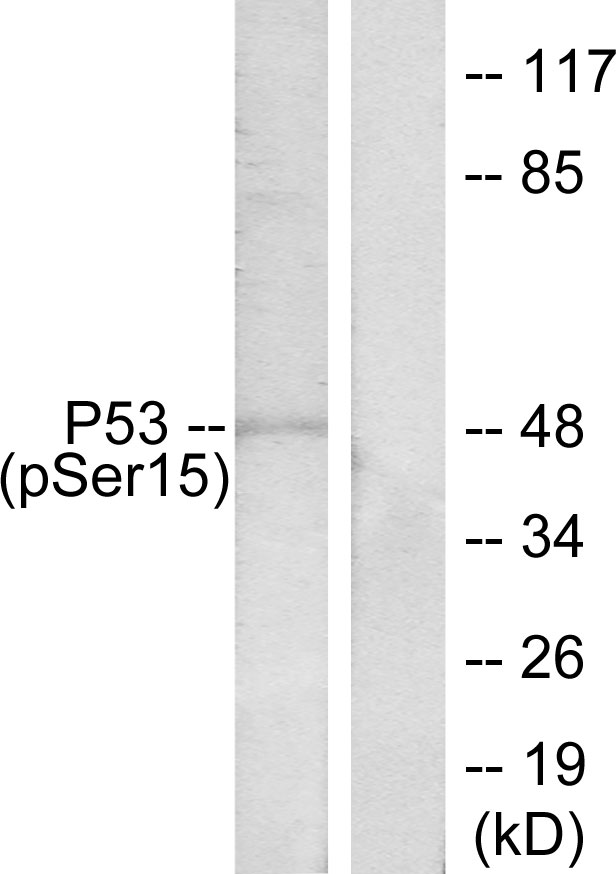
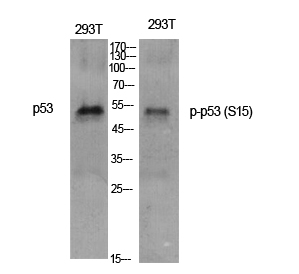
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 44 kDa; Observed MW: 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human p53 around the phosphorylation site of Ser15. AA range:1-50 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-p53 (Ser15)抗体的3-4篇参考文献及其简要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Activation of the ATM kinase by ionizing radiation and phosphorylation of p53*
**作者**:Canman, C.E. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次揭示了DNA损伤(如电离辐射)后,ATM激酶直接磷酸化p53蛋白的Ser15位点,阻断其与MDM2的相互作用,从而稳定p53并激活其转录活性,促进细胞周期阻滞或凋亡。
2. **文献名称**:*DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 alleviates inhibition by MDM2*
**作者**:Shieh, S.Y. et al.
**摘要**:通过体外激酶实验和细胞模型,证明DNA损伤后Ser15和Ser20的磷酸化是p53功能激活的关键步骤,磷酸化减弱了MDM2介导的p53泛素化降解,增强其在细胞核内的积累及靶基因调控能力。
3. **文献名称**:*A role for ATR in the DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53*
**作者**:Tibbetts, R.S. et al.
**摘要**:研究发现,在复制应激(如紫外线辐射)下,ATR激酶而非ATM负责磷酸化p53的Ser15位点,揭示了不同DNA损伤类型通过不同激酶通路调控p53活性的分子机制。
4. **文献名称**:*Site-specific phosphorylation of p53 by checkpoint kinases in response to UV radiation*
**作者**:Ko, L.J. et al.
**摘要**:利用特异性抗体(包括Phospho-p53 Ser15抗体),验证了UV诱导的DNA损伤通过ATR/Chk1通路触发p53的Ser15磷酸化,并阐明其与下游凋亡信号通路的关联。
**备注**:上述文献为p53磷酸化机制研究的经典论文,适用于抗体特异性验证、DNA损伤应答机制探讨或相关信号通路研究。
Phospho-p53 (Ser15) antibody is a key tool for studying the activation and regulatory mechanisms of the tumor suppressor protein p53. which plays a central role in maintaining genomic stability and preventing cancer. The p53 protein is activated in response to cellular stress, such as DNA damage, oncogene activation, or hypoxia, and functions primarily by inducing cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, or apoptosis. Post-translational modifications, particularly phosphorylation, tightly regulate its stability and activity. Phosphorylation at serine 15 (Ser15) is one of the earliest and most critical modifications occurring in the N-terminal transactivation domain of p53 following DNA damage. This modification is primarily mediated by the ATM/ATR kinases, which are activated by DNA damage checkpoints.
The Phospho-p53 (Ser15) antibody specifically detects p53 when phosphorylated at Ser15. serving as a marker for p53 activation. Researchers use this antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study DNA damage response pathways, assess p53-dependent transcriptional activity, and explore mechanisms of tumor suppression or chemoresistance in cancer models. Its application is vital in both basic research and preclinical studies, particularly in understanding how p53 dysfunction contributes to tumorigenesis or influences therapeutic outcomes.
×