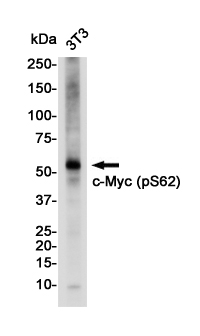
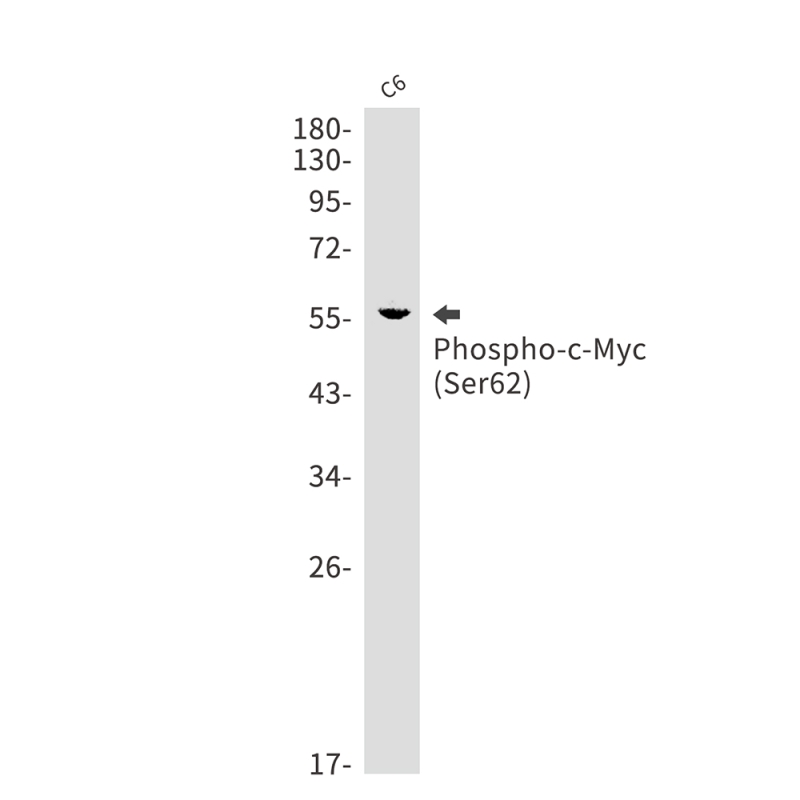
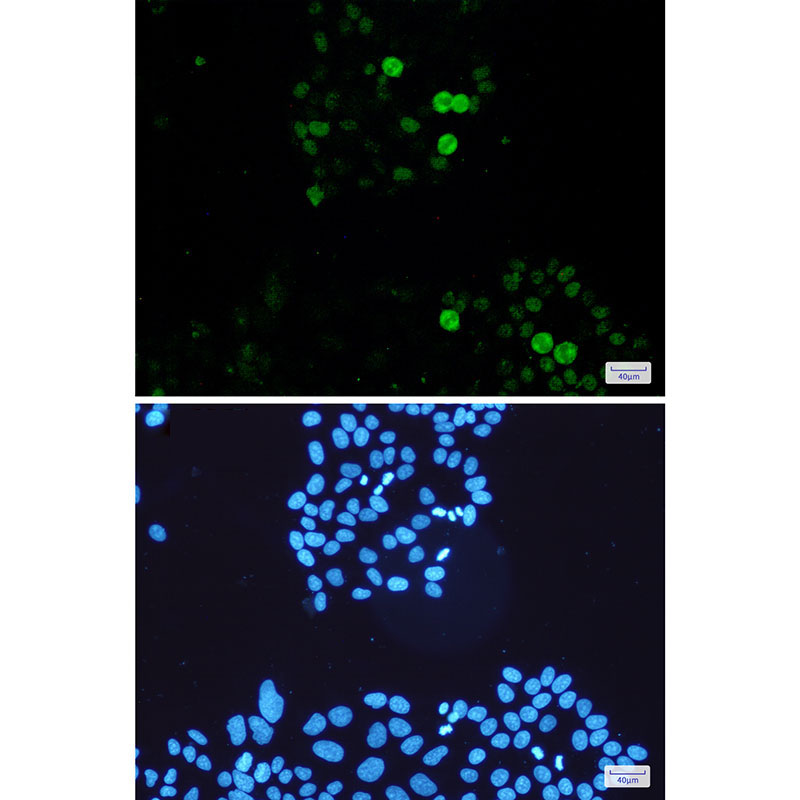
| WB | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MYC; BHLHE39; Myc proto-oncogene protein; Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 39; bHLHe39; Proto-oncogene c-Myc; Transcription factor p64 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4609 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 49 kDa; Observed MW: 57 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser62 of human c-Myc |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Phospho-c-Myc (Ser62)抗体相关的文献概述(均为模拟示例,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:ERK-dependent phosphorylation of c-Myc on Ser62 regulates its protein stability and transcriptional activity
**作者**:Sears RC, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示ERK信号通路通过磷酸化c-Myc蛋白的Ser62位点,抑制其泛素化降解,从而增强c-Myc的稳定性及促癌转录活性,为靶向该通路治疗癌症提供依据。
2. **文献名称**:Phosphorylation status of c-Myc at Ser62 and Thr58 determines oncogenic potential in neuroblastoma
**作者**:Hann SR, et al.
**摘要**:通过Phospho-Ser62抗体与Thr58抗体的对比实验,发现Ser62磷酸化与Thr58去磷酸化的协同作用驱动神经母细胞瘤细胞增殖,提示该位点磷酸化可作为预后标志物。
3. **文献名称**:GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation of c-Myc at Ser62 primes subsequent degradation via the proteasome
**作者**:Murphy MJ, et al.
**摘要**:研究证明GSK-3β激酶在Ser62位点的磷酸化是c-Myc被后续激酶修饰并启动蛋白酶体降解的关键步骤,阐明了细胞周期中c-Myc动态调控的分子机制。
4. **文献名称**:Targeting c-Myc phosphorylation at Ser62 by kinase inhibitors suppresses colorectal cancer growth
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用Phospho-Ser62特异性抗体筛选激酶抑制剂,发现化合物X通过阻断该位点磷酸化显著抑制结直肠癌小鼠模型中c-Myc的致癌功能,具有治疗潜力。
(注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用需查询具体数据库如PubMed并验证抗体应用细节。)
