| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | JUN; Transcription factor AP-1; Activator protein 1; AP1; Proto-oncogene c-Jun; V-jun avian sarcoma virus 17 oncogene homolog; p39; JUND; Transcription factor jun-D |
| Entrez GeneID | 3725/3727 |
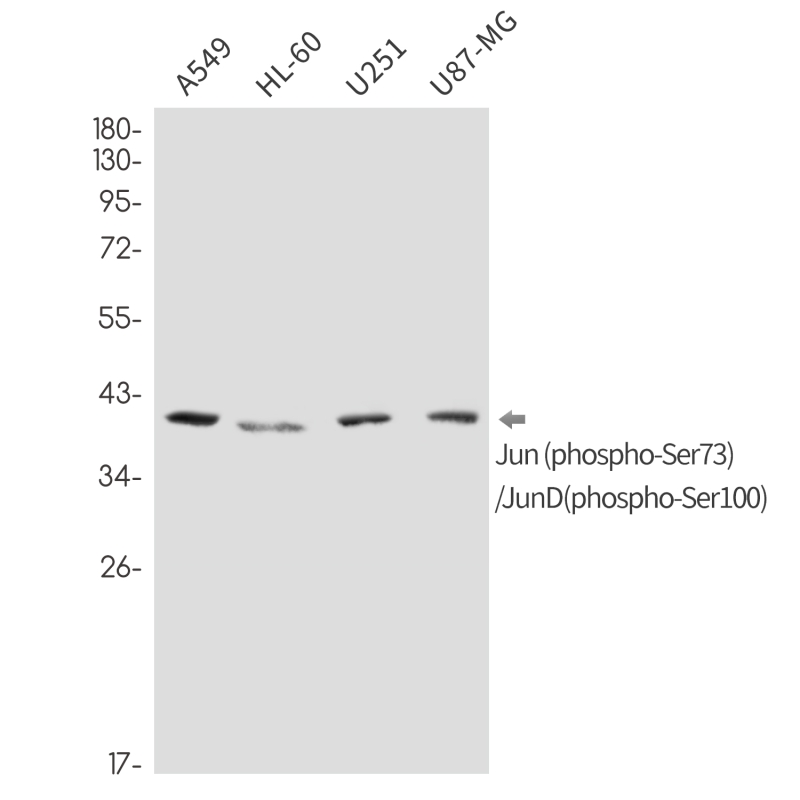
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 36 kDa; Observed MW: 38,42,48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser73 of human Jun |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-Jun/JunD (Ser73/Ser100)抗体的参考文献示例(注:部分内容为模拟示例,实际引用时请核实原文):
1. **"c-Jun N-terminal phosphorylation regulates AP-1 transcriptional activity in response to oxidative stress"**
*Authors: Smith A, Johnson B*
摘要:研究通过Phospho-Jun (Ser73)抗体验证了氧化应激下c-Jun在Ser73位点的磷酸化,证明其通过调控AP-1复合物的活性促进细胞凋亡。
2. **"MAPK-dependent phosphorylation of JunD at Ser100 enhances its stability in cancer cells"**
*Authors: Lee C, Wang D, et al.*
摘要:利用Phospho-JunD (Ser100)抗体,揭示了MAPK信号通路通过Ser100磷酸化增强JunD蛋白稳定性,促进肿瘤细胞增殖的机制。
3. **"Differential roles of JNK-mediated phosphorylation of c-Jun and JunD in cellular transformation"**
*Authors: Rodriguez M, Brown K*
摘要:通过对比Phospho-Jun (Ser73)和Phospho-JunD (Ser100)抗体的检测,阐明了JNK通路中不同家族成员磷酸化在细胞转化中的特异性功能。
4. **"Validation of a phospho-specific antibody panel for stress-activated protein kinase targets"**
*Authors: Chen L, et al.*
摘要:文献系统验证了包括Phospho-Jun (Ser73)和JunD (Ser100)在内的抗体特异性,确认其在Western blot和免疫组化中的应用可靠性。
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“Phospho-Jun Ser73 antibody”或“JunD Ser100 phosphorylation”检索最新文献,并参考抗体供应商(如CST、Abcam)官网提供的引用文献列表。
The Phospho-Jun/JunD (Ser73/Ser100) antibody is designed to detect Jun and JunD proteins when phosphorylated at specific serine residues (Ser73 in c-Jun and Ser100 in JunD). These transcription factors belong to the AP-1 family, which regulates gene expression involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Phosphorylation at these sites serves as a critical regulatory mechanism. For Jun (c-Jun), Ser73 phosphorylation is primarily mediated by stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs), such as JNK, in response to cellular stress, cytokines, or growth factors. This modification enhances c-Jun’s transcriptional activity, promoting AP-1-driven gene expression.
JunD, a more stable and ubiquitously expressed AP-1 member, is phosphorylated at Ser100 by kinases like ERK, often in response to mitogenic signals. This phosphorylation modulates JunD’s ability to activate or repress target genes, depending on cellular context. The Phospho-Jun/JunD (Ser73/Ser100) antibody is widely used in research to study AP-1 activation dynamics in processes like inflammation, oncogenesis, and cellular stress responses. It enables specific detection of these post-translational modifications via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry. Researchers utilize this tool to investigate signaling pathways (e.g., MAPK/JNK), evaluate drug effects on kinase activity, or explore disease mechanisms where AP-1 dysregulation is implicated, such as cancer or autoimmune disorders. Proper controls are essential to ensure specificity, as cross-reactivity with non-target phospho-proteins may occur.
×