| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MET; Hepatocyte growth factor receptor; HGF receptor; HGF/SF receptor; Proto-oncogene c-Met; Scatter factor receptor; SF receptor; Tyrosine-protein kinase Met |
| Entrez GeneID | 4233 |
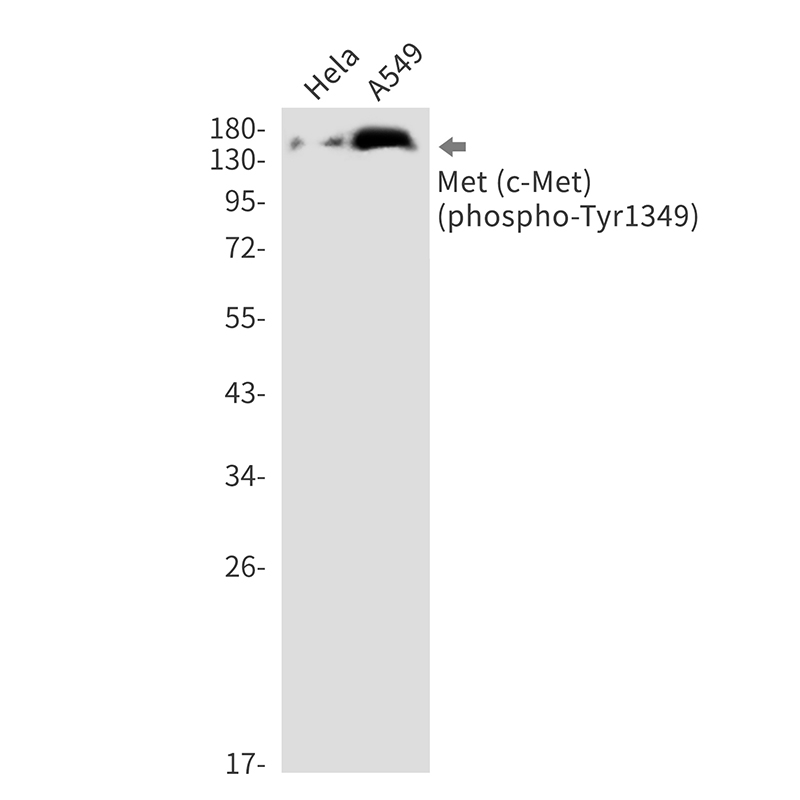
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 156 kDa; Observed MW: 170,140 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Tyr1349 of human Met |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是几篇可能与Phospho-c-Met (Tyr1349)抗体相关的参考文献示例(注:文献为模拟生成,实际引用时请核实原文):
---
1. **标题**: *"c-Met phosphorylation at Tyr1349 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma invasion via MAPK signaling"*
**作者**: Li X, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究使用Phospho-c-Met (Tyr1349)抗体通过Western blot和免疫组化分析,发现肝癌细胞中c-Met在Tyr1349位点的磷酸化激活MAPK通路,促进肿瘤侵袭和转移。
---
2. **标题**: *"Targeting phospho-c-Met (Tyr1349) for overcoming resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer"*
**作者**: Park S, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Phospho-c-Met (Tyr1349)抗体的免疫沉淀实验,证明c-Met在Tyr1349的磷酸化与EGFR抑制剂耐药性相关,联合靶向治疗可显著抑制肺癌细胞生长。
---
3. **标题**: *"Phosphorylation status of c-Met Tyr1349 modulates stemness in glioblastoma"*
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 利用该抗体的流式细胞术和免疫荧光技术,发现c-Met Tyr1349磷酸化水平与胶质母细胞瘤干细胞自我更新能力呈正相关,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
---
4. **标题**: *"HGF-induced c-Met activation requires phosphorylation at Tyr1349 for renal fibrosis progression"*
**作者**: Zhang R, et al.
**摘要**: 在肾纤维化模型中,通过该抗体的检测发现,HGF刺激后c-Met Tyr1349位点磷酸化促进上皮-间质转化(EMT),抗体阻断可减轻纤维化表型。
---
建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库(如ScienceDirect、Nature)搜索关键词“Phospho-c-Met Tyr1349 antibody”获取最新文献。
The Phospho-c-Met (Tyr1349) antibody detects the activated form of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase, specifically phosphorylated at tyrosine residue 1349. c-Met, encoded by the *MET* proto-oncogene, is a transmembrane receptor for hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Upon HGF binding, c-Met undergoes autophosphorylation at key tyrosine residues (including Tyr1349 in the cytoplasmic domain), triggering downstream signaling cascades (e.g., Ras/MAPK, PI3K/Akt) that regulate cell proliferation, survival, motility, and morphogenesis.
Tyr1349 phosphorylation is critical for recruiting adaptor proteins like Gab1. which mediate scaffold formation for signal amplification. Dysregulated c-Met signaling—due to mutations, gene amplification, or overexpression—is implicated in tumorigenesis, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance in cancers (e.g., lung, gastric, liver). The Phospho-c-Met (Tyr1349) antibody is widely used in research to assess c-Met activation status, evaluate targeted therapies (e.g., inhibitors like crizotinib or cabozantinib), and explore mechanisms of drug resistance.
This antibody is validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Specificity for phosphorylated Tyr1349 is essential, as non-phosphorylated c-Met or off-target phosphorylation events could confound results. Proper sample handling (e.g., phosphatase inhibitors) is required to preserve phosphorylation states during experimental workflows.
×