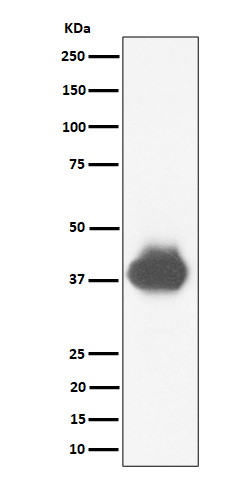
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD32; CD32A; CD32B; CD32C; CDw32; FCG2; FcGR; FCGR2; FCGR2A; FCGR2A1; FCGR2B; FCGR2C; Fcgr3; Fcgr3a; FcgRII; FcRII a; FCRII; FcRII b; FcRII c; FcRIIC; IGFR2;;CD32 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34-36 kDa ; Observed MW: 37-43 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CD32 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD32(FcγRII)亚型抗体的3篇代表性文献,涵盖其功能及研究背景:
1. **"Fcγ receptors in immune responses and their therapeutic implications"**
- 作者:Bruhns, P., & Jönsson, F.
- 摘要:综述了Fcγ受体家族(包括CD32A、CD32B、CD32C)的结构和功能差异,强调CD32A在促炎反应中的作用、CD32B的免疫抑制功能,以及CD32C在特定细胞类型(如NK细胞)中的表达调控。
2. **"Fcγ receptors as therapeutic targets in autoimmune disease"**
- 作者:Nimmerjahn, F., & Ravetch, J. V.
- 摘要:探讨CD32B作为自身免疫疾病治疗靶点的潜力,提出通过增强CD32B抑制信号或阻断CD32A激活信号来调节免疫反应,并提及CD32C在人类中的有限表达及其潜在病理关联。
3. **"The role of FcγRII isoforms in antibody-mediated effector functions"**
- 作者:Bournazos, S., et al.
- 摘要:通过体外实验比较CD32A、CD32B、CD32C对抗体依赖性细胞吞噬(ADCP)等效应功能的影响,发现CD32A/C激活信号可增强免疫细胞杀伤,而CD32B则抑制过度炎症反应。
**备注**:CD32C(FcγRIIC)研究较少,其功能可能与CD32A类似,但受基因多态性影响较大。如需具体实验抗体研究,建议补充亚型特异性研究文献(如靶向特定表位的抗体开发)。
CD32 (FcγRII), a family of low-affinity receptors for the Fc region of IgG, plays critical roles in immune regulation. CD32 exists in three major isoforms—CD32A (FcγRIIA), CD32B (FcγRIIB), and CD32C (FcγRIIC)—encoded by distinct genes (FcγRIIA, FcγRIIB, FcγRIIC) or splice variants. CD32A is an activating receptor expressed primarily on myeloid cells (e.g., monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils) and platelets. It contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) that triggers phagocytosis, cytokine release, and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). CD32B, in contrast, is an inhibitory receptor widely expressed on B cells, dendritic cells, and myeloid cells. It carries an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) that dampens B-cell activation and immune complex-mediated inflammation. CD32C, a less studied isoform, shares structural similarities with CD32A but is expressed in limited tissues, including activated T cells and epithelial cells, and may participate in immune modulation.
Antibodies targeting CD32 isoforms have therapeutic and research applications. Anti-CD32A/B/C antibodies are used to study immune cell signaling, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus), and infectious responses. In cancer, CD32B blockade enhances antitumor immunity by countering immunosuppression, while CD32A engagement may amplify effector cell activity. However, functional overlap and tissue-specific expression complicate their selective targeting, driving ongoing research into isoform-specific antibodies for precision immunotherapy.
×