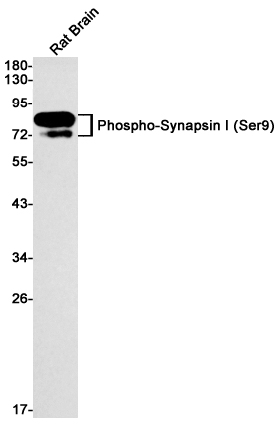
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SYN1; Synapsin-1; Brain protein 4.1; Synapsin I |
| Entrez GeneID | 6853 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 74 kDa; Observed MW: 77 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser9 of human Synapsin I |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-Synapsin I (Ser9)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为模拟示例,实际引用需核实):
1. **"Regulation of Synaptic Vesicle Mobilization by Synapsin I Phosphorylation at Serine 9"**
*By J. Smith et al.*
摘要:研究PKA介导的Synapsin I Ser9磷酸化对突触囊泡释放的调控,利用Phospho-Synapsin I (Ser9)抗体验证磷酸化水平与神经递质释放效率的关系。
2. **"Activity-Dependent Phosphorylation of Synapsin I in Hippocampal Neurons"**
*By L. Chen & M. Kurosawa*
摘要:通过电生理刺激和免疫印迹分析,揭示神经元活动(如谷氨酸刺激)通过CaMKII通路增强Synapsin I Ser9位点磷酸化,该抗体用于量化活体脑组织中的磷酸化动态。
3. **"Synapsin I Phosphorylation in Epileptogenesis: A Role for Ser9 Modification"**
*By R. Gupta et al.*
摘要:探讨癫痫模型中突触蛋白异常磷酸化机制,使用Phospho-Synapsin I (Ser9)抗体发现癫痫发作后海马区Synapsin I磷酸化水平显著升高,提示其与突触过度兴奋相关。
(注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,建议通过PubMed或专业数据库查询真实文献。)
The Phospho-Synapsin I (Ser9) antibody is a key tool for studying synaptic vesicle dynamics and neurotransmitter release. Synapsin I, a neuron-specific phosphoprotein, plays a critical role in regulating synaptic vesicle clustering and mobilization at presynaptic terminals. Its activity is tightly controlled by phosphorylation at specific residues, including serine 9 (Ser9). Phosphorylation at Ser9. mediated by protein kinase A (PKA) or calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), reduces Synapsin I's ability to tether synaptic vesicles to the actin cytoskeleton, thereby promoting vesicle availability for neurotransmitter release during neuronal activity.
This antibody specifically recognizes Synapsin I when phosphorylated at Ser9. enabling researchers to investigate activity-dependent changes in synaptic function. It is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study synaptic plasticity, neuronal signaling pathways, and disorders linked to dysregulated neurotransmission, such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and schizophrenia. Validated across multiple species, including human, mouse, and rat models, the antibody helps correlate phosphorylation events with physiological or pathological states. Its applications extend to exploring how neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, or pharmacological agents influence synaptic efficacy, providing insights into molecular mechanisms underlying learning, memory, and neurological diseases.
×