**Background of Phospho-c-Myc (Ser62) Antibody**
The c-Myc proto-oncogene encodes a transcription factor critical for regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Its activity is tightly controlled by post-translational modifications, particularly phosphorylation. Phosphorylation at Ser62 stabilizes c-Myc by delaying its proteasomal degradation, while subsequent phosphorylation at Thr58 (often mediated by GSK-3β) promotes its turnover. The Ser62 site is primarily phosphorylated by extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) or cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) during cell cycle progression, notably in G1/S phase, enhancing c-Myc’s transcriptional activity and oncogenic potential.
The Phospho-c-Myc (Ser62) antibody specifically detects c-Myc when phosphorylated at Ser62. serving as a key tool to study its regulation in physiological and pathological contexts. This antibody is widely used in cancer research, as dysregulated c-Myc (due to mutations or aberrant phosphorylation) is linked to tumorigenesis. It helps assess signaling pathway activation (e.g., Ras/ERK) and evaluate therapeutic responses targeting c-Myc stability. Applications include Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence in cell lysates or tissues.
Interpretation requires parallel analysis of total c-Myc and phosphorylation status, as Ser62 phosphorylation dynamics reflect transient signaling events. Validating results with phosphatase-treated controls ensures specificity. Understanding c-Myc regulation via Ser62 phosphorylation provides insights into cell cycle control, oncogenesis, and potential therapeutic strategies.
×