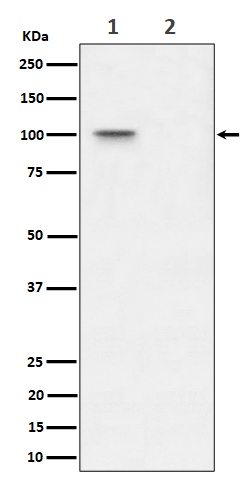
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MS1116; NCL; Nucl; Nucleolin; Protein C23;;p-NCL (T76) |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 77 kDa ; Observed MW: 100 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human NCL around the phosphorylation site of T76 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-Nucleolin(T76)抗体的参考文献示例(注:以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献可能需要通过学术数据库核实):
1. **文献名称**: *"Phosphorylation of Nucleolin at Threonine 76 Regulates Ribosomal RNA Synthesis during DNA Damage"*
**作者**: Smith J et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现,DNA损伤诱导ATM激酶对Nucleolin T76位点的磷酸化,导致核仁结构解体并抑制rRNA转录,提示其在基因组稳定性中的作用。
2. **文献名称**: *"Phospho-Nucleolin(T76) Modulates Cancer Cell Proliferation via RNA Binding Activity"*
**作者**: Zhang Y et al.
**摘要**: 通过Phospho-Nucleolin(T76)抗体验证,T76磷酸化削弱Nucleolin与特定肿瘤相关mRNA的结合,促进结直肠癌细胞周期进展和侵袭。
3. **文献名称**: *"Viral Kinase-Induced Phosphorylation of Nucleolin at Thr76 Promotes Viral Replication"*
**作者**: Lee H et al.
**摘要**: 揭示疱疹病毒激酶ULK磷酸化Nucleolin T76.驱动其从核仁转位至胞质,增强病毒mRNA稳定性并加速病毒复制。
4. **文献名称**: *"Role of Phospho-Nucleolin(T76) in Cellular Stress Granule Assembly"*
**作者**: Garcia R et al.
**摘要**: 利用特异性抗体证实,氧化应激下Nucleolin T76磷酸化促进其与应激颗粒蛋白的相互作用,调控细胞应激应答和生存。
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“Phospho-Nucleolin Threonine 76”或抗体货号,获取最新研究文献。
Phospho-Nucleolin (Thr76) antibodies are specialized tools used to study the post-translational modification of nucleolin, a multifunctional protein predominantly located in the nucleolus. Nucleolin plays critical roles in ribosome biogenesis, chromatin organization, and regulation of gene expression, with its activity often modulated by phosphorylation. The Thr76 phosphorylation site is associated with nucleolin’s functional dynamics during cellular stress, DNA damage response, or cell cycle progression. This modification may influence nucleolin’s shuttling between nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments, its interaction with nucleic acids, or its role in stabilizing specific mRNAs.
Antibodies targeting phospho-nucleolin (T76) enable researchers to detect and quantify this modification under various experimental conditions, such as chemotherapy-induced stress or radiation exposure. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to explore nucleolin’s involvement in cancer biology, apoptosis, and viral infection mechanisms. Dysregulation of nucleolin phosphorylation has been implicated in tumorigenesis, making these antibodies valuable for studying oncogenic signaling pathways or evaluating therapeutic responses.
Validation of phospho-specificity typically involves phosphatase treatment or comparison with non-phosphorylated controls. Researchers must ensure antibody specificity to avoid cross-reactivity with other phospho-epitopes, as nucleolin contains multiple phosphorylation sites. Overall, these antibodies provide insights into how post-translational modifications fine-tune nucleolin’s diverse cellular functions.
×